The modern workplace presents a fascinating paradox: while organizations invest heavily in comprehensive SaaS management platforms and governance policies, employees continue to independently adopt new software tools at an unprecedented rate. This phenomenon, often termed “shadow IT,” isn’t simply a matter of rebellious workers defying corporate policies. Instead, it reveals deep psychological drivers that, when understood and channeled properly, can transform potential chaos into competitive advantage.
The Psychology Behind Rogue SaaS Adoption
The Need for Autonomy and Control
At its core, unauthorized SaaS adoption stems from a fundamental human need for autonomy. Employees naturally gravitate toward tools that enhance their productivity and give them greater control over their work environment. When existing corporate software feels cumbersome or insufficient, workers instinctively seek alternatives that better serve their immediate needs.
This behavior mirrors what psychologists call “psychological reactance” – the tendency to resist perceived limitations on freedom of choice. When IT departments impose strict software restrictions, they may inadvertently trigger this reactance, driving employees to seek unauthorized alternatives. Rather than viewing this as defiance, organizations should recognize it as a signal that current tools may not be meeting user needs effectively.

The Instant Gratification Factor
Modern SaaS solutions are designed with user experience at their forefront, offering immediate value and seamless onboarding. Unlike traditional enterprise software that requires lengthy procurement processes and extensive training, cloud-based applications can be accessed within minutes of discovery. This instant gratification satisfies our brain’s reward system, creating positive associations with self-service software adoption.
The subscription model further reinforces this behavior by eliminating traditional barriers to entry. When employees can access powerful software for the cost of a lunch meeting, the psychological friction associated with trying new tools essentially disappears. This low-risk, high-reward scenario naturally encourages experimentation and adoption.
Social Proof and Peer Influence
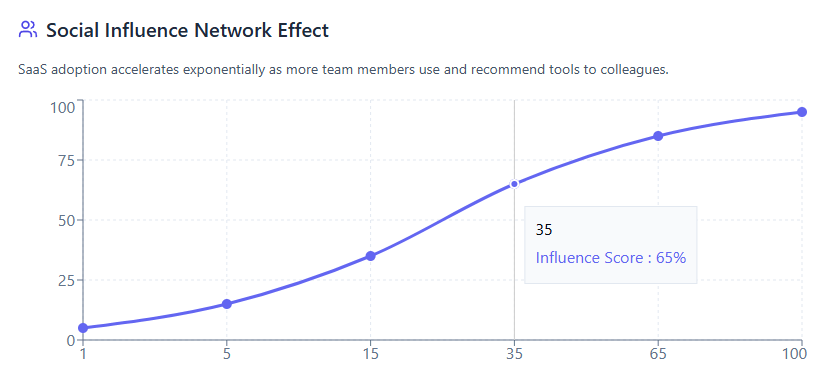
SaaS adoption often spreads through organizations via social networks and peer recommendations. When colleagues share success stories about productivity tools or collaboration platforms, it creates powerful social proof that influences behavior. This viral nature of software adoption means that a single positive experience can rapidly multiply throughout teams and departments.
The rise of remote and hybrid work has amplified this effect. As employees become more self-directed in choosing their work tools, they rely heavily on peer recommendations and online communities for guidance. This shift from top-down technology decisions to grassroots adoption represents a fundamental change in how software proliferates within organizations.
The Hidden Costs of Uncontrolled SaaS Proliferation
Financial Implications of Shadow IT
Uncontrolled SaaS adoption creates several financial challenges that extend far beyond simple subscription costs. Organizations often discover they’re paying for multiple tools that serve similar functions, creating redundancy and waste. According to industry research, companies use approximately 80 different SaaS applications on average, with significant overlap in functionality.
The lack of centralized visibility makes it difficult to negotiate volume discounts or enterprise pricing arrangements. When individual departments purchase software independently, they miss opportunities for cost optimization through consolidated procurement. Additionally, forgotten subscriptions and underutilized licenses contribute to ongoing financial drain that can accumulate substantially over time.
Perhaps most concerning is the challenge of budget forecasting when SaaS adoption occurs outside official channels. Finance teams struggle to predict software costs when they lack visibility into actual usage patterns and renewal dates across the organization.
Security and Compliance Risks
Each unauthorized SaaS application represents a potential security vulnerability. Without proper vetting and integration with existing security frameworks, these tools may lack adequate data protection measures or fail to meet industry compliance requirements. Sensitive company information might be stored in applications that don’t align with organizational security policies.
The proliferation of user accounts across multiple platforms also increases the risk of credential management issues. Employees may reuse passwords or fail to properly secure accounts, creating entry points for potential security breaches. When IT departments are unaware of all the software in use, they cannot implement comprehensive security monitoring or incident response procedures.
Understanding the Root Causes
Gaps in Current Software Offerings
Rogue SaaS adoption often highlights deficiencies in existing corporate software solutions. When employees consistently choose alternative tools, it suggests that current offerings may be lacking in functionality, user experience, or integration capabilities. Organizations should view this behavior as valuable feedback about their technology stack’s effectiveness.
Common complaints about enterprise software include slow performance, complex user interfaces, and limited customization options. Employees naturally seek tools that eliminate these frustrations and enhance their productivity. By analyzing which unauthorized tools are being adopted, IT leaders can identify specific improvement opportunities for their current software environment.
Inadequate Communication and Training
Sometimes rogue adoption occurs simply because employees are unaware of existing solutions or don’t understand how to effectively use available tools. Poor communication about software capabilities or insufficient training programs can drive workers to seek external alternatives unnecessarily.
This situation represents a missed opportunity for organizations that have already invested in comprehensive software solutions. When employees don’t fully leverage existing tools, companies fail to realize the return on their technology investments while simultaneously incurring additional costs through duplicate functionality.
Rigid Procurement Processes
Traditional IT procurement processes, designed for major software purchases, often prove inadequate for the fast-paced needs of modern teams. When requesting new software requires multiple approvals and lengthy evaluation periods, employees may choose to bypass these processes entirely.
The disconnect between business velocity and procurement speed creates natural pressure toward unauthorized adoption. Teams facing urgent project deadlines cannot afford to wait weeks or months for official software approval, leading them to seek immediate solutions through self-service platforms.
The Benefits of Strategic SaaS Adoption
Innovation and Competitive Advantage
When properly channeled, employee-driven software adoption can become a source of innovation and competitive advantage. Workers on the front lines often identify productivity opportunities that management might miss. Their grassroots software discoveries can reveal emerging tools and trends that provide early competitive benefits.
Organizations that embrace this innovative spirit while maintaining appropriate oversight can stay ahead of technology curves and adapt more quickly to changing business needs. The key lies in creating processes that harness employee initiative while maintaining necessary controls and visibility.
Enhanced Employee Satisfaction and Productivity
Allowing employees input into their software environment typically leads to higher job satisfaction and productivity. When workers feel empowered to choose tools that enhance their effectiveness, they become more engaged and invested in their work outcomes. This psychological ownership often translates into better utilization and more creative application of software capabilities.
The modern workforce, particularly younger employees, expects a certain level of technology choice in their work environment. Organizations that provide this flexibility while maintaining appropriate governance can attract and retain top talent who value technological empowerment.
Strategies for Productive SaaS Adoption
Implementing Controlled Shadow IT Programs
Rather than prohibiting unauthorized software adoption entirely, progressive organizations are implementing controlled shadow IT programs that channel employee initiative productively. These programs establish clear guidelines for software experimentation while maintaining necessary oversight and security standards.
Such programs typically include approved vendor lists, budget allocations for departmental software trials, and streamlined evaluation processes for promising tools. By providing legitimate channels for software exploration, organizations can reduce truly unauthorized adoption while benefiting from employee innovation.
Creating User-Centric Procurement Processes
Modernizing procurement processes to be more responsive to user needs can significantly reduce unauthorized software adoption. This might involve creating fast-track approval processes for low-risk applications, establishing pre-approved software catalogs, or implementing user-friendly request systems that prioritize speed and simplicity.
The goal is to make authorized software acquisition as convenient as unauthorized adoption while maintaining necessary controls. When legitimate processes become competitive with self-service alternatives, employees naturally gravitate toward official channels.
Leveraging SaaS Management Platforms
Comprehensive SaaS management platforms like Binadox provide the visibility and control necessary to manage distributed software adoption effectively. These platforms can discover unauthorized applications, analyze usage patterns, and provide insights that inform strategic software decisions.
Modern SaaS spend management tools offer automated tracking of software subscriptions, license utilization monitoring, and cost optimization recommendations. By implementing such platforms, organizations can maintain oversight of their software environment while allowing appropriate flexibility for user-driven adoption.
Best Practices for Channel Rogue Adoption
Establish Clear Governance Frameworks
Effective SaaS governance requires clear policies that balance flexibility with control. These frameworks should define approval processes for different types of software, establish security requirements for various risk categories, and outline responsibilities for different organizational roles.
The most successful governance frameworks focus on outcomes rather than rigid processes. Instead of prohibiting all unauthorized software, they establish criteria that help employees make appropriate decisions about software adoption while ensuring organizational objectives are met.
Foster Open Communication
Regular communication between IT departments and end users helps identify software needs before they result in unauthorized adoption. This might include quarterly technology reviews, user feedback sessions, or formal processes for requesting new software capabilities.
Creating channels for employees to suggest software improvements or alternatives helps organizations stay ahead of adoption trends. When workers feel their input is valued and acted upon, they’re more likely to work within established processes rather than seeking independent solutions.
Implement Regular Software Audits
Periodic audits of software usage help organizations understand the full scope of their SaaS environment and identify optimization opportunities. These audits should examine both authorized and unauthorized applications, analyzing usage patterns, cost effectiveness, and security compliance.
The insights from these audits can inform future software strategy, helping organizations make data-driven decisions about which tools to standardize, which to eliminate, and where gaps exist that might drive future unauthorized adoption.
Provide User Education and Training
Comprehensive training programs help employees maximize the value of existing software while reducing the perceived need for alternative tools. These programs should focus on practical applications and productivity enhancement rather than generic feature overviews.
Additionally, education about security risks and compliance requirements helps employees make more informed decisions when considering unauthorized software adoption. When workers understand the potential implications of their choices, they often become advocates for appropriate governance practices.
Technology Solutions for SaaS Management
Automated Discovery and Monitoring
Modern SaaS management solutions can automatically discover unauthorized applications through various methods including network monitoring, browser extension analysis, and financial transaction tracking. This visibility enables organizations to understand the full scope of their software environment without relying solely on self-reporting.
Continuous monitoring capabilities help track software usage patterns, identify underutilized licenses, and detect potential security risks. These insights enable proactive management of the software portfolio rather than reactive responses to discovered issues.
Integration and Consolidation Opportunities
SaaS management platforms can identify opportunities for software consolidation by analyzing functional overlap and usage patterns. When multiple tools serve similar purposes, organizations can potentially reduce costs and complexity through strategic consolidation efforts.
These platforms also facilitate integration opportunities by identifying applications that could work better together or highlighting gaps where integration tools might provide value. The goal is to create a more cohesive and efficient software ecosystem.
Cost Optimization and Budget Planning
Advanced SaaS management tools provide detailed cost analysis and forecasting capabilities that help organizations optimize their software spending. These features can identify opportunities for volume discounts, highlight unused licenses, and predict future spending based on usage trends.
Budget planning becomes more accurate when organizations have comprehensive visibility into their software portfolio. This improved forecasting enables better resource allocation and strategic planning around technology investments.
Creating a Culture of Strategic Software Adoption
Leadership Support and Modeling
Successful transformation of rogue adoption patterns requires strong leadership support and appropriate modeling behavior. When executives demonstrate commitment to balanced governance approaches, it encourages similar behavior throughout the organization.
Leaders should actively participate in software evaluation processes and demonstrate how to balance innovation with appropriate oversight. This modeling helps establish cultural norms around responsible software adoption.
Recognizing and Rewarding Positive Behaviors
Organizations should recognize and reward employees who identify valuable software solutions while following appropriate governance processes. This positive reinforcement helps establish desired behaviors while encouraging continued innovation within appropriate boundaries.
Recognition programs might highlight successful software discoveries, cost savings achieved through proper procurement processes, or security improvements resulting from appropriate governance practices.
Continuous Improvement of Processes
The most effective organizations treat their software governance processes as continuously evolving systems that adapt to changing needs and technologies. Regular review and refinement of policies ensures they remain relevant and effective as the software landscape evolves.
This continuous improvement approach should incorporate feedback from all stakeholders including end users, IT professionals, and business leaders. The goal is to create processes that evolve with organizational needs while maintaining necessary controls.
Measuring Success and ROI
Key Performance Indicators
Organizations should establish clear metrics for measuring the success of their SaaS management initiatives. These might include reductions in unauthorized software adoption, improvements in software utilization rates, cost savings achieved through consolidation efforts, or enhanced security compliance scores.
Regular measurement and reporting of these metrics helps demonstrate the value of strategic software management while identifying areas for continued improvement. The most effective measurement approaches focus on business outcomes rather than just technical metrics.
Long-term Strategic Benefits
The benefits of properly managed SaaS adoption extend beyond immediate cost savings or risk reduction. Organizations that successfully channel employee initiative often experience improved innovation rates, higher employee satisfaction, and enhanced competitive positioning.
These strategic benefits may take longer to materialize but often provide more substantial long-term value than short-term operational improvements. Measuring and communicating these benefits helps justify continued investment in strategic software management initiatives.
Conclusion
The psychology driving rogue SaaS adoption reflects fundamental human needs for autonomy, efficiency, and innovation. Rather than viewing this behavior as problematic, progressive organizations are learning to channel these impulses productively through strategic governance frameworks and modern management tools.
Success requires balancing control with flexibility, providing legitimate channels for innovation while maintaining necessary oversight. Organizations that master this balance can harness the innovative energy of their workforce while avoiding the risks and costs associated with completely uncontrolled software proliferation.
The future belongs to organizations that can adapt their governance approaches to the realities of modern software consumption patterns. By understanding the psychological drivers behind rogue adoption and implementing appropriate management strategies, companies can transform potential chaos into competitive advantage while ensuring security, compliance, and cost optimization objectives are met.
Through comprehensive SaaS management platforms, clear governance frameworks, and cultures that value both innovation and responsibility, organizations can successfully navigate the complex landscape of modern software adoption. The key lies in recognizing that employee initiative represents an asset to be channeled rather than a problem to be eliminated.

