Enterprise organizations today are drowning in SaaS subscriptions. The average company uses 80 different software applications, with many departments independently procuring tools without centralized oversight. This SaaS sprawl creates a perfect storm of wasted spending, security vulnerabilities, and operational inefficiencies that drain budgets and productivity.
But what happens when enterprises take control? Real-world case studies show that systematic SaaS rationalization can deliver 30% or more in cost savings while simultaneously improving security, user experience, and operational efficiency. This comprehensive analysis examines actual enterprise transformations and reveals the tangible benefits of strategic SaaS optimization.
The Hidden Costs of Unmanaged SaaS Spending
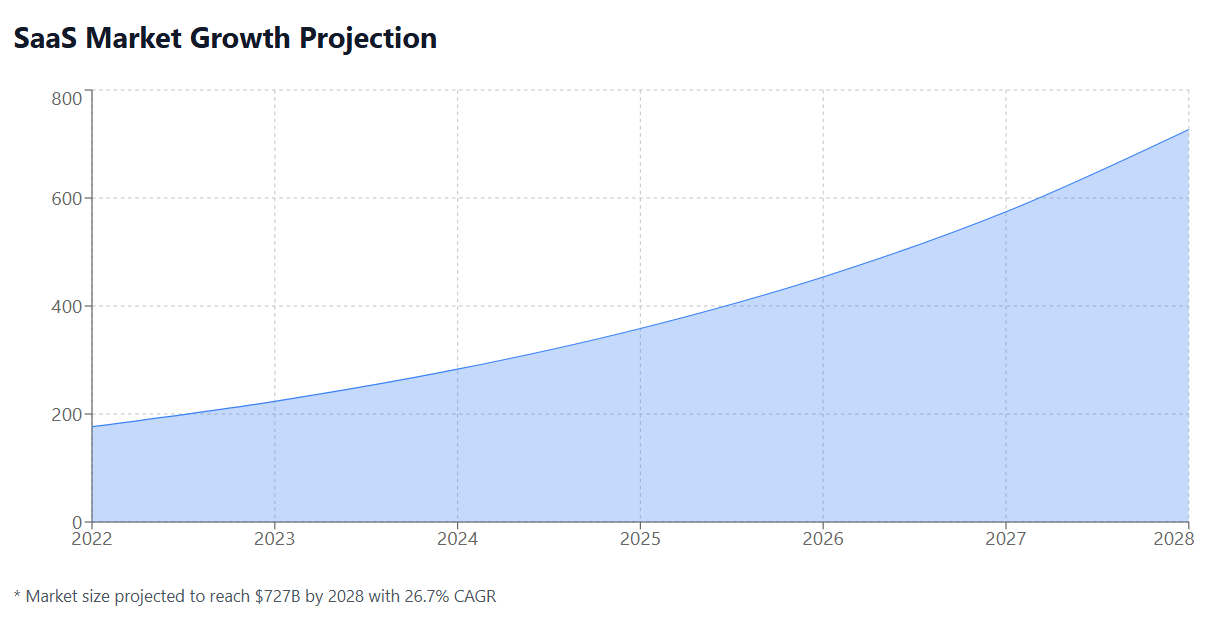
Before diving into success stories, it’s crucial to understand the scope of the problem. Enterprise SaaS spending has exploded, with global spending on cloud-based applications reaching $482 billion in 2022 according to Gartner. However, much of this spending is ineffective and poorly managed.
Common SaaS Spending Inefficiencies
Duplicate Applications: Different departments often purchase similar tools independently. Marketing might use HubSpot while Sales uses Salesforce, when a single integrated platform could serve both needs more cost-effectively.
Unused Licenses: The typical enterprise wastes 30-40% of its SaaS spending on unused or underutilized licenses. Employees leave, roles change, or teams abandon tools, but the subscriptions continue auto-renewing.
Feature Oversubscription: Organizations frequently purchase premium plans with advanced features that only a small percentage of users actually need, leading to significant overspending on unused functionality.
Shadow IT: When procurement processes are too slow or restrictive, departments bypass official channels and purchase software independently, creating billing fragmentation and security risks.
Poor Renewal Management: Without centralized tracking, enterprises miss renewal opportunities, fail to negotiate better terms, and often discover forgotten subscriptions only when conducting audits. Implementing proper SaaS subscription management practices can eliminate these costly oversights.
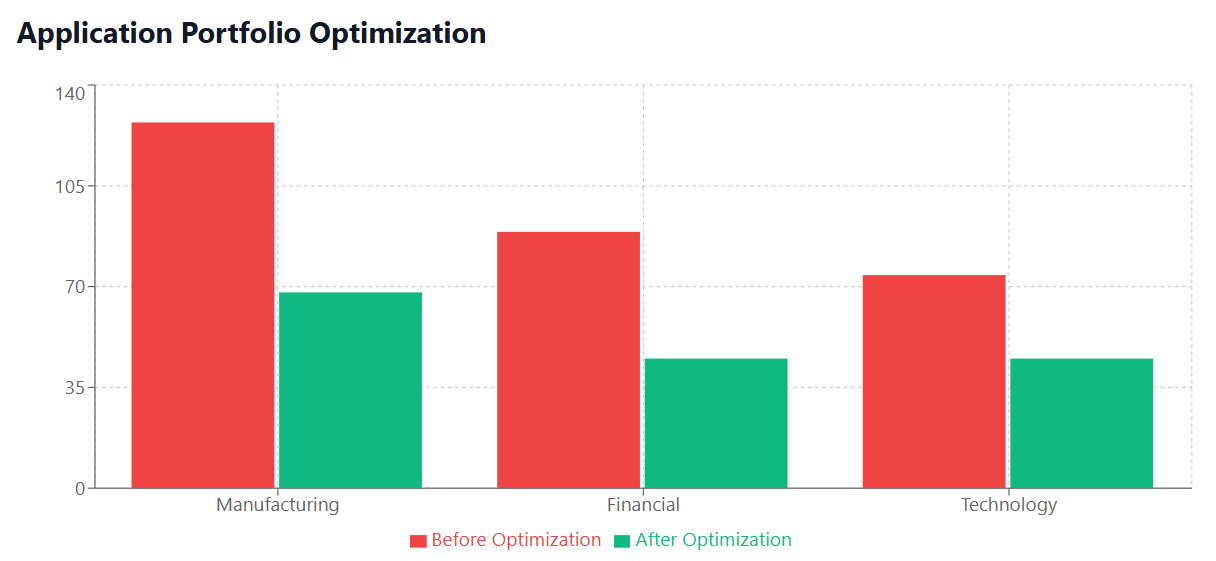
Case Study 1: Global Manufacturing Company – 35% SaaS Cost Reduction
A Fortune 500 manufacturing company with 15,000 employees across 40 countries faced escalating software subscription costs that had grown organically without oversight. Their challenge exemplified typical enterprise SaaS management problems.
Initial State Analysis
The company’s audit revealed shocking inefficiencies:
- 127 different SaaS applications across various departments
- $2.8 million annual SaaS spending with no centralized visibility
- 42% of licenses unused or underutilized based on login data analysis
- 23 duplicate applications serving similar functions
- No standardized procurement process for software purchases
Rationalization Strategy Implementation
Working with a SaaS spend management platform, the company implemented a comprehensive optimization strategy:
Discovery and Inventory: Automated tools scanned all corporate cards, expense reports, and invoices to create a complete application inventory, revealing several “ghost” subscriptions that had been forgotten.
Usage Analysis: Deep dive into actual user engagement showed that many expensive licenses were barely used. For example, their Adobe Creative Suite had 500 licenses but only 89 active users in the past 90 days.
Consolidation Planning: The team identified opportunities to replace multiple point solutions with integrated platforms. Instead of using separate tools for project management, communication, and file sharing, they migrated to Microsoft 365 ecosystem.
Vendor Negotiations: Armed with usage data and consolidation plans, procurement renegotiated contracts, achieving volume discounts and eliminating redundant features. This strategic approach to cloud cost optimization enabled significant savings beyond simple license reductions.
Results and Savings Breakdown
The 18-month rationalization effort delivered exceptional results:
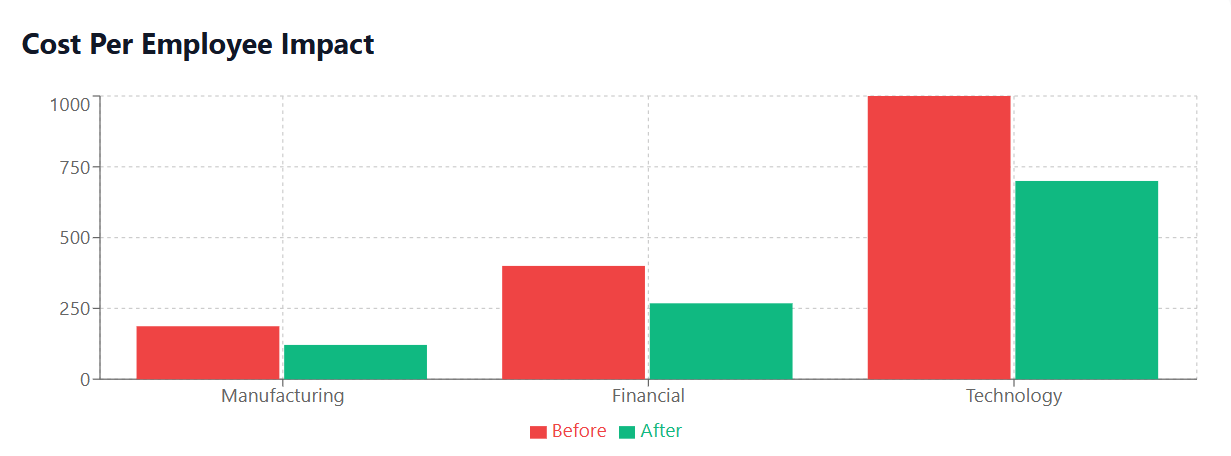
- Total savings: $980,000 annually (35% reduction)
- License optimization: $420,000 saved by rightsizing subscriptions
- Application consolidation: $310,000 saved by eliminating duplicate tools
- Vendor renegotiation: $250,000 saved through better contract terms
- Reduced applications from 127 to 68 while maintaining functionality
- Improved security posture through reduced attack surface
The company also reported significant operational improvements beyond cost savings, including reduced training complexity, better data integration, and enhanced compliance management.
Case Study 2: Financial Services Firm – Strategic SaaS Portfolio Optimization
A mid-sized financial services company with 3,500 employees demonstrated how strategic SaaS management tools can transform not just costs but entire operational workflows.
The Challenge: Fragmented Tool Ecosystem
The firm’s decentralized approach to software procurement had created significant challenges:
- 89 different applications with substantial functional overlap
- $1.4 million annual spending across multiple vendors
- Security compliance issues due to ungoverned software adoption
- Integration difficulties causing data silos and workflow disruptions
- Audit findings highlighting governance weaknesses
Comprehensive Optimization Approach
The company implemented a holistic rationalization strategy focusing on both immediate savings and long-term operational excellence:
Centralized SaaS Procurement: Established a software review board with representatives from IT, Finance, and Security to evaluate all software requests against existing capabilities and strategic objectives.
Automated SaaS Tracking: Deployed specialized tools to monitor usage patterns, track renewal dates, and identify optimization opportunities in real-time rather than relying on periodic manual audits.
Security-First Evaluation: Prioritized applications that met stringent financial services compliance requirements, eliminating tools that posed unnecessary regulatory risks. This approach aligns with cloud security best practices for enterprise environments.
Integration Assessment: Evaluated each application’s ability to integrate with core systems, prioritizing platforms that enhanced rather than fragmented their technology ecosystem.
Quantified Business Impact
The rationalization program delivered measurable improvements across multiple dimensions:
Direct Cost Savings: $462,000 annually (33% reduction)
- Subscription optimization: $198,000 through rightsizing and usage-based adjustments
- Vendor consolidation: $156,000 by reducing the number of software vendors from 47 to 22
- Contract renegotiation: $108,000 leveraging improved buying power and longer-term commitments
Operational Efficiency Gains:
- 65% reduction in software onboarding time through standardized, integrated platforms
- 40% decrease in IT support tickets related to software issues
- Improved employee productivity with streamlined, familiar interfaces across tools
Risk Reduction Benefits:
- Enhanced security posture through vetted, compliant applications
- Reduced audit complexity with centralized software governance
- Better data governance through integrated rather than siloed systems
Case Study 3: Technology Startup – Scaling Smart with SaaS Optimization
Even rapidly growing organizations can benefit from proactive SaaS spend management. A technology startup that grew from 150 to 800 employees in two years provides valuable insights into scaling efficiently.
Rapid Growth Challenges
The company’s explosive growth created typical scaling challenges:
- Subscription costs growing 340% faster than revenue
- 74 different applications purchased reactively to meet immediate needs
- No usage monitoring leading to significant waste
- Decentralized purchasing by different teams and departments
- Approaching $800,000 annual SaaS spending with limited visibility
Proactive Optimization Strategy
Rather than waiting for cost pressures to force action, the company implemented preventive measures:
Usage-Based Licensing: Migrated from fixed-seat licenses to usage-based models where possible, ensuring costs scaled proportionally with actual utilization rather than planned headcount. This approach helps organizations avoid common pitfalls in cloud cost anomaly detection and spending management.
Regular Optimization Reviews: Implemented quarterly reviews of all subscriptions, analyzing usage patterns and adjusting licenses proactively rather than reactively.
Integrated Platform Strategy: Prioritized platforms that could serve multiple functions, reducing the total number of vendor relationships and training requirements.
Employee Education: Trained team leads on the financial impact of software decisions, creating a culture of cost-conscious tool selection.
Scaling Success Results
The optimization program enabled efficient scaling:
- Cost growth controlled to 180% (vs. 340% previous trajectory)
- Annual savings: $240,000 (30% vs. unmanaged trajectory)
- Reduced applications to 45 while supporting 5x larger team
- Improved new employee onboarding through standardized tool stack
- Better vendor relationships through strategic partnerships rather than ad-hoc purchases
The Technology Behind Successful SaaS Rationalization
These case studies highlight the critical role of specialized SaaS management platforms in achieving optimization success. Manual tracking spreadsheets and periodic audits simply cannot provide the visibility and control needed for effective cost management.
Essential SaaS Management Capabilities
Automated Discovery: Modern platforms can automatically discover all SaaS subscriptions across corporate cards, invoices, and even browser extensions, providing complete visibility into the application portfolio.
Usage Analytics: Detailed usage tracking reveals which applications and features are actually being used, enabling data-driven decisions about license optimization and tool consolidation.
Renewal Management: Centralized renewal calendars prevent surprise charges and create opportunities for proactive vendor negotiations before contracts auto-renew.
Cost Attribution: Assignment of costs to departments, projects, or cost centers enables better budgeting and accountability for software spending decisions.
Integration Monitoring: Tracking of application integrations and dependencies helps identify consolidation opportunities while avoiding disruptions to critical workflows.
Industry-Specific Optimization Patterns
Different industries show distinct patterns in SaaS optimization opportunities, reflecting their unique operational requirements and regulatory constraints.
Healthcare Organizations
Healthcare organizations typically achieve 25-40% savings through rationalization, with particular opportunities in:
- Clinical workflow tools that often overlap between departments
- Communication platforms where HIPAA compliance creates vendor consolidation benefits
- Administrative systems with significant integration potential, including Microsoft Office 365 optimization for healthcare environments
Financial Services
Financial services firms average 30-45% savings, focusing on:
- Compliance management tools where vendor consolidation reduces audit complexity
- Client communication platforms with stringent security requirements
- Analytics and reporting tools that benefit from data integration
Manufacturing Companies
Manufacturing organizations typically achieve 28-38% savings through:
- Supply chain management tools with significant integration potential
- Quality management systems often duplicated across facilities
- Training and certification platforms that benefit from standardization
Implementation Best Practices for SaaS Rationalization
Successful optimization requires systematic approaches rather than ad-hoc cost-cutting measures.
Discovery and Assessment Phase
Comprehensive Application Inventory: Use automated tools to discover all applications, including shadow IT purchases and forgotten subscriptions that may not appear in centralized systems.
Usage Pattern Analysis: Analyze actual usage data over at least 90 days to understand genuine utilization patterns rather than relying on user surveys or assumptions.
Functional Overlap Mapping: Identify applications with overlapping capabilities that could be consolidated without losing essential functionality.
Integration Dependency Assessment: Map application integrations and data flows to avoid disrupting critical business processes during consolidation.
Optimization Strategy Development
Optimization Strategy Development: Develop criteria for evaluating applications based on cost, usage, strategic importance, and integration complexity to focus optimization efforts on high-impact opportunities. Implementing FinOps principles ensures a structured approach to cost management across all cloud and SaaS investments.
Vendor Relationship Strategy: Plan vendor negotiations strategically, leveraging consolidation opportunities and longer-term commitments to achieve better pricing.
Change Management Planning: Prepare employees for tool changes with training programs and support resources to minimize productivity disruption.
Security and Compliance Review: Ensure optimization decisions maintain or improve security posture and regulatory compliance requirements.
Implementation and Monitoring
Phased Rollout Approach: Implement changes gradually to allow for adjustment and minimize business disruption, starting with lowest-risk optimization opportunities.
Continuous Monitoring: Establish ongoing tracking of usage patterns, costs, and user satisfaction to identify new optimization opportunities as they emerge.
Success Metrics Tracking: Monitor both cost metrics and operational indicators to ensure optimization efforts deliver comprehensive business value.
Regular Review Cycles: Schedule quarterly or semi-annual reviews to maintain optimization momentum and prevent the return of SaaS sprawl.
Beyond Cost Savings: Additional Benefits of SaaS Rationalization
While cost reduction drives most rationalization initiatives, enterprises consistently discover additional benefits that often exceed the financial savings in long-term value.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Reduced Attack Surface: Fewer applications mean fewer potential security vulnerabilities and breach points, significantly improving overall security posture.
Simplified Compliance: Concentrated vendor relationships make audit processes more manageable and reduce compliance complexity across regulatory frameworks.
Improved Access Management: Standardized applications enable more effective identity and access management, reducing the risk of inappropriate data access.
Operational Excellence Improvements
Streamlined Workflows: Integrated platforms eliminate data silos and reduce the need for manual data transfer between systems, improving process efficiency.
Reduced Training Complexity: Fewer applications mean less training overhead for new employees and easier skill development for existing staff.
Better Data Quality: Consolidated platforms improve data consistency and accuracy by eliminating redundant data entry and synchronization issues.
Strategic Business Advantages
Vendor Relationship Leverage: Concentrated spending with fewer vendors increases negotiating power for better terms, support, and strategic partnerships.
Innovation Focus: Reduced tool management overhead allows IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine software administration.
Improved Decision Making: Integrated data from consolidated platforms enables better business intelligence and more informed strategic planning.
Looking Forward: The Future of Enterprise SaaS Management
As enterprises continue to rely heavily on SaaS solutions, the importance of systematic optimization will only increase. Emerging trends suggest even greater opportunities for cost optimization and operational improvement.
Artificial Intelligence in SaaS Management
AI-powered SaaS optimization tools are beginning to provide predictive insights into usage patterns, automatically identifying optimization opportunities and even suggesting specific consolidation strategies based on usage behavior analysis.
Integration-First Platform Selection
Organizations are increasingly prioritizing platforms with robust integration capabilities, recognizing that data connectivity and workflow integration often provide more value than feature richness in isolated applications.
Outcome-Based SaaS Procurement
Forward-thinking enterprises are moving beyond seat-based licensing toward outcome-based agreements that align software costs with actual business value delivered, creating natural incentives for optimization.
Conclusion: The Strategic Imperative for SaaS Rationalization
The case studies and analysis presented demonstrate that SaaS rationalization delivers far more than cost savings. Organizations achieving 30% or greater reductions in software spending consistently report improved security, enhanced operational efficiency, and better strategic positioning for future growth.
The key to success lies not in reactive cost-cutting but in proactive, strategic optimization supported by appropriate technology platforms and systematic processes. Enterprise SaaS spending will continue to grow, but organizations that implement effective management practices will achieve better outcomes at lower costs while building more resilient, scalable technology foundations.
For enterprises currently struggling with SaaS sprawl, the evidence is clear: systematic rationalization delivers measurable, sustainable benefits that compound over time. The question is not whether to optimize, but how quickly to begin and how comprehensively to approach the opportunity. A comprehensive cloud management strategy should encompass both traditional cloud resources and SaaS applications for maximum effectiveness.
With the right strategy, tools, and commitment, any organization can achieve similar results to these case studies, transforming software spending from a cost center into a competitive advantage. The investment in proper SaaS spend management pays dividends not just in immediate cost savings but in long-term operational excellence and strategic capability.

