Economic downturns create unprecedented pressure on businesses to optimize their spending while maintaining opePlanning SaaS Expense Cuts in a Downturn: Prioritization Framework
Economic downturns create unprecedented pressure on businesses to optimize their spending while maintaining operational efficiency. For modern organizations heavily reliant on Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions, this challenge becomes particularly complex. With companies using an average of 80+ SaaS applications, effective SaaS spend management during economic uncertainty requires a strategic, data-driven approach that balances cost reduction with business continuity.
This comprehensive guide presents a proven prioritization framework for planning SaaS expense cuts during downturns, helping organizations make informed decisions that protect their core operations while achieving meaningful cost savings.
Understanding the SaaS Spending Landscape During Economic Uncertainty
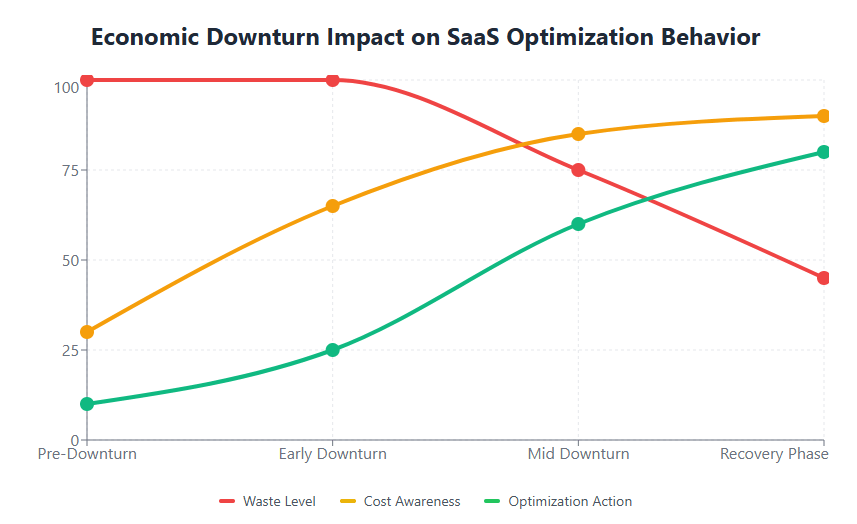
The rise of affordable SaaS solutions has transformed how businesses operate, but economic downturns expose the hidden costs and inefficiencies in many organizations’ software portfolios. Unlike traditional software investments, SaaS applications often proliferate organically across departments, creating a complex web of subscriptions that can be difficult to manage and optimize.
During economic uncertainty, organizations face unique challenges in SaaS spend management:
Shadow IT Proliferation: Teams often subscribe to SaaS tools independently, creating visibility gaps that become critical during cost-cutting initiatives. Without centralized oversight, organizations may discover duplicate subscriptions, underutilized licenses, or unauthorized software purchases that drain budgets unnecessarily.
Subscription Creep: The ease of subscribing to SaaS applications means costs can accumulate gradually, making it difficult to track total software spending until it becomes a significant budget line item. This gradual increase often goes unnoticed during prosperous periods but becomes a major concern during economic downturns.
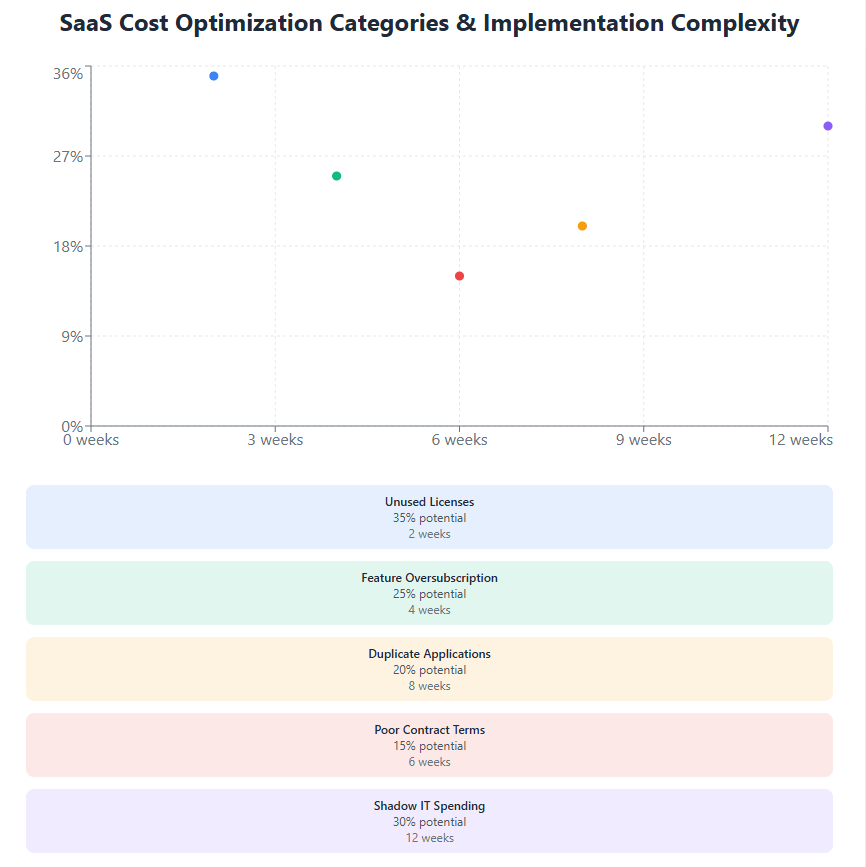
Feature Oversubscription: Many organizations pay for premium features they don’t use, representing immediate opportunities for cost reduction without operational impact. App budget management becomes crucial in identifying these inefficiencies.
Contract Commitments: Annual and multi-year SaaS contracts can create inflexibility during economic downturns, requiring careful evaluation of termination costs versus ongoing expenses. Understanding renewal dates and contract terms becomes critical for effective budget management for startups and established enterprises alike.
The Strategic Importance of SaaS Optimization
Effective SaaS cost management during downturns serves multiple strategic purposes beyond immediate cost savings. Organizations that approach SaaS optimization systematically often discover operational improvements and efficiency gains that persist long after economic conditions improve.
Operational Resilience: By identifying and eliminating redundant or underutilized software, companies can streamline their technology stack, reducing complexity and improving team productivity. This consolidation often leads to improved workflow efficiency and reduced training requirements.
Financial Predictability: Implementing robust SaaS governance policies creates better visibility into software spending, enabling more accurate budget forecasting and financial planning. This transparency becomes invaluable for maintaining investor confidence and securing funding during uncertain economic periods.
Vendor Relationship Optimization: Economic downturns often present opportunities to renegotiate SaaS contracts with better terms. Vendors may offer discounts, extended payment terms, or additional features to retain customers during challenging periods.
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that optimize their SaaS stack efficiently can redirect resources toward core business activities and growth initiatives, potentially gaining market share while competitors struggle with bloated software costs.
The Four-Phase Prioritization Framework
Phase 1: Discovery and Assessment
The foundation of effective SaaS expense reduction lies in comprehensive visibility into your current software portfolio. This discovery phase involves identifying all SaaS applications across your organization, regardless of how they were acquired or who manages them.
Complete SaaS Inventory: Begin by conducting a thorough audit of all SaaS subscriptions, including those paid through corporate credit cards, expense reports, or departmental budgets. Automated SaaS subscription management tools can help identify applications that might otherwise be overlooked, providing a complete picture of your software ecosystem.
Usage Analysis: For each identified application, gather detailed usage metrics including active users, feature utilization, and frequency of access. Many SaaS management tools provide analytics that reveal the true utilization rates of your software investments, highlighting opportunities for optimization.
Cost Categorization: Organize your SaaS spending into categories such as core business applications, productivity tools, specialized departmental software, and experimental or trial applications. This categorization helps prioritize which areas offer the greatest potential for cost reduction.
Contract Analysis: Review contract terms, renewal dates, and cancellation policies for each SaaS subscription. Understanding your contractual obligations is crucial for planning cost reduction initiatives that minimize termination fees and maximize savings opportunities.
Phase 2: Business Impact Evaluation
Once you have complete visibility into your SaaS portfolio, the next phase involves evaluating the business impact of each application. This evaluation helps ensure that cost-cutting decisions don’t inadvertently harm critical business operations.
Criticality Assessment: Classify each SaaS application based on its importance to core business operations. Critical applications that directly support revenue generation, customer service, or regulatory compliance should be protected from cuts, while nice-to-have tools become candidates for elimination or downgrading.
Redundancy Identification: Look for applications that provide overlapping functionality. Many organizations discover they’re paying for multiple tools that serve similar purposes, presenting immediate consolidation opportunities. For example, teams might use several project management tools or communication platforms that could be consolidated into a single solution.
ROI Analysis: Calculate the return on investment for each SaaS application by comparing its cost against the business value it provides. Applications with poor ROI that don’t serve critical functions become prime candidates for elimination.
User Feedback Integration: Gather input from actual users about which applications they find most valuable and which they could live without. This qualitative data helps inform decisions about applications that might have low usage metrics but high user satisfaction, or vice versa.
Phase 3: Optimization Strategy Development
With a clear understanding of your SaaS portfolio and business impact assessment complete, you can develop targeted optimization strategies that balance cost reduction with operational continuity.
Subscription Rightsizing: Analyze user counts and feature utilization to identify opportunities for downgrading to less expensive plans. Many organizations pay for enterprise features that benefit only a small subset of users, making plan optimization a quick win for cost reduction.
Consolidation Planning: Develop plans to consolidate redundant applications onto single platforms where possible. This might involve migrating from multiple specialized tools to comprehensive platforms that offer integrated functionality.
Vendor Negotiation Strategy: Prepare for contract renegotiations by researching alternative solutions and understanding your negotiating position. Economic downturns often provide leverage for securing better terms, extended payment schedules, or additional features at current pricing. Learn more about implementing effective SaaS renewal strategies to maximize your negotiating power.
Phased Implementation: Create a timeline for implementing changes that minimizes business disruption. Consider factors such as contract renewal dates, seasonal business cycles, and team availability for transitions.
Phase 4: Implementation and Monitoring
The final phase involves executing your optimization plan while maintaining careful monitoring to ensure changes don’t negatively impact business operations.
Gradual Rollout: Implement changes incrementally, starting with low-risk applications and gradually moving to more complex consolidations. This approach allows you to learn from early implementations and adjust your strategy as needed.
Performance Monitoring: Establish metrics to track the impact of changes on both costs and business operations. Monitor user satisfaction, productivity metrics, and operational efficiency to ensure optimizations don’t create hidden costs elsewhere in the organization.
Continuous Optimization: SaaS optimization isn’t a one-time activity. Establish regular review cycles to assess new applications, monitor usage patterns, and identify emerging optimization opportunities. This ongoing process helps prevent future subscription creep and maintains cost efficiency.
Documentation and Governance: Document your optimization decisions and establish governance policies to prevent future inefficiencies. Clear approval processes for new SaaS subscriptions and regular usage reviews help maintain the benefits of your optimization efforts.
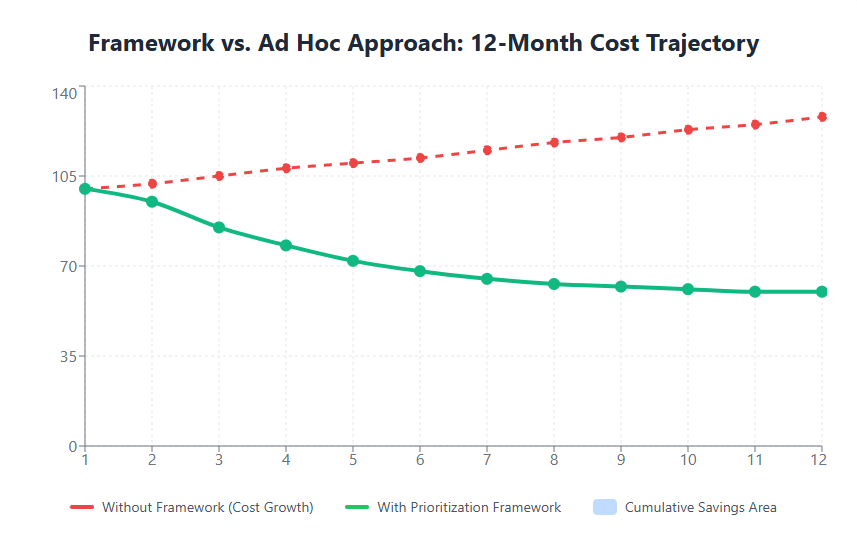
Practical Implementation Guidelines
Establishing SaaS Governance
Effective SaaS governance policies are essential for maintaining cost efficiency and preventing future subscription sprawl. These policies should address procurement processes, usage monitoring, and regular optimization reviews.
Centralized Procurement: Implement centralized SaaS procurement processes that require approval for new subscriptions and ensure new applications align with existing tools and business objectives. This centralization helps prevent duplicate subscriptions and ensures new software purchases receive proper evaluation. Effective SaaS spend management requires clear governance from the procurement stage through renewal decisions.
Usage Monitoring: Establish regular monitoring of SaaS usage patterns to identify underutilized applications before they become costly problems. Automated SaaS management tools can provide alerts when usage drops below predetermined thresholds, enabling proactive optimization.
Regular Reviews: Schedule quarterly or semi-annual reviews of your SaaS portfolio to assess usage, evaluate alternatives, and identify optimization opportunities. These regular assessments help maintain cost efficiency and ensure your software stack evolves with business needs.
Leveraging SaaS Management Tools
Modern SaaS management platforms provide powerful capabilities for implementing and maintaining your optimization framework. These tools automate many aspects of SaaS discovery, monitoring, and optimization, making it easier to maintain cost efficiency at scale.
Automated Discovery: SaaS management tools can automatically identify applications across your organization, including shadow IT and forgotten subscriptions that drain budgets unnecessarily. This automated discovery ensures comprehensive visibility into your software portfolio.
Usage Analytics: Advanced analytics capabilities provide detailed insights into how teams use different applications, identifying opportunities for consolidation, rightsizing, or elimination. These insights enable data-driven optimization decisions that balance cost reduction with operational needs.
Cost Optimization Recommendations: Many SaaS management platforms provide automated recommendations for cost optimization based on usage patterns, contract terms, and alternative solutions. These recommendations help prioritize optimization efforts and quantify potential savings. Comprehensive SaaS optimization strategies can guide organizations through systematic cost reduction while maintaining operational effectiveness.
Renewal Management: Automated tracking of renewal dates and contract terms helps organizations proactively manage SaaS subscriptions, avoiding automatic renewals for underutilized applications and creating opportunities for renegotiation.
Measuring Success and ROI
Effective SaaS optimization requires clear metrics for measuring success and demonstrating return on investment. These metrics help justify optimization initiatives and guide future decision-making.
Cost Reduction Metrics: Track direct cost savings from eliminated subscriptions, downgrades, and renegotiated contracts. These immediate savings provide clear evidence of optimization success and help build support for ongoing initiatives.
Efficiency Improvements: Monitor operational efficiency improvements resulting from software consolidation and streamlined workflows. These qualitative benefits often provide long-term value that exceeds immediate cost savings.
User Satisfaction: Measure user satisfaction with optimized software tools to ensure cost reductions don’t negatively impact productivity or employee experience. Maintaining high user satisfaction ensures optimization initiatives support rather than hinder business objectives.
Budget Predictability: Assess improvements in budget forecasting accuracy and financial planning resulting from better SaaS visibility and governance. Enhanced predictability provides strategic value for business planning and investment decisions.
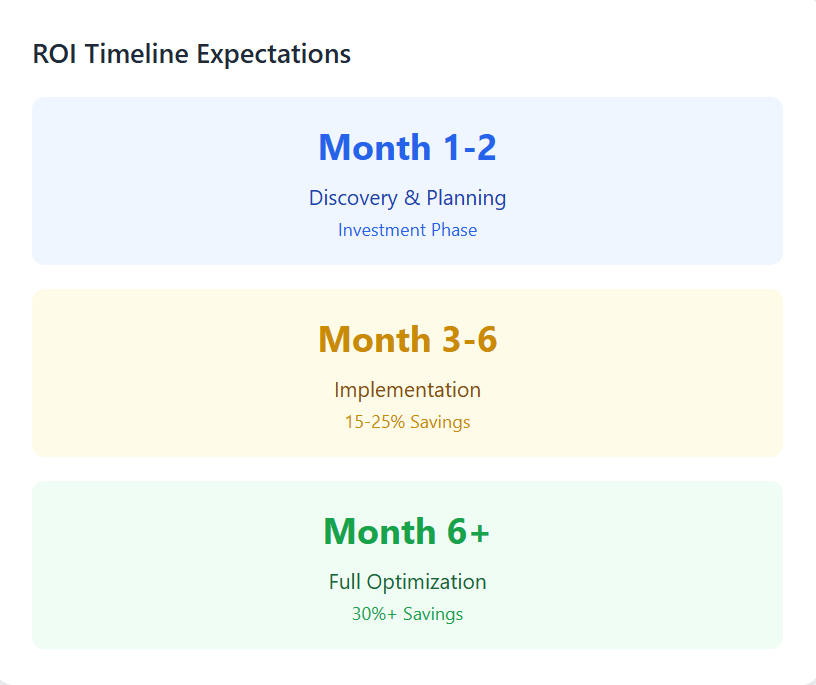
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Many organizations encounter predictable challenges when implementing SaaS optimization initiatives. Understanding these common pitfalls helps ensure successful implementation of your prioritization framework.
Over-Aggressive Cutting: Eliminating too many applications too quickly can disrupt business operations and create hidden costs elsewhere in the organization. Take a measured approach that prioritizes low-risk optimizations before tackling more complex consolidations. Consider exploring application rationalization strategies that balance cost reduction with operational continuity.
Ignoring User Needs: Failing to consider actual user requirements and workflows can result in optimization decisions that reduce productivity or force teams to find workaround solutions. Involve users in the evaluation process to ensure optimization decisions support rather than hinder their work.
Neglecting Integration Complexity: Some applications may be deeply integrated with other systems, making elimination or replacement more complex and costly than anticipated. Carefully assess integration dependencies before making optimization decisions.
Short-Term Focus: Focusing exclusively on immediate cost reduction without considering long-term strategic needs can result in decisions that create future problems or require costly reversals. Balance short-term savings with long-term strategic objectives.
Future-Proofing Your SaaS Strategy
While immediate cost reduction may be the primary driver for SaaS optimization during economic downturns, successful organizations use these initiatives to build more resilient and efficient software strategies for the future.
Scalable Architecture: Design your optimized SaaS stack with scalability in mind, ensuring you can easily add or remove applications as business needs change. This flexibility provides resilience for future economic uncertainty and growth opportunities.
Vendor Diversification: Avoid over-dependence on single vendors by maintaining a diversified portfolio of SaaS providers. This diversification reduces risk and provides leverage for future negotiations.
Continuous Learning: Use optimization initiatives as learning opportunities to better understand your organization’s software needs and usage patterns. This knowledge informs future procurement decisions and helps prevent inefficient spending.
Strategic Partnerships: Develop strategic relationships with key SaaS vendors that provide value beyond immediate software functionality. These partnerships can offer preferential pricing, early access to new features, and collaboration opportunities that provide competitive advantages.
Conclusion
Planning SaaS expense cuts during economic downturns requires a systematic approach that balances immediate cost reduction with long-term strategic objectives. The prioritization framework outlined in this guide provides a proven methodology for optimizing SaaS spending while maintaining operational efficiency and preparing for future growth.
Success in SaaS optimization depends on comprehensive visibility, careful business impact evaluation, strategic planning, and disciplined implementation. Organizations that approach these initiatives systematically often discover that the benefits extend far beyond immediate cost savings, creating more efficient operations, better budget predictability, and stronger vendor relationships.
By implementing robust SaaS governance policies and leveraging modern management tools, organizations can maintain the benefits of their optimization efforts long after economic conditions improve. This proactive approach to SaaS spend management provides resilience for future challenges and creates a foundation for sustainable growth in an increasingly software-dependent business environment. Understanding strategies for reducing IT costs can further enhance your organization’s financial efficiency during uncertain times.
The key to successful SaaS optimization lies in viewing it not as a one-time cost-cutting exercise, but as an ongoing strategic initiative that continuously aligns software investments with business objectives. Organizations that embrace this perspective position themselves not just to survive economic downturns, but to emerge stronger and more efficient when conditions improve.

