
The allure of “free” Software as a Service (SaaS) applications has transformed how businesses approach software adoption. With promises of zero upfront costs and immediate functionality, these platforms attract millions of organizations seeking affordable SaaS solutions and cost-effective app management. However, beneath the surface of seemingly budget-friendly software lies a complex web of hidden expenses that can derail even the most carefully planned IT budgets.
As businesses increasingly rely on SaaS applications for critical operations, understanding the true financial implications of “free” tools becomes essential for effective SaaS spend management. This comprehensive analysis reveals the concealed costs that transform initial savings into substantial expenditures, providing actionable insights for better SaaS cost optimization.
What is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS) represents a cloud-based software delivery model where applications are hosted remotely and accessed via the internet. Unlike traditional on-premises software requiring substantial upfront licensing fees and infrastructure investments, SaaS solutions offer subscription-based access to applications ranging from communication tools to enterprise resource planning systems.
The SaaS distribution model leverages cloud computing infrastructure to deliver applications through web browsers or dedicated client applications. This approach eliminates the need for organizations to manage software installation, maintenance, and updates locally, shifting these responsibilities to the SaaS vendor.
The Psychology Behind “Free” SaaS Marketing
Freemium Strategy Fundamentals
The freemium model has become the cornerstone of modern SaaS marketing, offering basic functionality at no cost while monetizing advanced features through premium subscriptions. This strategy exploits psychological biases that make “free” offerings irresistible to decision-makers seeking immediate solutions without budget approval delays.
Marketing teams understand that once organizations integrate free tools into their workflows, switching costs create natural barriers to migration. This calculated approach transforms initial free users into paying customers through gradual feature limitations and usage restrictions.
The Illusion of Cost Savings
Free SaaS tools create an illusion of substantial cost savings by eliminating upfront expenses. Finance teams often view these solutions as budget-neutral additions that provide immediate value without impacting quarterly expenditures. However, this perspective overlooks the total cost of ownership implications that emerge over time.
The perceived savings mask underlying expenses related to integration, training, data migration, and eventual scaling requirements. Organizations frequently discover that their “free” solutions have generated significant hidden costs months after initial adoption.
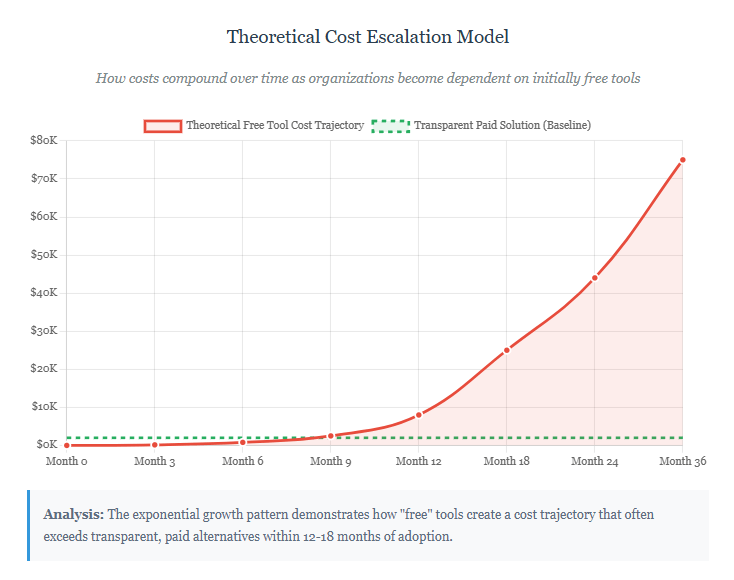
Categories of Hidden Costs in Free SaaS Tools
1. User Limit Restrictions and Scaling Costs
Most free SaaS applications impose strict user limitations that seem reasonable during initial evaluation but quickly become restrictive as organizations grow. A communication tool offering free access for up to 10 users may serve small teams effectively, but expanding to 11 users triggers immediate upgrade requirements.
These scaling costs often involve tier jumps that dramatically increase monthly expenses. For example, upgrading from a free plan to the next tier might cost $15 per user monthly, transforming a zero-cost solution into a $1,800 annual expense for just 10 additional users.
The unpredictable nature of scaling costs makes budget planning challenging. Organizations often face urgent upgrade decisions when user limits are reached, leaving little time for alternative evaluations or negotiation.
2. Feature Limitations and Premium Add-Ons
Free versions typically provide basic functionality while reserving essential features for paid tiers. These limitations become apparent only after organizations have integrated the tool into their workflows and discovered critical missing capabilities.
Common restricted features include:
- Advanced reporting and analytics
- Enhanced security and compliance tools
- Integration capabilities with existing systems
- Priority customer support
- Data export and backup functionality
- Custom branding and white-labeling options
The gradual discovery of feature limitations creates a “feature creep” phenomenon where organizations incrementally upgrade to access necessary functionality, resulting in cumulative costs that exceed alternatives with transparent pricing.
3. Integration and API Costs
Free SaaS tools often limit integration capabilities or charge separately for API access, creating unexpected expenses when organizations attempt to connect systems. While basic integrations may be included in free tiers, advanced connectivity features typically require premium subscriptions.
These integration costs can be particularly significant for organizations with complex technology stacks requiring seamless data flow between applications. The need for custom integrations or third-party middleware solutions adds substantial development and maintenance expenses.
4. Storage and Bandwidth Limitations
Free SaaS applications typically impose strict storage quotas and bandwidth restrictions that seem adequate initially but quickly become constraining as usage grows. Exceeding these limits often triggers automatic upgrades or additional charges that catch organizations unprepared.
Storage overages can be particularly expensive, with some providers charging premium rates for additional capacity. Organizations may face difficult decisions between deleting valuable data or accepting unexpected storage costs.
5. Support and Service Level Agreements
Free SaaS users typically receive limited customer support, often restricted to community forums or basic email assistance. This limitation becomes costly when organizations encounter critical issues requiring immediate resolution.
The absence of guaranteed response times or dedicated support channels can result in productivity losses that far exceed the cost of premium plans with comprehensive support included. Organizations may need to invest in additional technical resources to compensate for limited vendor support.
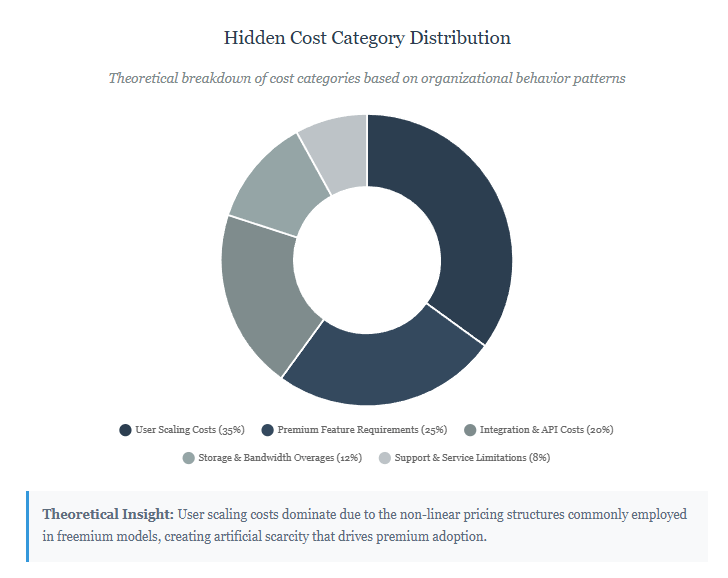
The Compound Effect of Multiple Free Tools
SaaS Sprawl and Management Complexity
Organizations rarely adopt single SaaS applications; instead, they accumulate multiple free tools across different departments and functions. This SaaS sprawl creates management complexity that generates indirect costs through:
- Increased IT overhead for user provisioning and access management
- Security risks from ungoverned application adoption
- Compliance challenges across multiple platforms
- Training requirements for diverse tool sets
- Integration maintenance and troubleshooting
The administrative burden of managing numerous free tools often requires dedicated staff time or specialized SaaS management platforms, negating the initial cost savings.
Shadow IT and Governance Issues
Free SaaS tools enable shadow IT adoption, where departments independently select and implement solutions without central IT approval. While this autonomy can accelerate innovation, it creates governance challenges that generate hidden costs:
- Duplicated functionality across multiple tools
- Data fragmentation and synchronization issues
- Security vulnerabilities from unvetted applications
- Compliance gaps in data handling and privacy
- Inconsistent user experiences and training requirements
The cost of retrospectively implementing governance controls and consolidating redundant tools can exceed the expense of centralized procurement from the beginning.
Industry-Specific Hidden Cost Scenarios
Healthcare Organizations
Healthcare providers adopting free communication or file-sharing tools may discover that HIPAA compliance requires premium features or specialized configurations. The cost of achieving regulatory compliance often involves:
- Business associate agreements with enhanced terms
- Advanced encryption and audit capabilities
- Dedicated infrastructure or private cloud options
- Specialized training and certification requirements
These compliance-related expenses can transform free tools into expensive solutions that exceed purpose-built healthcare software costs.
Financial Services
Financial institutions face stringent regulatory requirements that free SaaS tools rarely address in basic offerings. Compliance with regulations like SOX, PCI-DSS, or regional financial standards typically requires:
- Enhanced security controls and monitoring
- Detailed audit logs and reporting capabilities
- Data residency and sovereignty guarantees
- Regular security assessments and certifications
The investment required to achieve regulatory compliance often makes premium financial services software more cost-effective than upgrading free tools.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Manufacturing organizations may adopt free project management or communication tools without considering integration requirements with existing ERP or MES systems. The hidden costs include:
- Custom integration development and maintenance
- Data synchronization and quality management
- Real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities
- Scalability to handle production volumes
These integration expenses can quickly overshadow the benefits of free tools, particularly in complex manufacturing environments.
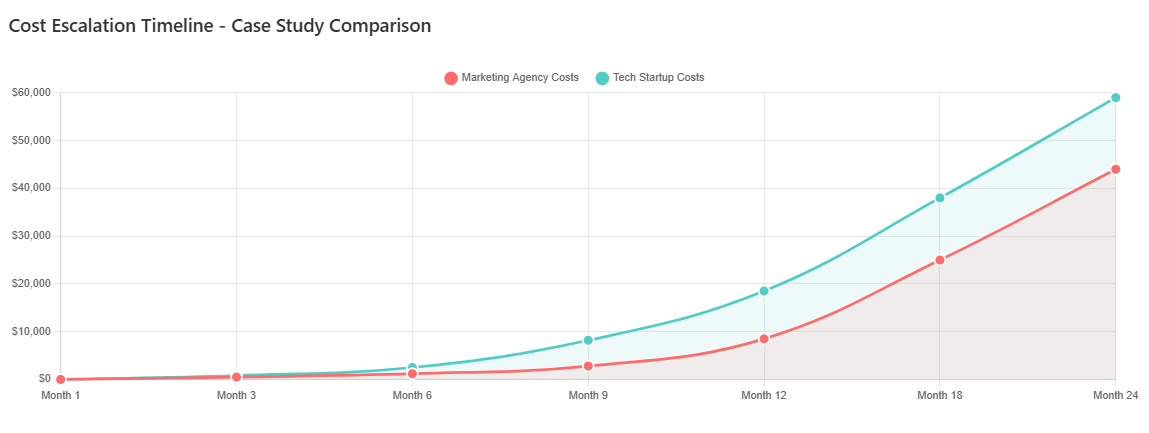
Real-World Case Studies
Case Study 1: Marketing Agency SaaS Sprawl
A mid-sized marketing agency initially adopted free versions of project management, communication, and file-sharing tools across different client teams. Over 18 months, hidden costs accumulated through:
- User limit upgrades for growing client teams ($2,400 annually)
- Premium features for client reporting ($1,800 annually)
- Additional storage for creative assets ($1,200 annually)
- Integration platform for tool connectivity ($3,600 annually)
- Administrative overhead for tool management (0.5 FTE = $35,000 annually)
Total hidden costs: $44,000 annually, equivalent to a comprehensive agency management platform with transparent pricing.
Case Study 2: Technology Startup Growth Pains
A technology startup leveraged free SaaS tools during its initial phase but encountered scaling challenges during rapid growth:
- Communication platform upgrade from 25 to 100 users ($18,000 annually)
- Project management tool enterprise features for compliance ($12,000 annually)
- File storage expansion for development assets ($6,000 annually)
- Customer support platform upgrade for growing user base ($15,000 annually)
- Additional bandwidth and API usage charges ($8,000 annually)
Total scaling costs: $59,000 annually, representing a 15x increase from the original “free” baseline.
Strategic Approaches to Free SaaS Evaluation
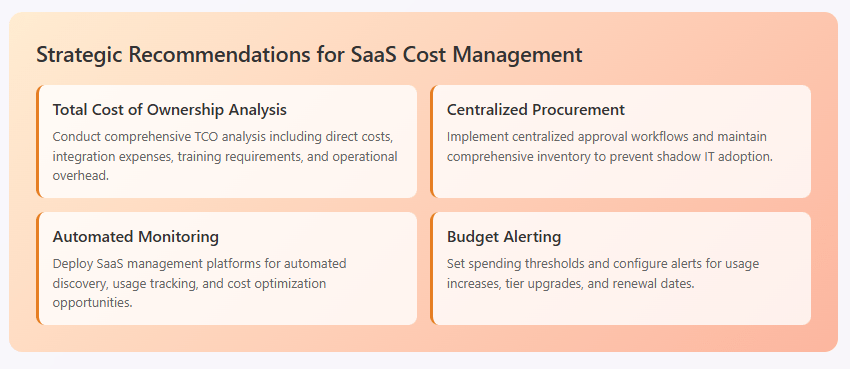
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Organizations should conduct comprehensive total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis before adopting free SaaS tools, considering:
- Direct Costs: Subscription fees, user licenses, and usage-based charges
- Integration Costs: API access, custom development, and middleware solutions
- Training Costs: User education, change management, and ongoing support
- Operational Costs: Administration, governance, and compliance activities
- Opportunity Costs: Alternative solutions and migration expenses
This analysis provides realistic cost projections that account for hidden expenses and scaling requirements.
Pilot Program Methodology
Implementing structured pilot programs helps organizations evaluate free SaaS tools systematically:
- Define Success Criteria: Establish measurable objectives and evaluation metrics
- Set Time Boundaries: Limit pilot duration to prevent unconscious commitment
- Document All Costs: Track direct expenses and indirect resource allocation
- Evaluate Alternatives: Compare multiple solutions simultaneously
- Plan for Scaling: Project costs based on realistic growth scenarios
This methodology prevents emotional attachment to free tools and enables objective decision-making based on comprehensive evaluation data.
Vendor Negotiation Strategies
Organizations can leverage free tool evaluation as negotiation leverage with paid solution providers:
- Request extended trial periods for comprehensive evaluation
- Negotiate pricing based on competitive free alternatives
- Seek bundled solutions that eliminate integration costs
- Obtain scaling guarantees that prevent surprise cost increases
Effective negotiation can result in paid solutions with lower TCO than free alternatives with hidden costs.
Best Practices for SaaS Budget Management
Centralized SaaS Procurement
Implementing centralized SaaS procurement processes helps organizations avoid the hidden costs of unmanaged free tool adoption:
- Establish approval workflows for new SaaS applications
- Maintain comprehensive inventory of all software tools
- Implement standardized evaluation criteria and processes
- Negotiate enterprise agreements for commonly used applications
- Monitor usage patterns and optimization opportunities
Centralized procurement provides visibility and control that prevents hidden costs from accumulating across the organization.
Automated SaaS Management
SaaS management platforms offer automated solutions for tracking and optimizing software expenses:
- Discover all SaaS applications across the organization
- Monitor usage patterns and identify underutilized licenses
- Track renewal dates and prevent automatic charge surprises
- Analyze spending trends and optimization opportunities
- Implement governance controls and approval workflows
These platforms help organizations maintain visibility into their complete SaaS landscape and prevent hidden costs from emerging undetected.
Budget Monitoring and Alerting
Implementing proactive budget monitoring systems helps organizations identify cost escalations before they impact budgets significantly:
- Set spending thresholds for individual applications and categories
- Configure alerts for usage increases or tier upgrades
- Monitor user addition patterns and scaling requirements
- Track integration costs and API usage charges
- Review vendor billing regularly for unexpected charges
Proactive monitoring enables organizations to make informed decisions about continued usage or alternative solutions before costs become prohibitive.
The Future of SaaS Pricing Transparency
Regulatory Pressure for Clarity
Growing awareness of hidden SaaS costs is generating regulatory pressure for pricing transparency. Industry organizations and government bodies are advocating for clearer disclosure of total costs, including:
- Comprehensive feature limitation documentation
- Transparent scaling cost projections
- Clear integration and API pricing structures
- Detailed service level agreement terms
- Honest comparison with competitive alternatives
This regulatory pressure may drive vendors toward more transparent pricing models that reduce hidden costs.
Emerging Pricing Models
New pricing models are emerging that address hidden cost concerns:
- Usage-based pricing: Charges based on actual consumption rather than user tiers
- Outcome-based pricing: Costs tied to business results rather than feature access
- Transparent scaling: Predictable cost increases based on growth metrics
- All-inclusive packages: Comprehensive pricing that includes integrations and support
These models provide greater cost predictability and reduce the likelihood of surprise expenses.
Industry Standardization Efforts
Industry associations are working toward standardization efforts that improve SaaS pricing transparency:
- Standard metrics for comparing total cost of ownership
- Common terminology for feature limitations and restrictions
- Benchmark pricing data for different application categories
- Best practices for vendor evaluation and selection
These standardization efforts will help organizations make more informed decisions about SaaS investments.
Improve SaaS Cost Management with Binadox
Cloud-based platforms are used to distribute SaaS software, which enables users to access and utilize applications via the Internet. Despite its provision of convenience and scalability, it has the potential to increase subscriptions drastically and accrue hidden costs when SaaS spend management is done poorly. Binadox tackles this task by providing one platform where you can monitor, analyze and optimize your SaaS spending.
SaaS software is distributed through cloud-based platforms, allowing users to access and utilize applications over the internet. While this model offers convenience and scalability, it can also lead to sprawling subscriptions and hidden costs if not managed effectively. With Binadox, you can discover all SaaS applications deployed in your organization, some of which might have been ignored or excluded. It is through the platform’s rich analytics and reporting features that you can unveil underutilized instances or duplications that provide you with data-driven content for consolidation or cancellation decisions.
Additionally, the process of purchasing and renewing SaaS vendors can be made more efficient through Binadox as it protects against expiry dates’ oversight leading to surprise expenditure. You may negotiate for better rates, hence save from greater purchase volumes, thus reducing the expenditure on your SaaS spend management overall.
Your business growth should not be affected by unmanaged SaaS expenditure. By using Binadox, you will fully harness effective SaaS spend management, hence optimizing software investment and maintaining operational efficiency.
Conclusion
The true cost of “free” SaaS tools extends far beyond initial adoption expenses, encompassing a complex ecosystem of hidden costs that can derail carefully planned IT budgets. From user scaling requirements and premium feature necessities to integration complexities and support limitations, these concealed expenses often exceed the cost of transparent, paid alternatives.
Organizations must adopt systematic approaches to SaaS evaluation that account for total cost of ownership rather than focusing solely on upfront savings. This includes implementing centralized procurement processes, conducting comprehensive pilot programs, and utilizing SaaS management tools to maintain visibility across their software landscape.
The evolution toward pricing transparency in the SaaS industry offers hope for more predictable and honest cost structures. However, organizations cannot wait for industry changes to address current challenges. By understanding the hidden cost landscape and implementing proactive management strategies, businesses can harness the benefits of SaaS solutions while avoiding the budget disruptions that plague unprepared organizations.
Effective SaaS spend management requires ongoing vigilance, systematic evaluation processes, and comprehensive tools that provide visibility into the complete software ecosystem. Organizations that invest in these capabilities will be better positioned to optimize their software investments and achieve sustainable growth in an increasingly SaaS-dependent business environment.
Through careful analysis, strategic planning, and continuous monitoring, businesses can navigate the complex landscape of SaaS pricing and achieve true cost optimization while maintaining the agility and functionality that modern software solutions provide.

