
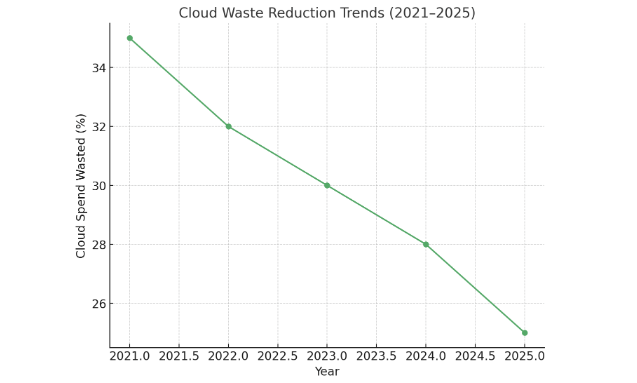
Cloud computing has become the foundation of modern business operations, powering everything from data storage and analytics to AI-driven applications. Yet, with this rapid adoption comes an equally pressing issue: cloud waste. Gartner estimates that organizations waste up to 30% of their cloud spend due to underutilized or idle resources. As cloud environments grow more complex and multi-cloud adoption expands, reducing waste is no longer optional—it is a financial and operational necessity.
This article explores how companies in 2025 can identify and eliminate unused cloud resources, streamline operations, and ensure that every dollar invested in cloud delivers measurable value. We’ll also examine practical strategies, emerging technologies, and tools—like Binadox—that help IT and finance teams combat waste effectively.
What is Cloud Waste?
Cloud waste refers to any cloud resources that an organization pays for but does not use effectively. These resources include:
- Idle virtual machines left running outside business hours.
- Overprovisioned instances sized larger than needed.
- Unused SaaS subscriptions or licenses.
- Orphaned storage volumes and snapshots.
- Redundant cloud services running in parallel.
While individually these may seem minor, collectively they snowball into millions in unnecessary spend annually, especially in enterprises managing thousands of cloud resources.
Why Cloud Waste Reduction Matters in 2025
The urgency of waste reduction in 2025 is driven by several forces:
- Escalating Cloud Spend: With organizations scaling AI, IoT, and data-intensive applications, global cloud spend continues to grow at double-digit rates. Waste directly undermines ROI.
- Economic Pressure: Market volatility forces CIOs and CFOs to scrutinize IT budgets more closely than ever. Eliminating waste is a quick path to cost savings without halting innovation.
- Sustainability Goals: Idle resources also represent wasted energy. Many enterprises align cloud optimization with green IT initiatives, linking waste reduction with corporate ESG metrics.
- FinOps Adoption: The FinOps movement emphasizes financial accountability for cloud usage. Reducing waste is at the core of these practices.
By tackling waste, businesses not only save money but also build a leaner, more resilient IT foundation.
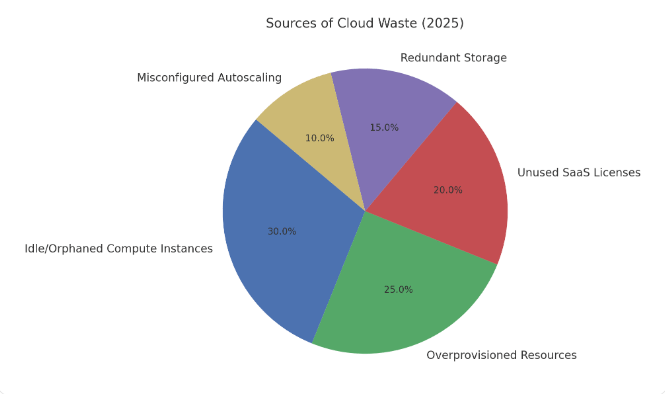
Key Sources of Cloud Waste
1. Idle and Orphaned Compute Instances
Instances that run without workloads or remain unattached to applications are the top culprits. Many organizations leave development and testing environments active overnight or during weekends, racking up costs unnecessarily.
2. Overprovisioning
Engineering teams often provision resources “just in case,” leading to instances and databases with far more capacity than workloads demand.
3. Unused SaaS Licenses
Shadow IT and lack of SaaS visibility result in employees holding unused or duplicate subscriptions. For example, multiple teams may pay for Zoom, Slack, or Trello under separate accounts.
4. Redundant Storage
Forgotten snapshots, unattached volumes, and excessive replication across regions waste storage budgets.
5. Misconfigured Autoscaling Policies
Incorrect scaling rules either over-allocate resources during peak or fail to deallocate them afterward.
Strategies for Identifying Cloud Waste
Identifying waste is the first and most critical step toward optimization. Many organizations are surprised at the scale of unused resources they uncover once they establish proper visibility. In 2025, with cloud infrastructures spanning multi-cloud providers and SaaS ecosystems, detection strategies must be systematic, data-driven, and automated.
1. Rightsizing Resources
Rightsizing ensures workloads are matched with the most appropriate instance type, storage class, or database configuration. Instead of relying on overprovisioned “safety buffers,” rightsizing uses utilization data—CPU, memory, I/O, and network traffic—to recommend leaner resource options.
- Example: A company running a fleet of
m5.4xlargeinstances on AWS may discover average CPU utilization under 20%. By rightsizing tom5.2xlarge, they cut costs by nearly 50% without affecting performance. - Key Practice: Review workload metrics monthly, and implement rightsizing recommendations incrementally to avoid disruption.
2. Automated Discovery of Unused Assets
Cloud environments often contain “zombie resources”—assets that remain active despite serving no purpose. These include unattached storage volumes, orphaned load balancers, or test VMs forgotten after project completion.
- Why it Matters: While individual orphaned assets may cost only a few dollars monthly, at enterprise scale they accumulate into hundreds of thousands in unnecessary charges.
- How to Do It: Employ discovery tools that automatically flag resources with no associated workloads or low activity levels. Automation eliminates the guesswork and ensures nothing slips through the cracks.
3. SaaS Spend Visibility and License Utilization
Cloud waste isn’t limited to IaaS or PaaS—it’s equally prevalent in SaaS. Enterprises frequently pay for unused licenses, duplicate subscriptions across departments, or premium features no one actually uses.
- Strategy: Track logins, last activity dates, and feature usage to determine which employees actively use their licenses.
- Case in Point: One large firm found that 35% of its project management SaaS licenses hadn’t been accessed in over 90 days. Cancelling those saved nearly $200,000 annually.
4. Implementing Strong Tagging and Labeling Policies
Tags and labels are critical for identifying ownership, purpose, and lifecycle of cloud resources. Without consistent tagging, it’s impossible to know whether a database snapshot belongs to a retired project or a critical workload.
- Best Practice: Standardize tags such as
Project,Owner,Environment (Dev/Test/Prod), andExpirationDate. - Outcome: Tagged resources can be filtered easily, enabling IT teams to highlight and delete non-essential assets.
5. Cost Anomaly Detection and Predictive Analytics
Waste is not always obvious—sometimes it emerges from unexpected spikes or misconfigurations. Modern platforms leverage machine learning to establish baselines of normal usage and flag anomalies.
- Example: If daily storage costs suddenly double, anomaly detection can pinpoint a misconfigured backup policy that’s replicating data unnecessarily.
- Next-Gen Trend: In 2025, predictive analytics not only highlight anomalies but also forecast future waste, allowing teams to fix inefficiencies before they escalate.
6. Shadow IT Discovery
Departments often purchase SaaS subscriptions without IT oversight, leading to fragmented and redundant spending. This shadow IT is a hidden driver of waste.
- Solution: Use spend management platforms to consolidate billing data from corporate cards and bank accounts.
- Result: By unifying financial visibility, organizations uncover subscriptions no one admits to owning, making cancellation decisions easier.
7. Lifecycle Reviews and Expiration Policies
Cloud resources created for temporary projects, pilots, or hackathons often outlive their intended lifespan. Conducting lifecycle reviews ensures old resources are either archived or terminated.
- Automation Tip: Set expiration tags (e.g., “DeleteAfter=2025-03-30”) so that resources automatically shut down after a defined period.
- Benefit: Prevents lingering costs from projects that ended months ago.
8. Benchmarking and KPI Tracking
Cloud efficiency must be measured against clear metrics. Organizations should set KPIs such as cost per workload, utilization per resource type, or SaaS license adoption rate. Regular benchmarking helps detect waste early.
Example: If database utilization falls below a defined threshold for two consecutive quarters, it triggers a review for downsizing or decommissioning
Eliminating Unused Resources
Identifying waste is only half the battle; the real savings come from systematically eliminating or repurposing unused resources. In 2025, organizations are adopting a mix of automation, governance, and cultural practices to ensure that once waste is detected, it doesn’t linger in the environment.
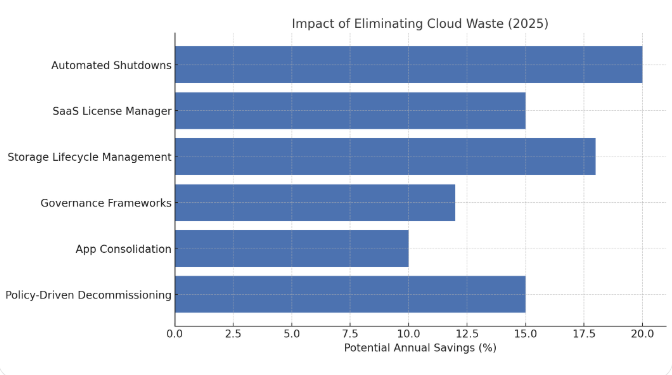
1. Automated Shutdown Policies
One of the most effective ways to eliminate waste is through scheduled shutdowns. Many development and testing environments only operate during working hours, yet remain active 24/7.
- Best Practice: Configure automated schedules that stop non-production instances overnight and on weekends.
- Real-World Impact: A company running 100 test VMs in AWS achieved a 65% cost reduction simply by shutting them down outside business hours.
- Tools: AWS Instance Scheduler, Azure Automation, or third-party platforms like Binadox make it easy to enforce these policies.
2. License Manager for SaaS Subscriptions
Unused SaaS licenses are a silent budget killer. Employees change roles, leave the company, or switch tools, but licenses remain active.
- Solution: Use license managers that track utilization, highlight inactive users, and cancel or downgrade unused subscriptions.
- Example: A global HR firm discovered that 22% of its video conferencing licenses were inactive. By reclaiming them, it saved nearly $400,000 annually.
- Binadox Advantage: With its Renewals Calendar, Binadox not only tracks license usage but also prevents organizations from accidentally auto-renewing inactive subscriptions.
3. Storage Lifecycle Management
Storage is often the biggest hidden contributor to waste. Old snapshots, redundant backups, and orphaned volumes continue to accrue costs long after they’re forgotten.
How to Eliminate Waste:
- Implement data retention policies to automatically delete aged backups.
- Archive infrequently accessed data into cheaper storage classes (e.g., AWS Glacier, Azure Archive).
- Use object lifecycle rules to migrate files to low-cost tiers.
Outcome: Organizations typically reduce storage costs by 20–40% with proper lifecycle management.
4. Governance Frameworks and Approval Workflows
Cloud waste often arises from the ease of provisioning resources. Without governance, teams spin up resources freely but rarely decommission them.
Approach: Introduce approval workflows for resource creation. For example, every VM request must include a project tag and expiration date.
Governance Example: A healthcare provider implemented a mandatory “resource justification form” for new workloads. Within a year, they cut redundant provisioning by 30%.
5. Consolidation of SaaS Applications
Departments often procure overlapping SaaS tools for the same purpose—think of teams using both Slack and Microsoft Teams. Consolidating these into a single enterprise-wide solution prevents duplication.
- Process: Conduct SaaS audits to identify functionally redundant tools.
- Negotiation Tip: By consolidating into one vendor, companies can negotiate enterprise discounts of up to 25%.
- Long-Term Benefit: Beyond cost savings, consolidation improves collaboration and reduces IT security risks.
6. Policy-Driven Decommissioning
Relying on manual intervention to decommission unused resources is inefficient. Instead, enforce automated deprovisioning policies.
- Policy Example: Any VM inactive for 30 consecutive days is automatically stopped, and if unused for another 15 days, terminated.
- SaaS Example: Any license unused for 60 days is automatically flagged for cancellation unless explicitly renewed by the team lead.
- Benefit: This prevents the recurrence of waste by embedding efficiency into daily operations.
7. Cloud-Native Optimization Services
Major cloud providers now integrate optimization services that automate waste elimination.
- AWS: Instance Scheduler and Trusted Advisor for idle resources.
- Azure: Cost Management + Advisor for underutilized workloads.
- GCP: Recommender for VM rightsizing and storage cleanup.
- Limitation: These tools work best within their ecosystems but struggle in multi-cloud environments, where third-party platforms like Binadox provide unified control.
8. Cultural Shift Toward Accountability
Finally, eliminating waste is as much a cultural challenge as a technical one. Engineering, finance, and business teams must adopt a FinOps mindset, where everyone takes responsibility for the cost implications of their decisions.
- Practice: Share regular reports showing departmental cloud spend, highlighting waste reduction progress.
- Outcome: When teams see their usage tied directly to budgets, they become proactive in shutting down what they don’t need.
Tools for Cloud Waste Reduction
Binadox
Binadox offers a unified platform for cloud and SaaS cost management. It enables businesses to:
- Track spend across AWS, Azure, GCP, and SaaS apps in one dashboard.
- Rightsize cloud resources with actionable recommendations.
- Detect unused SaaS licenses with user activity tracking.
- Automate anomaly alerts to catch overspending.
- Simplify procurement with centralized SaaS visibility.
Native Cloud Tools
Cloud providers offer tools like AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Advisor, and GCP Recommender. While useful, they often lack cross-platform insights.
Third-Party FinOps Platforms
Beyond Binadox, platforms like Apptio or CloudHealth provide granular analytics for large-scale enterprises.
Case Study: Cutting 30% Cloud Waste with Visibility
A mid-size tech company adopted Binadox to audit their SaaS and cloud usage. Within the first quarter:
- 27% of virtual machines were identified as idle and shut down.
- Over 40 duplicate SaaS licenses were canceled.
- Rightsizing saved 18% on database workloads.
Total savings exceeded $1.2 million annually, achieved without compromising performance. This demonstrates the power of visibility and automation in waste reduction.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Waste Reduction (2025)
- AI-Driven Optimization: Machine learning models now predict workload needs and auto-adjust resources in real time.
- Green Cloud Initiatives: Waste reduction aligns with carbon neutrality goals. Providers increasingly publish energy consumption dashboards.
- SaaS Market Consolidation: With SaaS stacks sprawling, businesses prioritize integrated ecosystems to minimize duplication.
- Edge Computing Efficiency: By processing data at the edge, organizations reduce latency and avoid unnecessary cloud traffic.
Best Practices for Sustainable Cloud Management
- Conduct quarterly SaaS and cloud audits.
- Adopt a FinOps culture across engineering, finance, and procurement teams.
- Standardize tagging and governance policies.
- Set up anomaly alerts and automated shutdowns.
- Continuously benchmark cloud usage against KPIs.
Conclusion
Cloud waste is not just an IT inefficiency—it is a direct drain on profitability and sustainability. In 2025, as businesses scale AI, SaaS, and multi-cloud ecosystems, waste reduction becomes central to operational excellence. By combining rightsizing, SaaS license management, anomaly detection, and automated governance, organizations can cut costs by up to 30% while building greener, leaner digital infrastructures.
Platforms like Binadox are essential allies in this journey, offering the visibility and automation needed to transform cloud chaos into cost-efficient order. The future of cloud is not only scalable but also sustainable—provided we eliminate the waste.

