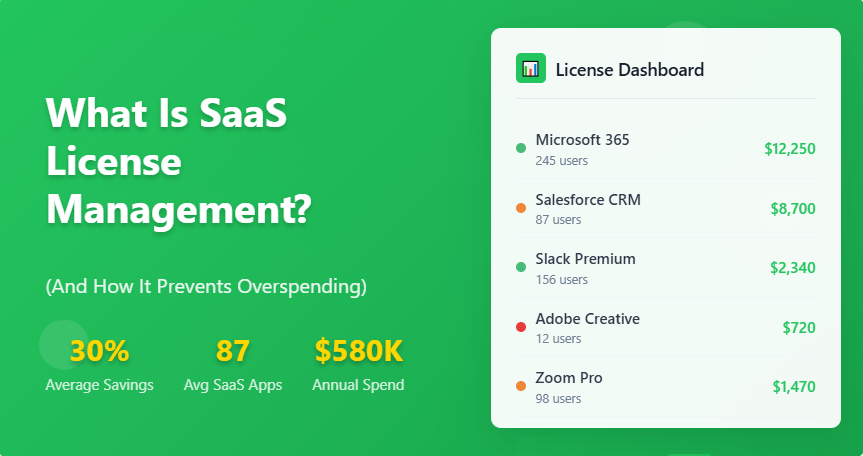
Software as a Service (SaaS) has revolutionized how businesses access and utilize software applications. With the average organization now using approximately 80 SaaS applications, managing these subscriptions and licenses has become a critical challenge for IT departments and financial teams alike. Poor SaaS license management can lead to significant overspending, with many organizations wasting 30% or more of their SaaS budget on unused or underutilized subscriptions.
SaaS license management has emerged as an essential discipline that helps organizations gain visibility, control costs, and optimize their software investments. This comprehensive guide explores what SaaS license management entails and how it serves as a powerful tool for preventing overspending while maximizing the value of your software portfolio.
What is SaaS License Management?
SaaS license management is the systematic approach to tracking, monitoring, and optimizing software-as-a-service subscriptions throughout their entire lifecycle. Unlike traditional software licensing that involved one-time purchases and permanent installations, SaaS license management deals with recurring subscription models, user-based pricing, and cloud-delivered applications.
At its core, SaaS license management encompasses several key activities:
- Subscription Tracking: Maintaining a comprehensive inventory of all SaaS applications, their subscription details, renewal dates, and associated costs across the organization.
- User Access Management: Monitoring who has access to which applications, tracking usage patterns, and ensuring that license allocations align with actual business needs.
- Cost Optimization: Identifying opportunities to reduce spending through rightsizing subscriptions, eliminating duplicate applications, and negotiating better pricing with vendors.
- Compliance Management: Ensuring that the organization remains compliant with licensing terms and conditions while avoiding unexpected overage charges or audit penalties.
- Renewal Management: Proactively managing subscription renewals to prevent service disruptions while providing opportunities to renegotiate terms or make strategic decisions about continuing services.
The discipline extends beyond simple inventory management to include strategic decision-making about which SaaS solutions provide the best value, how to optimize usage across teams, and how to align software investments with business objectives.
The Growing Challenge of SaaS Sprawl
The rapid adoption of SaaS applications has created what many IT professionals call “SaaS sprawl” – the uncontrolled proliferation of software subscriptions across an organization. This phenomenon has several contributing factors:
- Democratized Software Procurement: Unlike traditional enterprise software that required extensive IT involvement, many SaaS applications can be purchased directly by department heads or even individual employees using corporate credit cards. This ease of procurement, while enabling agility, often leads to shadow IT and duplicate subscriptions.
- Department-Specific Solutions: Different departments often adopt specialized SaaS tools to meet their unique needs, sometimes without considering whether existing solutions could fulfill the same requirements. Marketing teams might subscribe to multiple analytics platforms, while sales teams accumulate various CRM add-ons and prospecting tools.
- Multi-Currency and Multi-Regional Complexity: Global organizations face additional challenges managing SaaS subscriptions across different countries, currencies, and regulatory environments. This complexity makes it difficult to maintain centralized visibility and control over software spending.
- Subscription Model Characteristics: The subscription model itself contributes to sprawl, as monthly or annual commitments can seem less significant than large upfront software purchases, leading to more casual adoption decisions.
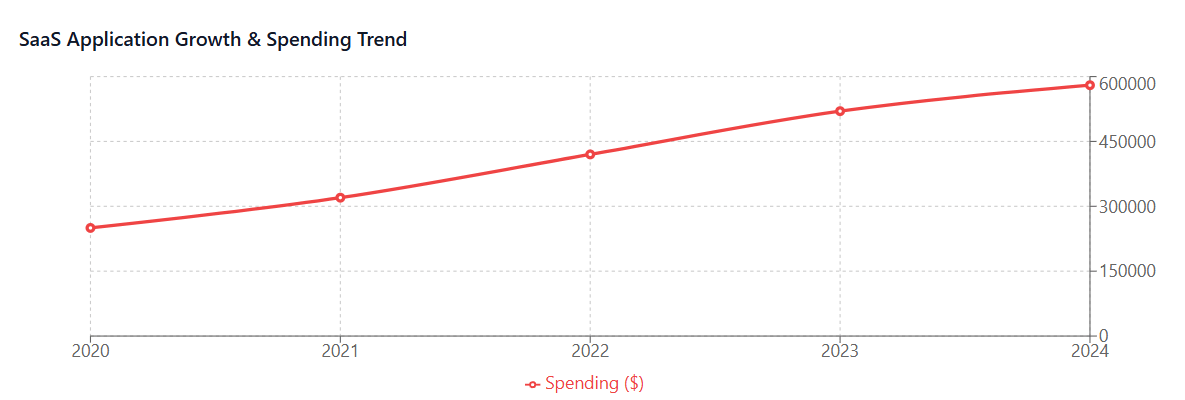
The consequences of unmanaged SaaS sprawl are significant. Organizations typically discover that they’re paying for far more software than they actually use, with studies showing that 30-40% of SaaS spending goes toward unused or underutilized applications. Without proper SaaS license management, companies also face security risks from unmonitored applications, compliance issues, and the administrative burden of managing numerous vendor relationships.
Key Components of Effective SaaS License Management
Effective SaaS license management requires a structured approach that addresses multiple dimensions of software subscription oversight. The most successful implementations incorporate several key components:
Centralized Discovery and Inventory: The foundation of good SaaS license management is knowing what applications your organization uses. This involves discovering both sanctioned and shadow IT applications through various methods including expense report analysis, network traffic monitoring, and integration with identity management systems. A comprehensive inventory should include application names, vendors, subscription tiers, user counts, renewal dates, and total costs.
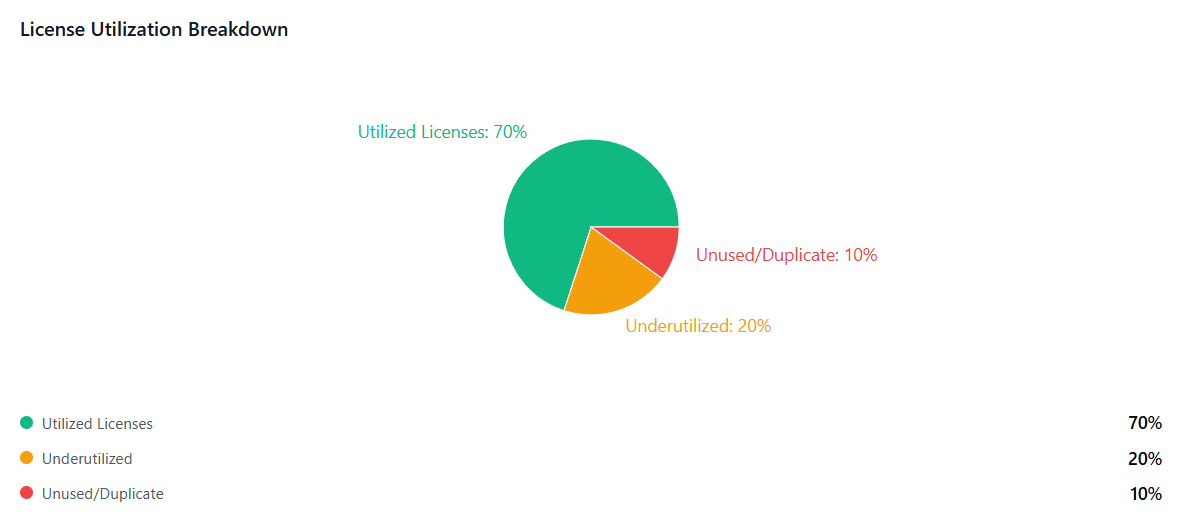
Usage Analytics and Monitoring: Understanding how applications are actually used is crucial for optimization decisions. Effective SaaS license management platforms track user login frequencies, feature utilization, and engagement levels to identify underutilized subscriptions. This data helps distinguish between essential applications that drive business value and those that represent wasted spending.
Financial Management and Reporting: SaaS license management requires robust financial tracking capabilities that can handle complex pricing models, multiple currencies, and various billing cycles. Organizations need clear visibility into spending trends, budget allocation across departments, and forecasting capabilities for future renewal costs.
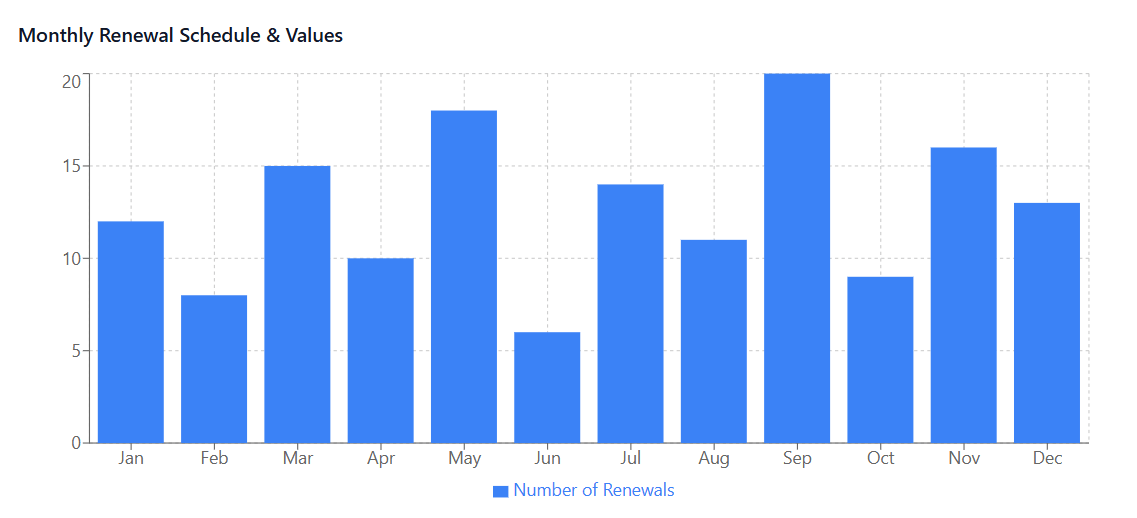
Renewal and Contract Management: With subscriptions renewing on different schedules throughout the year, effective license management must include automated renewal tracking, early warning systems for upcoming renewals, and contract management capabilities that store important terms and conditions.
Governance and Approval Workflows: Mature SaaS license management includes governance frameworks that establish approval processes for new subscriptions, guidelines for application selection, and policies for user access management. These workflows help prevent unauthorized spending while maintaining business agility.
Vendor Relationship Management: As organizations work with dozens or even hundreds of SaaS vendors, managing these relationships becomes increasingly important. This includes tracking vendor performance, managing contract negotiations, and maintaining records of support interactions and service level agreements.
How SaaS License Management Prevents Overspending
SaaS license management serves as a powerful cost control mechanism through several specific strategies and practices that directly address common sources of overspending:
Elimination of Duplicate Applications: One of the most immediate sources of savings comes from identifying and eliminating duplicate or overlapping applications. Organizations often discover that different departments have subscribed to similar tools that perform the same functions. For example, multiple teams might use different project management platforms when a single enterprise solution could serve everyone’s needs.
Rightsizing Subscriptions: Many SaaS applications offer multiple pricing tiers with different feature sets and user limits. Without proper monitoring, organizations often maintain higher-tier subscriptions than necessary or pay for more user licenses than they actually need. License management helps identify these opportunities by analyzing actual usage patterns against subscription levels.
Proactive Renewal Management: Automatic subscription renewals can lead to continued spending on applications that are no longer needed or could be replaced with more cost-effective alternatives. A renewal calendar and proactive review process ensure that each renewal decision is intentional and based on current business needs rather than administrative oversight.
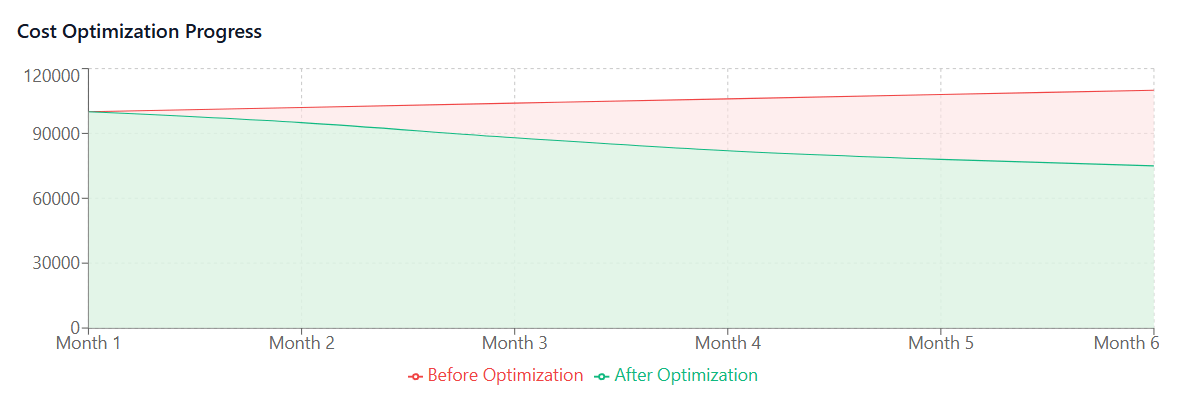
Usage-Based Optimization: By tracking how intensively different users engage with various applications, organizations can make informed decisions about license allocation. Users who rarely log in or use only basic features might be moved to lower-cost tiers, while power users can be prioritized for premium features.
Negotiation Leverage: Centralized license management provides better visibility into total spending with individual vendors, creating opportunities for volume discounts and improved contract terms. When organizations can demonstrate their total commitment to a vendor across multiple products or departments, they gain significant negotiation leverage.
Prevention of Shadow IT Costs: By implementing proper governance and approval processes, organizations can prevent unauthorized SaaS purchases that often result in duplicate functionality and wasted spending. This doesn’t mean slowing down business operations, but rather channeling software requests through appropriate evaluation processes.
Seasonal and Project-Based Optimization: Some SaaS applications are only needed for specific projects or seasonal business activities. Effective license management helps organizations identify these patterns and adjust subscriptions accordingly, perhaps scaling down during off-seasons or canceling subscriptions when projects conclude.
Common SaaS Licensing Challenges
Organizations implementing SaaS license management typically encounter several recurring challenges that must be addressed for successful cost optimization:
Lack of Visibility: The most fundamental challenge is simply not knowing what SaaS applications are being used across the organization. Shadow IT adoption, decentralized purchasing, and the ease of SaaS procurement mean that comprehensive discovery requires ongoing effort and multiple detection methods.
Complex Pricing Models: SaaS vendors often employ sophisticated pricing strategies that can be difficult to analyze and optimize. Per-user pricing, feature-based tiers, usage-based billing, and various add-on services create complexity that makes it challenging to compare alternatives or forecast costs accurately.
User Resistance to Change: Employees often develop strong preferences for specific tools and may resist efforts to consolidate applications or switch to alternative solutions. Change management becomes a critical component of successful license optimization initiatives.
Integration Dependencies: Some SaaS applications become deeply integrated into business processes or connected to other systems, making it difficult to replace them even when they appear underutilized. These technical dependencies must be carefully mapped and considered in optimization decisions.
Vendor Lock-in: Long-term contracts, data migration challenges, and proprietary integrations can create vendor lock-in situations that limit an organization’s ability to optimize their SaaS portfolio. Early identification of these situations helps inform future purchasing decisions.
Multi-Department Coordination: When applications are used across multiple departments, optimization decisions require coordination and compromise among various stakeholders. What appears underutilized from one perspective might be critical from another.
Compliance and Security Requirements: Certain industries or business functions have specific compliance requirements that limit the available SaaS options. Security policies may also restrict the use of certain applications or require specific configurations that affect licensing decisions.
Best Practices for SaaS License Management
Successful SaaS license management requires implementing proven practices that address both technical and organizational aspects of software subscription oversight:
Establish a Centralized SaaS Management Office: Organizations should designate a central team or individual responsible for SaaS license management across the organization. This team serves as the primary point of contact for subscription requests, renewal decisions, and optimization initiatives while maintaining relationships with key vendors.
Implement Regular Usage Reviews: Monthly or quarterly reviews of application usage help identify optimization opportunities before they become significant cost drains. These reviews should examine both quantitative usage data and qualitative feedback from users about application value and necessity.
Create Standardized Evaluation Processes: Before approving new SaaS subscriptions, organizations should have standardized evaluation criteria that consider functionality overlap, total cost of ownership, security requirements, and integration capabilities. This process helps prevent duplicate purchases and ensures new applications align with broader IT strategy.
Negotiate Strategic Vendor Relationships: Rather than managing numerous individual subscriptions, organizations should identify their most critical SaaS vendors and develop strategic relationships that provide better pricing, support, and contract terms. This might involve committing to higher volumes in exchange for significant discounts.
Maintain Accurate Financial Forecasting: SaaS subscriptions create ongoing financial commitments that must be properly forecasted and budgeted. Organizations should maintain rolling forecasts that account for known renewals, planned expansions, and anticipated optimization savings.
Implement Automated Alerts and Workflows: Manual license management becomes unsustainable as SaaS portfolios grow. Automated alerts for renewal dates, usage thresholds, and budget variances help ensure that important decisions don’t fall through administrative cracks.
Regular Vendor Performance Reviews: Beyond cost optimization, organizations should regularly evaluate vendor performance in terms of service quality, support responsiveness, and feature development. Poor vendor performance might justify switching to alternatives even when direct cost savings aren’t significant.
Document and Share Best Practices: As teams gain experience with SaaS license management, they should document successful strategies and share them across the organization. This knowledge sharing accelerates improvement and helps avoid repeated mistakes.
The Role of SaaS Management Platforms
Specialized SaaS management platforms have emerged as essential tools for organizations serious about optimizing their software subscriptions. These platforms provide comprehensive capabilities that would be difficult to implement manually:
Automated Discovery: Advanced SaaS management platforms can automatically discover applications through multiple methods including expense integration, network monitoring, and single sign-on system analysis. This automated discovery ensures that the application inventory remains current without requiring manual updates.
Usage Analytics: These platforms provide detailed analytics about how applications are used, including login frequency, feature utilization, and user engagement levels. This data enables data-driven decisions about license optimization and renewal priorities.
Financial Management: Specialized platforms can handle complex SaaS pricing models, multi-currency environments, and various billing cycles while providing clear reporting and forecasting capabilities. They often integrate with existing financial systems to provide comprehensive cost visibility.
Renewal Management: Automated renewal calendars with configurable alert schedules ensure that upcoming renewals receive appropriate attention and evaluation. Some platforms can even initiate renewal workflows automatically based on usage patterns and business rules.
Vendor Management: Centralized vendor information management helps organizations maintain important contract details, track vendor performance, and manage communication across multiple stakeholder groups.
Governance and Approval Workflows: Built-in workflow capabilities support approval processes for new subscriptions while maintaining audit trails for compliance purposes. These workflows can be customized to match organizational policies and approval hierarchies.
Binadox represents a leading example of comprehensive SaaS management platforms, providing organizations with the tools needed to gain complete visibility into their software subscriptions while implementing effective cost optimization strategies.
Implementation Strategies
Successfully implementing SaaS license management requires a structured approach that addresses both technical and organizational challenges:
Phase 1: Discovery and Assessment: Begin by conducting a comprehensive audit of existing SaaS applications across the organization. This includes both sanctioned applications and shadow IT discoveries. Gather information about costs, renewal dates, user counts, and current usage levels.
Phase 2: Platform Selection and Setup: Choose a SaaS management platform that meets your organization’s specific needs and integrate it with existing systems such as expense management, identity management, and financial reporting tools. Configure automated discovery mechanisms and establish baseline metrics.
Phase 3: Governance Framework Development: Establish policies and procedures for SaaS procurement, approval workflows, and ongoing management responsibilities. Define roles and responsibilities for different stakeholders including IT, finance, and business unit leaders.
Phase 4: Initial Optimization: Based on the discovery phase findings, implement immediate optimization opportunities such as eliminating duplicate subscriptions, rightsizing obvious oversights, and consolidating vendor relationships where possible.
Phase 5: Ongoing Management: Establish regular review cycles, automated monitoring, and continuous improvement processes. This includes monthly usage reviews, quarterly strategic assessments, and annual vendor relationship evaluations.
Phase 6: Advanced Optimization: As the program matures, implement more sophisticated optimization strategies such as dynamic license allocation, predictive analytics for usage forecasting, and strategic vendor partnerships.
Measuring Success in SaaS License Management
Effective SaaS license management programs require clear metrics to demonstrate value and guide continuous improvement:
Cost Reduction Metrics: Track total SaaS spending reductions, cost per user improvements, and eliminated waste from unused subscriptions. Many organizations achieve 20-30% cost reductions within the first year of implementing comprehensive license management.
Operational Efficiency Indicators: Measure improvements in procurement cycle times, renewal processing efficiency, and vendor management overhead. These operational improvements often provide significant value beyond direct cost savings.
Compliance and Risk Metrics: Monitor license compliance rates, security policy adherence, and vendor risk assessment completion. These metrics help demonstrate the risk management value of proper license management.
User Satisfaction Measures: Track user satisfaction with approved applications and the efficiency of the request and approval process. Successful license management should improve rather than hinder user productivity.
Financial Predictability: Measure improvements in budget accuracy, forecast reliability, and financial planning confidence. Better license management should lead to more predictable and manageable software costs.
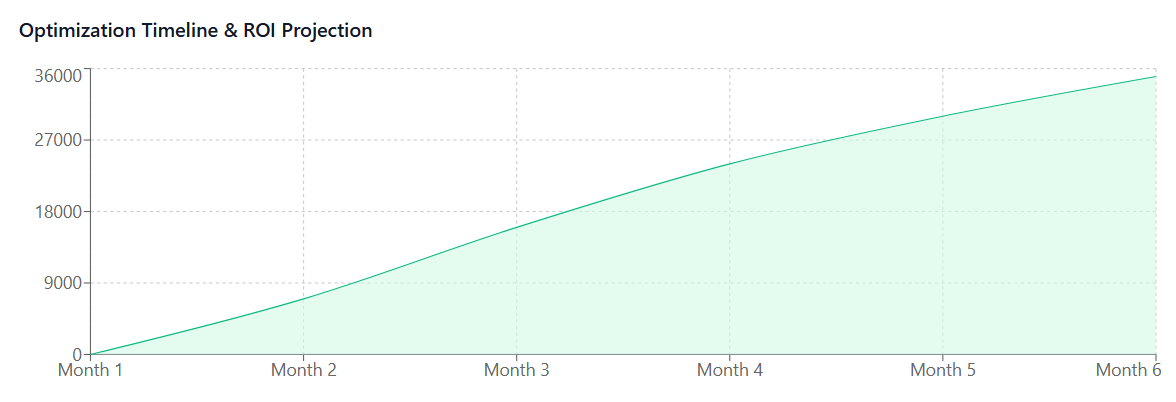
Future Trends in SaaS License Management
The SaaS license management landscape continues to evolve with several emerging trends:
AI-Powered Optimization: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are beginning to enable more sophisticated usage pattern analysis and automated optimization recommendations. These technologies can identify optimization opportunities that might not be apparent through manual analysis.
Integration with Business Intelligence: SaaS management platforms are increasingly integrating with broader business intelligence systems to provide context about how software usage relates to business outcomes and productivity metrics.
Dynamic License Allocation: Some organizations are experimenting with dynamic license allocation systems that automatically adjust user access based on actual usage patterns and business needs.
Sustainability Metrics: As organizations become more focused on environmental impact, SaaS license management may begin incorporating sustainability metrics related to cloud resource consumption and vendor environmental practices.
Conclusion
SaaS license management has evolved from a nice-to-have administrative function to an essential business discipline that directly impacts organizational cost efficiency and operational effectiveness. As businesses continue to adopt more SaaS applications and subscription spending grows, the ability to effectively manage these investments becomes increasingly critical for maintaining competitive advantage.
The benefits of comprehensive SaaS license management extend far beyond simple cost reduction. Organizations that implement effective license management practices gain better visibility into their software investments, improve compliance and security posture, enhance vendor relationships, and create more predictable financial planning processes.
However, successful SaaS license management requires more than just implementing the right tools. It demands organizational commitment to establishing proper governance frameworks, maintaining ongoing optimization processes, and fostering collaboration between IT, finance, and business stakeholders.
The organizations that master SaaS license management will find themselves better positioned to take advantage of the continuing innovation in cloud-based software while maintaining cost discipline and operational efficiency. As the SaaS ecosystem continues to mature and expand, the importance of sophisticated license management capabilities will only continue to grow.
By implementing the strategies, best practices, and tools outlined in this guide, organizations can transform their approach to SaaS spending from reactive cost management to proactive investment optimization. The result is not just reduced costs, but better alignment between software investments and business objectives, leading to improved productivity and competitive advantage in an increasingly digital business environment.

