What is SaaS Integration Sprawl?
Software as a Service (SaaS) integration sprawl refers to the uncontrolled proliferation of app-to-app connections within an organization’s technology stack. As businesses adopt more SaaS solutions across different departments, they inevitably create a complex web of integrations to enable data flow and workflow automation between applications.
While individual integrations often provide clear business value, the cumulative effect can lead to a tangled ecosystem that becomes increasingly difficult and expensive to manage. This sprawl occurs when organizations lack centralized oversight of their integration landscape, allowing teams to create connections ad hoc without considering the broader architectural implications or long-term costs.
The challenge intensifies as organizations typically use 80+ applications on average, with each application potentially connecting to multiple others. This creates an exponential growth in connection complexity that can quickly spiral out of control without proper SaaS spend management strategies in place.
The Hidden Costs of App-to-App Connections
Understanding the true cost of SaaS integrations requires looking beyond the initial setup fees. The hidden expenses associated with app-to-app connections often dwarf the apparent integration costs and can significantly impact your organization’s bottom line.
Direct Integration Costs
Most SaaS vendors charge for integration capabilities through tiered pricing models. Premium plans typically include more integration slots, advanced API access, or higher data transfer limits. Organizations frequently upgrade to more expensive subscription tiers solely to access integration features they need, creating immediate cost escalation across multiple applications.
Integration platform as a service (iPaaS) solutions like Zapier, MuleSoft, or Microsoft Power Automate add another layer of subscription costs. While these platforms promise to simplify integration management, they introduce additional licensing fees that scale with usage volume and complexity.
Maintenance and Support Expenses
Every integration becomes a potential point of failure that requires ongoing maintenance. API changes, software updates, and data format modifications can break existing connections, necessitating developer time to investigate and fix issues. The cumulative maintenance burden grows quadratically with the number of integrations, as each new connection potentially affects existing ones.
Support costs also multiply as teams need specialized knowledge to troubleshoot integration issues across multiple platforms. When integrations fail, businesses often experience operational disruptions that carry their own hidden costs through reduced productivity and delayed processes.
Security and Compliance Overhead
Each integration creates additional attack vectors and data exposure points that require security monitoring and compliance oversight. Organizations must implement proper authentication, authorization, and data encryption across all connections, adding complexity to their cloud security posture.
Compliance requirements become more complex when data flows between multiple systems, potentially crossing geographical boundaries or touching regulated data types. This necessitates additional auditing, documentation, and control mechanisms that increase administrative overhead significantly.
Understanding the SaaS Integration Landscape
The modern SaaS ecosystem has evolved to encourage integration through APIs, webhooks, and pre-built connectors. Vendors actively promote their integration capabilities as competitive advantages, making it easier than ever for organizations to connect their software tools.
Integration Types and Their Cost Implications
Native Integrations appear cost-effective initially but often lock organizations into specific vendor ecosystems. While these integrations typically work reliably, they create vendor dependency that can become expensive when migration becomes necessary.
API-Based Custom Integrations provide maximum flexibility but require significant development resources. The initial investment in custom integration development is substantial, and ongoing maintenance costs can be unpredictable as APIs evolve.
Third-Party Integration Platforms offer middle-ground solutions with pre-built connectors and visual integration builders. However, these platforms introduce additional licensing costs and potential performance bottlenecks as they serve as intermediaries in data flow.
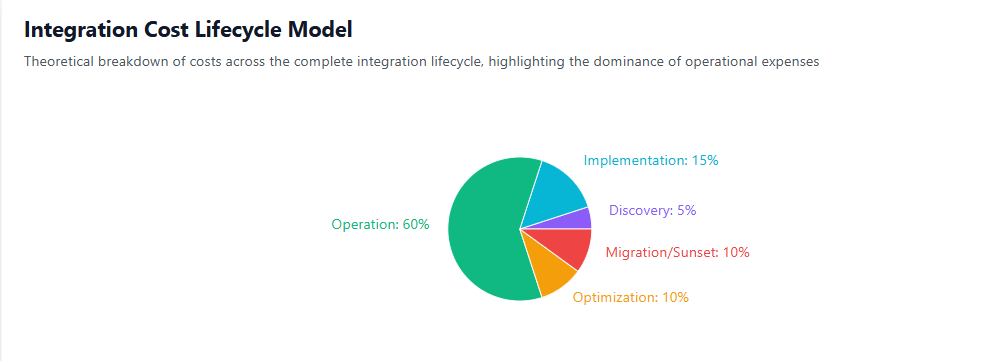
The Integration Lifecycle Cost Model
Integration expenses follow a predictable lifecycle pattern that organizations must account for in their SaaS procurement planning. Initial setup costs represent only a fraction of the total cost of ownership, with ongoing operational expenses typically exceeding the initial investment over time.
The discovery phase involves evaluating integration options and planning data flows. Implementation requires development resources and testing cycles. The operational phase includes monitoring, maintenance, and support. Finally, eventual decommissioning or migration introduces additional costs when business requirements change or vendor relationships end.
Common Causes of Integration Sprawl
Integration sprawl rarely occurs intentionally but results from organizational dynamics and technological pressures that create conditions for uncontrolled growth.
Departmental Autonomy and Shadow IT
Different departments often select and implement SaaS tools independently, choosing applications that best serve their specific needs. Marketing teams might adopt multiple tools for campaign management, lead tracking, and analytics, while sales teams select complementary CRM and communication platforms.
This departmental autonomy leads to overlapping functionality and redundant integrations. When teams discover they need to share data between their chosen tools, they often implement point-to-point integrations without considering existing connections or enterprise-wide integration standards.
Lack of Integration Governance
Organizations without formal integration governance policies allow teams to create connections based on immediate operational needs rather than strategic architectural considerations. This reactive approach results in inconsistent integration patterns, duplicated efforts, and missed opportunities for consolidation.
Without centralized oversight, organizations lose visibility into their integration landscape, making it impossible to identify redundant connections or optimize data flows. The absence of integration standards also leads to inconsistent security implementations and varying levels of reliability across connections.
Vendor Lock-in and Ecosystem Effects
SaaS vendors actively encourage integration adoption through marketplace partnerships and pre-built connectors. While these integrations solve immediate business problems, they can create invisible dependencies that become expensive to unwind later.
Ecosystem lock-in occurs when organizations build extensive integration networks around specific platforms, making it costly to switch vendors or adopt alternative solutions. This dependency gives vendors pricing power and reduces organizational flexibility in technology decision-making.
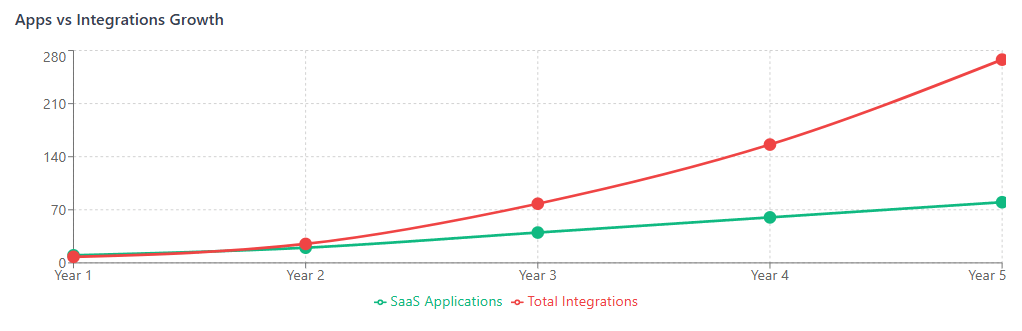
Financial Impact of Unmanaged Integrations
The financial implications of integration sprawl extend far beyond obvious integration costs, affecting multiple aspects of organizational spending and operational efficiency.
Subscription Cost Escalation
Integration requirements frequently drive organizations to upgrade SaaS subscription tiers, even when the additional features aren’t needed for core functionality. These upgrades can double or triple per-user costs across multiple applications, creating significant expense increases.
Premium integration features often come bundled with other advanced capabilities, forcing organizations to pay for unused functionality. This bundling strategy maximizes vendor revenue but inflates customer costs beyond actual integration needs.
Hidden Opportunity Costs
Complex integration landscapes make it difficult to evaluate and adopt new technologies that might provide better value. Organizations become hesitant to change existing tools due to integration dependencies, even when superior alternatives become available.
The technical debt created by extensive integrations also slows development velocity for new business initiatives. Development teams spend increasing amounts of time maintaining existing connections rather than building new capabilities that drive business growth.
Operational Inefficiencies
Fragmented integration architectures often result in data silos and workflow bottlenecks that reduce overall operational efficiency. When integrations fail or perform poorly, the resulting manual workarounds can be more expensive than the original integration investment.
Troubleshooting integration issues across multiple platforms requires specialized expertise and significant time investment. These diagnostic efforts often involve multiple vendor support teams and can take days or weeks to resolve, creating substantial productivity losses.
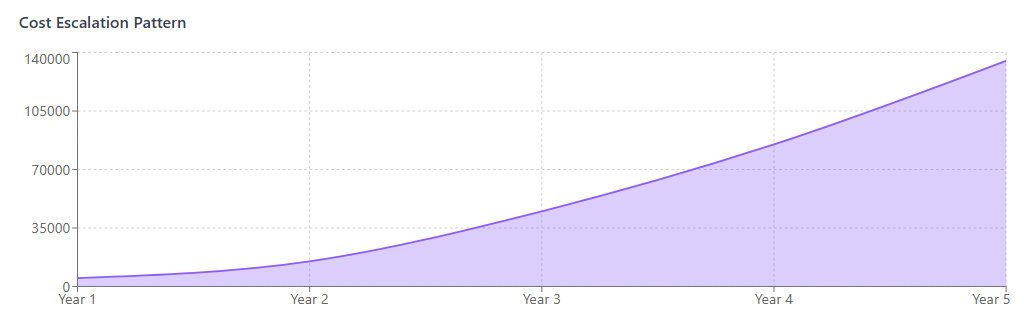
Strategies for Managing Integration Costs
Effective integration cost management requires proactive planning, architectural discipline, and ongoing governance to prevent sprawl from undermining SaaS cost optimization efforts.
Centralized Integration Planning
Organizations should establish centralized integration review processes that evaluate all proposed connections against architectural standards and business objectives. This centralized approach enables optimization opportunities through connection consolidation and standardized integration patterns.
Integration planning should include total cost of ownership analysis that accounts for implementation, maintenance, and potential migration costs over the expected integration lifetime. This comprehensive cost assessment helps organizations make informed decisions about integration investments.
API Management and Standardization
Implementing enterprise API management practices provides visibility and control over integration activities. API gateways enable monitoring, security enforcement, and performance optimization across all integrations while providing usage analytics that inform cost optimization decisions.
Standardizing on specific integration technologies and patterns reduces complexity and maintenance costs. Organizations benefit from economies of scale in training, tooling, and support when they limit the variety of integration approaches used across the enterprise.
Integration Portfolio Optimization
Regular integration audits help identify redundant, underutilized, or inefficient connections that can be consolidated or eliminated. These audits should evaluate both technical performance and business value to prioritize optimization efforts effectively.
Portfolio optimization also involves rightsizing integration capabilities based on actual usage patterns. Organizations often discover they’re paying for integration capacity far exceeding their actual needs, presenting immediate cost reduction opportunities.
Best Practices for SaaS Integration Governance
Establishing comprehensive governance frameworks prevents integration sprawl while enabling teams to access the connectivity they need for business success.
Integration Review Processes
Formal integration review processes should evaluate proposed connections against architectural standards, security requirements, and cost implications. These reviews help prevent integration decisions that might seem beneficial in isolation but create broader organizational problems.
Review processes should include technical assessment of integration options, business case evaluation, and consideration of alternative approaches that might achieve the same objectives more efficiently.
Documentation and Inventory Management
Maintaining comprehensive integration inventories provides visibility into the organization’s connection landscape and enables proactive management. Documentation should include technical specifications, business justification, cost information, and maintenance responsibilities for each integration.
Regular inventory updates help identify changes in integration usage patterns and highlight opportunities for optimization or consolidation. This documentation also proves invaluable during vendor negotiations or technology migration projects.
Security and Compliance Framework
Integration governance must include robust security and compliance frameworks that address the unique risks created by data sharing between systems. These frameworks should specify authentication requirements, data encryption standards, and access control policies for all connections.
Compliance considerations become increasingly complex as data flows between multiple systems and potentially crosses jurisdictional boundaries. Governance frameworks should address these complexities proactively rather than reactively discovering compliance gaps.
Tools and Platforms for Integration Management
Various tools and platforms can help organizations manage integration sprawl and optimize connection costs effectively.
SaaS Management Platforms
Comprehensive SaaS management tools provide visibility into application usage, integration relationships, and associated costs. These platforms help organizations understand their integration landscape and identify optimization opportunities.
Advanced SaaS management platforms include integration discovery capabilities that automatically map connections between applications and analyze data flows. This automated discovery helps organizations maintain accurate integration inventories without manual effort.
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS)
While iPaaS solutions add licensing costs, they can reduce overall integration expenses by standardizing connection approaches and reducing development requirements. These platforms often include monitoring and management capabilities that help control integration sprawl.
Modern iPaaS platforms provide governance features that enable centralized control over integration creation and modification. These capabilities help prevent unauthorized connections while enabling business teams to access approved integration patterns.
API Management Solutions
Enterprise API management platforms provide comprehensive visibility and control over integration activities. These solutions enable organizations to monitor API usage, enforce security policies, and optimize performance across all connections.
API management tools also provide analytics that inform cost optimization decisions by revealing usage patterns and identifying underutilized or inefficient integrations.
Case Studies: Good vs Poor Integration Practices
Real-world examples illustrate the dramatic differences in outcomes between organizations that effectively manage integration sprawl versus those that allow uncontrolled growth.
Effective Integration Management Example
A mid-sized marketing agency implemented centralized integration governance before expanding their SaaS toolkit from 15 to 40+ applications. By establishing integration standards and using a single iPaaS platform, they maintained integration costs at approximately 12% of total SaaS spending while achieving excellent operational efficiency.
Their approach included mandatory integration reviews, standardized connection patterns, and regular portfolio optimization. These practices enabled them to scale their integration landscape efficiently while avoiding the cost escalation typical of rapid SaaS adoption.
Poor Integration Management Example
A growing technology company allowed departments to implement integrations independently, resulting in over 200 point-to-point connections across 60+ applications. Integration costs reached nearly 35% of total SaaS spending, with maintenance consuming significant development resources.
The company experienced frequent integration failures that disrupted business operations and required emergency fixes. Troubleshooting efforts often involved multiple vendors and extended downtime periods that impacted customer service and internal productivity significantly.
How Binadox Helps Control Integration Sprawl
Binadox provides comprehensive visibility into SaaS integration costs and helps organizations optimize their connection strategies through advanced analytics and management capabilities.
Integration Discovery and Mapping
Binadox automatically discovers integrations across your SaaS portfolio, creating comprehensive maps of data flows and connection dependencies. This discovery capability helps organizations understand the true scope of their integration landscape and identify optimization opportunities.
The platform provides detailed cost analysis for integration-related expenses, including premium subscription fees, iPaaS licensing, and maintenance overhead. This visibility enables informed decisions about integration investments and portfolio optimization.
Cost Optimization Recommendations
Based on usage analytics and cost data, Binadox identifies specific opportunities to reduce integration expenses through consolidation, rightsizing, or alternative approaches. These recommendations include potential savings calculations and implementation guidance.
The platform also provides alerts for integration cost anomalies and subscription changes that might indicate sprawl development. Early warning capabilities help organizations address integration sprawl before it becomes expensive to remediate.
Governance Support Features
Binadox includes features that support integration governance initiatives, including approval workflows, documentation management, and compliance tracking. These capabilities help organizations implement and maintain effective integration governance practices.
The platform’s reporting capabilities provide stakeholders with visibility into integration costs, usage patterns, and optimization progress. This transparency enables effective governance decision-making and demonstrates the value of integration management initiatives.
Conclusion
SaaS integration sprawl represents a significant hidden cost that can undermine SaaS optimization efforts and inflate technology spending beyond budgeted levels. Organizations that fail to manage integration growth proactively often discover that connection costs have grown to represent 20-40% of their total SaaS spending, with much of this expense providing questionable business value.
Effective integration management requires comprehensive visibility into connection landscapes, proactive governance frameworks, and ongoing optimization efforts. Organizations that implement centralized integration planning, standardized connection approaches, and regular portfolio reviews can maintain integration costs at manageable levels while enabling the connectivity their business requires.
The key to controlling integration sprawl lies in treating integrations as strategic architectural decisions rather than tactical operational fixes. This strategic approach requires investment in governance processes, management tools, and organizational capabilities, but the resulting cost savings and operational benefits far exceed these investments.
By implementing the strategies and best practices outlined in this guide, organizations can harness the power of SaaS connectivity while avoiding the hidden costs that destroy SaaS stack cost-effectiveness. The future of successful SaaS adoption depends on mastering integration management as a core organizational capability.
Through comprehensive integration governance, organizations can achieve the connectivity they need while maintaining cost discipline and operational efficiency. The organizations that master this balance will gain significant competitive advantages through optimized technology investments and superior operational capabilities in the increasingly connected digital landscape.

