
In today’s digital-first business environment, Software as a Service (SaaS) has become the backbone of modern operations. From customer relationship management to project collaboration, cloud computing solutions have transformed how organizations access and utilize software. However, with this transformation comes a critical question that keeps CFOs and IT leaders awake at night: How much should we be spending on SaaS as a percentage of revenue?
Understanding SaaS spending benchmarks is crucial for businesses looking to maintain competitive advantage while optimizing costs. This comprehensive analysis explores the current landscape of B2B SaaS investments, providing actionable insights that help organizations benchmark their spending against industry standards and implement effective cost management strategies.
The rise of SaaS solutions has fundamentally altered the software procurement landscape. Unlike traditional on-premises software that required significant upfront capital investments, the subscription model enables businesses to access powerful applications with predictable monthly or annual costs. However, this accessibility has also led to what many experts call “SaaS sprawl” – the uncontrolled proliferation of software subscriptions across organizations.
Recent studies indicate that the average enterprise uses between 80 to 400 different SaaS applications, depending on company size and industry. This proliferation makes SaaS spend management more critical than ever, as organizations struggle to maintain visibility and control over their growing software portfolios.
Current State of B2B SaaS Spending
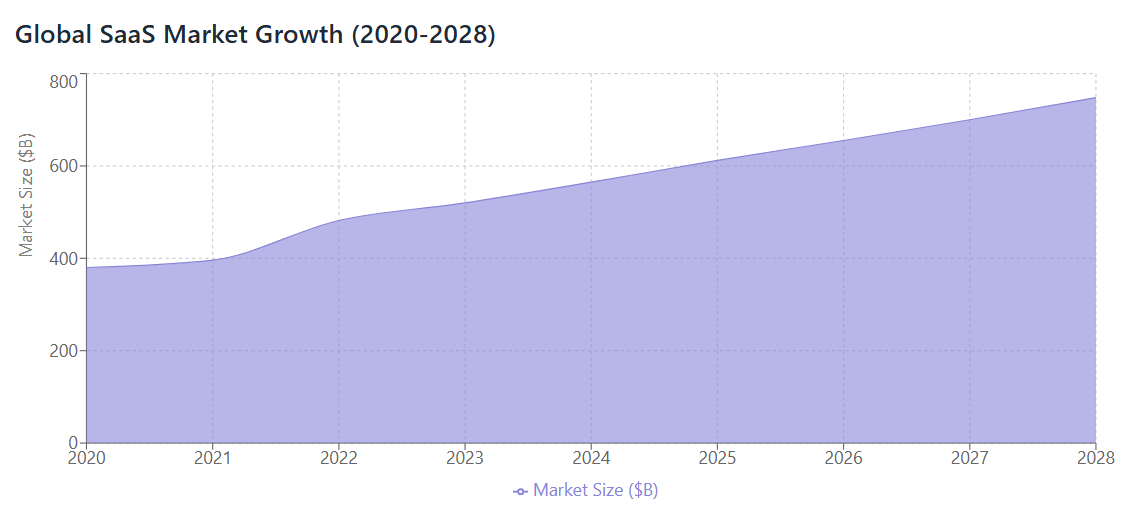
The B2B SaaS market has experienced unprecedented growth over the past decade. According to industry research, global SaaS spending reached $482 billion in 2022, representing a 21.7% increase from the previous year. This growth trajectory shows no signs of slowing, with predictions suggesting the market will reach $601 billion by 2028.
Industry Spending Overview:
- Average SaaS spending per employee: $2,000-$5,000 annually
- Typical SaaS portfolio size: 80-400 applications per enterprise
- Annual growth rate in SaaS adoption: 26.7%
- Percentage of IT budgets allocated to SaaS: 15-25%
The subscription model has proven particularly attractive to businesses because it transforms large capital expenditures into predictable operational expenses. This shift has enabled even small and medium-sized businesses to access enterprise-grade software solutions that were previously financially out of reach.
However, the ease of SaaS adoption has created new challenges. Many organizations lack comprehensive visibility into their SaaS spending, leading to duplicate subscriptions, unused licenses, and missed renewal dates. These inefficiencies can significantly impact the bottom line and reduce the overall return on investment in technology.
Industry Benchmark Analysis
Based on comprehensive market research and analysis of spending patterns across thousands of B2B companies, several key benchmarks have emerged for SaaS spending as a percentage of revenue:
General Industry Benchmarks:
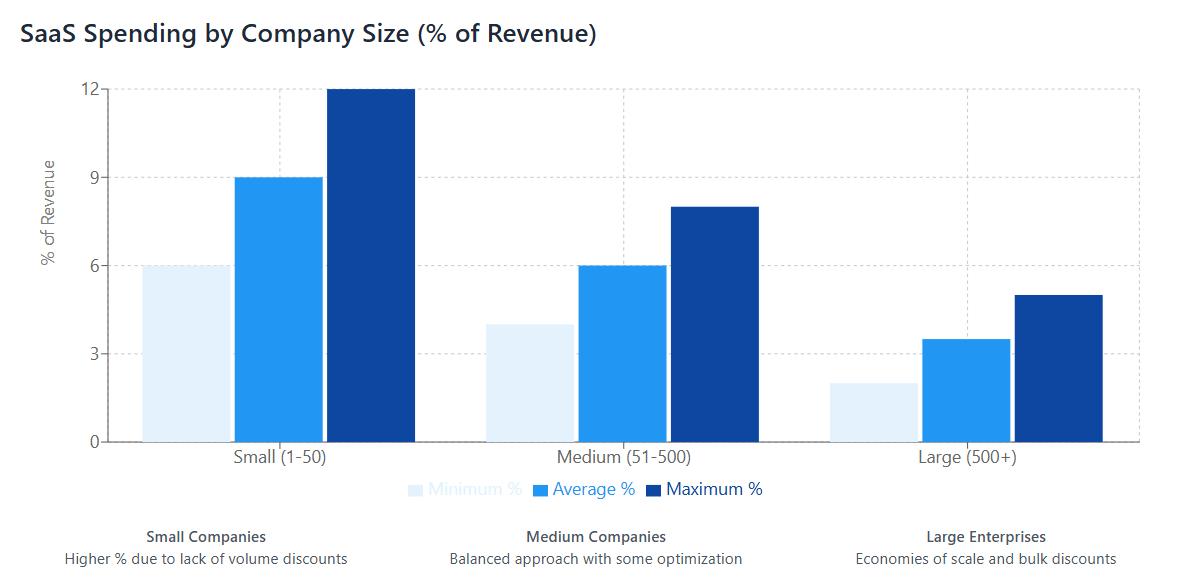
- Small businesses (1-50 employees): 6-12% of revenue
- Medium businesses (51-500 employees): 4-8% of revenue
- Large enterprises (500+ employees): 2-5% of revenue
These percentages represent total SaaS spending including all software subscriptions, from essential productivity tools to specialized industry applications. The inverse relationship between company size and SaaS spending percentage reflects economies of scale and more sophisticated procurement processes in larger organizations.
High-Growth Company Benchmarks: Companies experiencing rapid growth often invest more heavily in SaaS solutions to support scaling operations:
- Early-stage startups: 8-15% of revenue
- Growth-stage companies: 6-10% of revenue
- Mature high-growth companies: 4-7% of revenue
The higher investment percentages for growing companies reflect the need for robust infrastructure, automation tools, and scalable systems that can support expansion without proportional increases in headcount.
Profitability Impact Considerations: Organizations should also consider their profitability stage when evaluating SaaS spending benchmarks:
- Pre-revenue companies: Focus on efficiency over percentage benchmarks
- Break-even companies: 3-8% of revenue typical
- Profitable companies: 2-6% of revenue recommended
Spending Patterns by Company Size
SaaS spending patterns vary significantly based on company size, with distinct characteristics emerging across different organizational scales:
Startups and Small Businesses (1-50 employees): Small organizations typically exhibit the highest SaaS spending percentages relative to revenue, often ranging from 6-12%. This elevated spending reflects several factors:
- Higher per-employee software costs due to lack of volume discounts
- Need for comprehensive tool suites to compete with larger competitors
- Limited IT resources requiring SaaS management platforms for efficiency
- Emphasis on productivity tools that maximize small team output
Common SaaS categories for small businesses include customer relationship management, project management, communication tools, accounting software, and marketing automation platforms. The focus is typically on all-in-one SaaS platforms that can handle multiple functions to minimize complexity and integration challenges.
Medium-Sized Companies (51-500 employees): Mid-market companies generally spend 4-8% of revenue on SaaS solutions, representing a more balanced approach to software procurement:
- Implementation of centralized app management processes
- Beginning of formal SaaS governance and approval workflows
- Mix of departmental and enterprise-wide solutions
- Introduction of SaaS management tools for visibility and control
These organizations often struggle with the transition from startup agility to enterprise governance, making this a critical stage for implementing proper SaaS procurement processes and spend management practices.
Large Enterprises (500+ employees): Enterprise organizations typically maintain SaaS spending between 2-5% of revenue through sophisticated management approaches:
- Comprehensive SaaS governance policies and approval processes
- Dedicated procurement teams negotiating enterprise contracts
- Implementation of automated SaaS tracking and management systems
- Focus on cost saving through consolidation and optimization
Large enterprises benefit from volume discounts, longer-term contracts, and the resources to implement comprehensive management solutions that optimize spending efficiency.
Sector-Specific SaaS Investment Trends
Different industries exhibit distinct SaaS spending patterns based on their operational requirements, regulatory constraints, and digital maturity levels:
Technology Sector: Technology companies typically lead in SaaS adoption and spending, often investing 8-15% of revenue in software solutions. This high investment reflects:
- Need for cutting-edge development and collaboration tools
- Heavy reliance on cloud computing infrastructure
- Requirement for specialized technical applications
- Culture of early technology adoption
Financial Services: Financial institutions invest 3-7% of revenue in SaaS solutions, with spending focused on:
- Regulatory compliance and reporting tools
- Security risks mitigation platforms
- Customer relationship management systems
- Analytics and business intelligence solutions
The financial sector’s conservative approach to SaaS adoption is influenced by strict regulatory requirements and security considerations, but investment levels are steadily increasing as cloud security matures.
Healthcare: Healthcare organizations typically spend 4-9% of revenue on SaaS applications, driven by:
- Electronic health record systems
- Patient management platforms
- Telemedicine and remote care solutions
- Compliance and reporting tools
Healthcare SaaS spending has accelerated significantly since 2020, driven by digital transformation initiatives and changing patient care models.
Manufacturing and Industrial: Traditional manufacturing companies invest 2-6% of revenue in SaaS solutions, focusing on:
- Enterprise resource planning systems
- Supply chain management platforms
- Quality control and compliance tools
- Industrial IoT and monitoring solutions
Professional Services: Service-based businesses typically invest 5-10% of revenue in SaaS platforms, emphasizing:
- Project management and collaboration tools
- Time tracking and billing systems
- Customer relationship management
- Document management and workflow automation
Factors Influencing SaaS Spend Ratios
Several key factors influence how much organizations spend on SaaS as a percentage of revenue:
Business Model and Revenue Structure: Companies with recurring revenue models often invest more heavily in SaaS solutions because they understand the value of predictable, scalable costs. Organizations with project-based or seasonal revenue patterns may be more conservative in their SaaS investments due to cash flow considerations.
Growth Stage and Funding Status: Well-funded startups and growth-stage companies typically invest more aggressively in SaaS solutions to accelerate growth and scale operations efficiently. Bootstrap companies or those with limited funding may focus on affordable SaaS solutions and budget-friendly SaaS solutions to maximize value while minimizing costs.
Digital Maturity Level: Organizations with higher digital maturity tend to invest more in SaaS solutions because they better understand the value and ROI of software investments. These companies often have sophisticated SaaS cost trackers and management processes that enable confident investment in technology.
Industry Regulations and Compliance Requirements: Heavily regulated industries may invest more in specialized compliance and security solutions, driving up overall SaaS spending percentages. Conversely, organizations in less regulated sectors may focus on productivity and efficiency tools.
Geographic Considerations: Companies operating in different geographic markets may have varying SaaS spending patterns based on:
- Local market conditions and competition levels
- Regulatory requirements and data sovereignty laws
- Available infrastructure and connectivity options
- Cultural attitudes toward cloud adoption and technology investment
The Hidden Costs of Poor SaaS Management
While SaaS solutions offer significant benefits, poor management can lead to substantial hidden costs that aren’t immediately apparent in spending benchmarks:
Shadow IT and Ungoverned Spending: When employees subscribe to SaaS applications without IT oversight, organizations lose visibility and control over spending. This shadow IT phenomenon can increase actual SaaS costs by 20-40% beyond budgeted amounts.
Duplicate and Redundant Subscriptions: Without proper oversight, different departments may subscribe to similar or overlapping solutions, leading to unnecessary duplication. Common examples include multiple project management tools, communication platforms, or document storage solutions.
Unused and Underutilized Licenses: Studies suggest that 30-50% of SaaS licenses go unused or are significantly underutilized. This waste occurs due to:
- Employee turnover without license reassignment
- Feature creep in subscription tiers
- Seasonal usage patterns not reflected in annual contracts
- Lack of usage monitoring and optimization
Integration and Training Costs: The true cost of SaaS adoption extends beyond subscription fees to include:
- Integration and setup costs
- Employee training and adoption time
- Data migration and customization expenses
- Ongoing support and maintenance requirements
Compliance and Security Risks: Unmanaged SaaS adoption can create security risks and compliance gaps that result in costly remediation efforts, potential fines, and reputation damage.
Best Practices for SaaS Spend Optimization
Organizations looking to optimize their SaaS spending while maintaining operational efficiency should implement comprehensive management strategies:
Implement Centralized Procurement: Establishing centralized SaaS procurement processes ensures better visibility, negotiation power, and governance over software subscriptions. This approach typically reduces costs by 15-30% through volume discounts and elimination of duplicate subscriptions.
Regular Spend Auditing: Conducting quarterly or bi-annual SaaS audits helps identify:
- Unused or underutilized subscriptions
- Opportunities for plan optimization
- Duplicate applications across departments
- Upcoming renewal opportunities for renegotiation
Usage Monitoring and Analytics: Implementing SaaS usage monitoring provides data-driven insights for optimization decisions. Organizations should track:
- User login frequency and activity levels
- Feature utilization across different subscription tiers
- Department-specific usage patterns
- Seasonal variations in application demand
Right-sizing Subscriptions: Regularly review subscription levels to ensure alignment with actual usage:
- Downgrade overprovisioned accounts
- Negotiate custom pricing for high-volume usage
- Implement usage-based pricing where available
- Consider annual vs. monthly payment options for cost savings
Vendor Consolidation: Where possible, consolidate multiple point solutions into comprehensive platforms that offer:
- Better integration and workflow efficiency
- Simplified vendor management
- Volume discount opportunities
- Reduced training and support overhead
Implementing Effective SaaS Governance
Successful SaaS spending optimization requires robust governance frameworks that balance control with operational agility:
Approval Workflows: Implement tiered approval processes based on subscription cost and business impact:
- Automatic approval for low-cost, standard applications
- Department head approval for mid-range subscriptions
- Executive approval for high-cost or strategic applications
- IT security review for all applications handling sensitive data
Budget Allocation and Tracking: Establish clear budget allocations and tracking mechanisms:
- Department-specific SaaS budgets with spending limits
- Project-based allocation for temporary subscriptions
- Regular budget vs. actual reporting and variance analysis
- Forecasting tools for annual budget planning
Vendor Relationship Management: Develop structured approaches to vendor relationships:
- Regular business reviews with key SaaS vendors
- Performance monitoring and service level agreement tracking
- Renewal planning and negotiation strategies
- Risk assessment and vendor diversification planning
Policy Development and Training: Create comprehensive policies and training programs covering:
- SaaS procurement procedures and approval workflows
- Security and compliance requirements for SaaS adoption
- Data handling and privacy considerations
- License management and user provisioning processes
Tools and Technologies for SaaS Management
Modern SaaS management tools provide comprehensive visibility and control over software subscriptions, enabling data-driven optimization decisions:
SaaS Management Platforms: Comprehensive platforms like Binadox offer centralized visibility into SaaS spending and usage patterns. These SaaS management platforms typically provide:
- Automated discovery of SaaS applications across the organization
- Real-time spending tracking and budget monitoring
- Usage analytics and optimization recommendations
- Renewal calendar and contract management
- Integration with financial and IT systems
Key Features to Look For: When evaluating SaaS management solutions, consider platforms that offer:
- Multi-cloud and SaaS application discovery
- Automated spend tracking and categorization
- User access and license utilization monitoring
- Predictive analytics for cost saving opportunities
- Integration with existing IT and financial systems
- Customizable reporting and dashboard capabilities
Implementation Considerations: Successful SaaS management platform implementation requires:
- Executive sponsorship and change management support
- Integration with existing IT infrastructure and processes
- Training programs for IT and finance teams
- Establishment of governance processes and approval workflows
- Regular review and optimization of platform configuration
Cloud cost optimization strategies should be integrated with SaaS management approaches to provide comprehensive visibility across all software and infrastructure spending.
Future Trends in SaaS Spending
Several emerging trends are likely to influence SaaS spending patterns and benchmarks in the coming years:
AI and Machine Learning Integration: The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities into SaaS applications is driving premium pricing and increased investment in next-generation solutions. Organizations are allocating larger portions of their SaaS budgets to AI-enabled platforms that promise significant productivity improvements.
Vertical-Specific Solutions: The trend toward industry-specific SaaS solutions is creating new spending categories and potentially higher per-application costs. However, these specialized solutions often provide better ROI through improved functionality and compliance alignment.
Usage-Based Pricing Models: More SaaS vendors are adopting consumption-based pricing models that align costs with actual usage. This trend may help organizations optimize spending but requires more sophisticated monitoring and forecasting capabilities.
Integrated Platform Strategies: Organizations are increasingly favoring comprehensive platform solutions over point applications to reduce integration complexity and vendor management overhead. This trend may lead to higher individual subscription costs but lower overall spending through consolidation.
Enhanced Security and Compliance Requirements: Growing regulatory requirements and security concerns are driving increased investment in security-focused SaaS solutions and compliance platforms, potentially increasing overall spending percentages in regulated industries.
Improve SaaS Cost Management with Binadox
SaaS solutions distribution through cloud-based platforms enables organizations to access applications over the internet with unprecedented convenience and scalability. However, this model can lead to sprawling subscriptions and hidden costs without proper management. Binadox addresses these challenges by providing a unified platform for monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing SaaS spending.
With Binadox, organizations can discover all SaaS applications deployed across their environment, including shadow IT subscriptions that might otherwise go unnoticed. The platform’s comprehensive analytics and reporting features reveal underutilized licenses and duplicate subscriptions, providing data-driven insights for consolidation and optimization decisions.
The platform streamlines SaaS procurement and renewal processes by tracking renewal dates and preventing oversight that leads to unexpected expenses. Organizations can negotiate better rates and optimize spending through volume purchasing opportunities, ultimately reducing overall SaaS costs.
By implementing Binadox, businesses ensure that SaaS spending supports growth without compromising operational efficiency. The platform provides the visibility and control necessary to maintain optimal spending ratios while maximizing the value of software investments.
Conclusion
Understanding and optimizing SaaS spending as a percentage of revenue has become critical for modern businesses operating in increasingly competitive markets. While industry benchmarks provide useful guidance – with small businesses typically spending 6-12% of revenue, medium companies 4-8%, and large enterprises 2-5% – organizations must consider their unique circumstances, growth stage, and industry requirements when establishing spending targets.
The key to successful SaaS spend management lies not just in maintaining spending within benchmark ranges, but in ensuring that every software subscription contributes meaningful value to business operations. This requires implementing comprehensive governance frameworks, utilizing SaaS management tools for visibility and control, and maintaining ongoing optimization processes that adapt to changing business needs.
Organizations that successfully balance SaaS investment with operational efficiency gain significant competitive advantages through improved productivity, scalability, and agility. By adopting best practices for SaaS spend management, implementing proper governance structures, and leveraging modern management platforms, businesses can optimize their software investments while supporting sustainable growth.
The future of SaaS spending will continue to evolve with technological advances, changing business models, and emerging regulatory requirements. Organizations that establish strong foundational practices today will be better positioned to adapt to these changes while maintaining optimal spending efficiency and maximizing return on their software investments.
As the SaaS ecosystem continues to mature, the companies that thrive will be those that view software subscriptions not as necessary expenses, but as strategic investments that drive business value, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage in the digital economy.

