
In today’s fast-paced digital economy, Software as a Service (SaaS) has become the backbone of modern enterprises. Marketing teams rely on HubSpot and Mailchimp, engineers collaborate in GitHub and Jira, sales teams use Salesforce, while nearly every employee uses tools like Zoom, Google Workspace, or Microsoft 365. SaaS enables agility, scalability, and lower upfront costs compared to traditional on-premises software.
But with rapid growth comes complexity. Mid-sized companies now average 80–120 SaaS applications, and enterprises may manage several hundred. Each app has its own subscription model, billing cycle, license tiers, and renewal terms. Without proper oversight, organizations face redundant tools, wasted spend on unused licenses, and security gaps from shadow IT.
Optimizing SaaS spend is no longer just a cost-saving tactic; it’s a strategic imperative. Done right, it delivers financial discipline, operational efficiency, and a technology stack aligned to business needs. This article explores best practices for building a robust SaaS spend strategy—helping companies maximize value while minimizing waste.
Why SaaS Spend Optimization Matters
A thoughtful SaaS spend strategy delivers benefits that extend well beyond the finance team. It directly impacts cost savings, compliance, and overall business agility.
Financial Control
SaaS can account for up to 30% of IT budgets in some organizations. Without visibility, costs can spiral, with unexpected renewals and overlapping subscriptions. Optimization ensures spend is predictable and aligned to budget priorities.
Elimination of Waste
Research shows that 30–40% of SaaS licenses go unused or underutilized. This often happens when employees leave and licenses remain active, or when departments purchase similar tools that duplicate functionality. Optimization eliminates this “shelfware.”
Compliance and Security
Shadow IT—applications purchased outside of IT or procurement—creates risks. Unvetted tools may fail compliance checks (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2) or expose sensitive data. Spend management introduces governance, reducing regulatory and security risks.
Vendor Management
Managing dozens of SaaS vendors requires negotiation leverage. Accurate usage data helps procurement teams secure discounts, consolidate contracts, and avoid being locked into unfavorable agreements.
Scalability and Agility
An optimized SaaS portfolio reduces complexity, enabling smoother onboarding for new hires and making it easier to scale operations globally. Teams can work with the tools they need—without overspending or redundancy.
Best Practice 1: Gain Complete Visibility Into Your SaaS Stack
The foundation of any SaaS spend strategy is visibility. You can’t manage or optimize what you don’t know exists. In many organizations, SaaS adoption happens organically: a marketing manager signs up for a new automation tool, a design team experiments with a collaboration app, or employees purchase subscriptions with corporate cards. Over time, this creates a sprawling, fragmented ecosystem.
Discover All Applications
The first step is to conduct a SaaS inventory audit. This involves identifying every application in use across the company, regardless of whether it was procured officially or adopted informally. Methods include:
- Expense and invoice analysis: Reviewing credit card statements, procurement systems, and expense reports to identify recurring charges.
- Network and SSO monitoring: Scanning login activity through identity providers (Okta, Azure AD, Google Workspace) to uncover applications connected to employee accounts.
- Employee surveys: Asking teams directly which tools they use, including free or trial versions.
By combining these approaches, companies can build a single source of truth for their SaaS portfolio.
Classify and Categorize
Once identified, each app should be categorized by function (collaboration, CRM, analytics, HR, etc.), cost center, and business owner. This prevents duplication—for example, discovering that three departments use different project management tools when one could serve the entire company.
Address Shadow IT
One of the biggest revelations during SaaS discovery is the extent of shadow IT—tools adopted without IT or procurement approval. Shadow IT isn’t always malicious; often, teams are simply trying to move faster. However, it can create security, compliance, and cost inefficiencies. Visibility allows IT leaders to either approve, consolidate, or replace these apps.
Benefits of Full Visibility
- Transparency: Everyone, from finance to IT, has a clear picture of SaaS usage.
- Cost savings: Redundant and unnecessary apps are identified.
- Risk reduction: Unauthorized tools that don’t meet compliance standards can be flagged.
- Strategic alignment: Departments can collaborate to select tools that serve the entire business.
Gaining visibility may sound simple, but it lays the groundwork for every other optimization effort. Without it, organizations risk treating symptoms—like overspending—without addressing the root cause: uncontrolled SaaS adoption.
Best Practice 2: Monitor and Analyze SaaS Usage
Once visibility is established, the next step is to track how those applications are being used. Merely knowing what tools exist is not enough—organizations must understand who uses them, how often, and to what extent. This insight distinguishes necessary investments from wasted spend.
Track License Utilization
One of the most common sources of waste in SaaS spending is unused or underutilized licenses. For instance, a company may pay for 500 seats of a video conferencing platform, yet only 350 employees actively log in each month. That leaves 150 licenses—potentially thousands of dollars per year—going to waste.
By monitoring login frequency and feature adoption, IT teams can:
- Reclaim unused licenses and reassign them to new employees.
- Downgrade users from premium to basic tiers if advanced features go unused.
- Eliminate inactive accounts entirely.
Understand Feature Adoption
SaaS providers often tier pricing based on features. But paying for advanced capabilities is wasteful if employees use only the basics. For example, a sales team may subscribe to a CRM’s enterprise plan, but if they use only contact management and email tracking, a lower tier might suffice.
Usage analytics help identify where over-licensing is happening, enabling smarter allocation.
Identify Redundant Tools
Monitoring usage can also uncover redundancies. For example, two departments may use separate project management tools—Asana and Trello—when consolidating into one platform could reduce costs and improve collaboration.
Measure Business Value
Usage data should be tied back to business outcomes. High adoption of a customer support platform, for example, may correlate with improved resolution times and customer satisfaction. In contrast, low adoption of an analytics tool may indicate it doesn’t deliver the promised value.
Benefits of Usage Monitoring
- Cost optimization: Rightsize license counts and tiers to actual needs.
- Vendor negotiation: Usage metrics provide leverage in renewal discussions.
- Improved productivity: Ensures employees have access to the right tools without overspending.
By continuously monitoring and analyzing SaaS usage, organizations move from reactive management to proactive optimization—ensuring they get maximum return on every subscription.
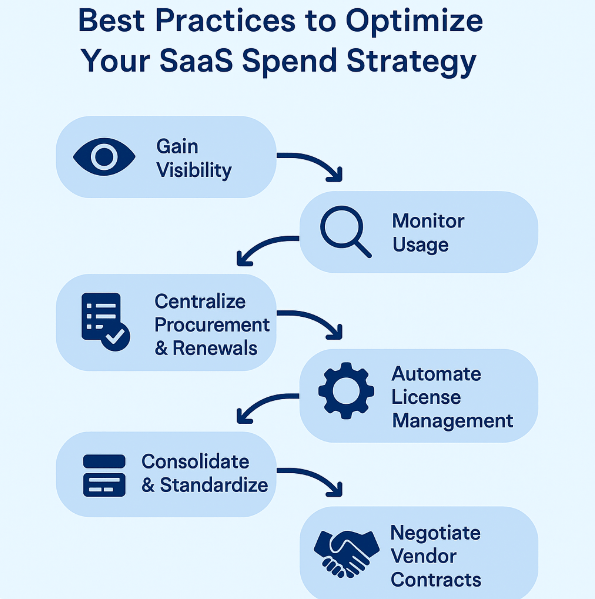
Best Practice 3: Centralize SaaS Procurement and Renewals
Decentralized purchasing is one of the biggest drivers of SaaS waste. In many organizations, departments or even individuals buy subscriptions with a company card, bypassing IT and procurement entirely. While this speeds up adoption, it leads to shadow IT, redundant tools, and uncontrolled costs.
Centralizing procurement and renewals helps organizations regain control and ensure SaaS investments align with business goals.
Consolidate Purchasing Power
When each department negotiates separately, vendors have the upper hand. By consolidating SaaS contracts under procurement, companies can leverage their total spend to negotiate discounts and better terms. For example, instead of five teams buying collaboration software individually, procurement can negotiate one enterprise license with volume-based savings.
Streamline Renewal Management
SaaS renewals often auto-renew annually or monthly, catching companies off guard. Without centralized oversight, teams may unknowingly renew redundant or underutilized subscriptions. A centralized renewal calendar ensures all stakeholders are notified in advance, providing time to:
- Assess current usage.
- Explore alternative vendors.
- Renegotiate terms.
- Cancel unnecessary subscriptions.
Align with IT and Security Policies
Procurement and IT must collaborate to evaluate new SaaS purchases against company policies. This prevents employees from adopting tools that don’t meet security, compliance, or integration requirements. Centralization ensures every app passes a consistent vetting process.
Improve Budgeting and Forecasting
Centralized SaaS management also supports more accurate budgeting. Finance teams gain full visibility into SaaS commitments, enabling them to forecast future spend and avoid unpleasant surprises.
Benefits of Centralized Procurement
- Stronger vendor leverage in negotiations.
- Fewer redundant tools across departments.
- Predictable renewals and reduced auto-renewal waste.
- Improved compliance with IT and security standards.
By shifting SaaS purchasing from an ad-hoc, decentralized process to a centralized strategy, companies gain both cost savings and operational efficiency.
Best Practice 4: Automate License Management and Provisioning
Manually tracking SaaS licenses across dozens or hundreds of applications is inefficient and error-prone. Employees join, switch roles, or leave the company every month, and each change affects the licenses they need. Without automation, licenses remain active long after they’re needed, wasting money and creating security risks.
Automate Onboarding
When a new employee starts, automated provisioning ensures they are assigned the right set of tools immediately. For example, a marketing hire might automatically receive access to HubSpot, Google Analytics, and the company’s design software. Automation eliminates delays, reduces IT workload, and provides consistency.
Automate Offboarding
Offboarding is even more critical. If departing employees retain access to SaaS accounts, it creates both unnecessary costs and potential data breaches. Automated workflows connected to HR systems can immediately revoke licenses when an employee exits, ensuring clean and secure deprovisioning.
Rightsize Licenses Continuously
Beyond onboarding and offboarding, automation helps continuously rightsize licenses. Rules can be set to downgrade users who haven’t accessed premium features in the last 90 days, or to reassign licenses that have been inactive for a certain period.
Integrate With Identity and Access Management
Automation works best when tied to identity providers like Okta, Azure AD, or Google Workspace. This creates a single source of truth for user access, streamlining management and strengthening security.
Benefits of Automation
- Cost savings by reclaiming unused or inactive licenses.
- Security improvements through immediate deprovisioning.
- Efficiency gains by reducing manual IT tasks.
- Better employee experience with seamless onboarding.
Automating license management transforms SaaS governance from a reactive scramble into a proactive, consistent process—cutting costs while safeguarding company data.
Best Practice 5: Consolidate and Standardize Tools
As organizations grow, different teams often adopt their own preferred applications. Marketing might use Trello, product development relies on Jira, while operations experiments with Asana. This fragmentation leads to redundant costs, inefficient collaboration, and data silos. A core best practice in SaaS spend optimization is to consolidate overlapping tools and standardize on shared platforms.
Identify Redundancies
Usage audits often reveal multiple apps serving the same purpose. For instance:
- Several video conferencing tools (Zoom, Webex, Google Meet).
- Multiple messaging platforms (Slack, Microsoft Teams).
- Duplicate cloud storage services (Dropbox, Google Drive, OneDrive).
Consolidating to one tool per category reduces spend and simplifies collaboration.
Standardize Across Departments
Once redundancies are identified, organizations should define preferred platforms for each business function. For example:
- Microsoft Teams for communication.
- Jira for project management.
- Salesforce for CRM.
Standardization ensures smoother collaboration, as all teams work within the same environment. It also reduces IT complexity, since integrations, security policies, and training can focus on fewer tools.
Improve Vendor Negotiations
Consolidation also increases purchasing power. Instead of splitting spend across multiple vendors, concentrating spend with one provider strengthens negotiation leverage. Vendors are more willing to provide discounts and flexible contract terms when they know they’re the company’s sole provider in a given category.
Support Employee Productivity
While consolidation drives efficiency, it must be balanced with employee needs. If a specific team requires unique features not supported by the standardized tool, exceptions may be justified. The goal is to consolidate where possible while maintaining productivity.
Benefits of Consolidation
- Lower costs by reducing overlapping apps.
- Improved collaboration through standardized workflows.
- Simplified management for IT and security teams.
- Stronger vendor leverage for discounts and favorable terms.
By consolidating and standardizing, companies not only cut costs but also create a more cohesive digital workplace.
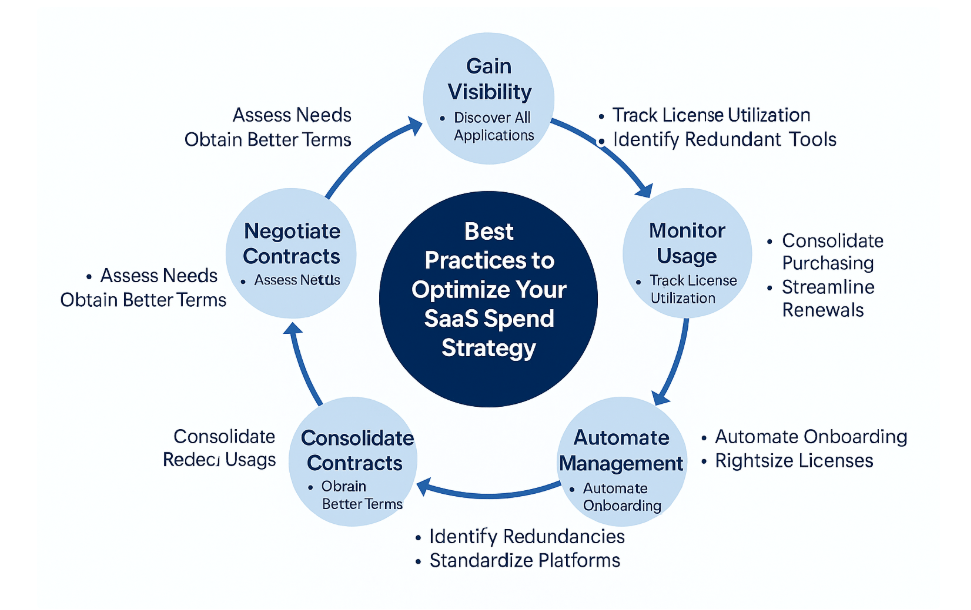
Conclusion
Optimizing SaaS spend is not just about cutting costs—it’s about building a smarter, more sustainable approach to technology management. With SaaS now powering nearly every aspect of modern business, organizations that fail to manage their subscriptions strategically risk wasting money, duplicating tools, and exposing themselves to compliance or security risks.
The best practices outlined in this article—gaining visibility, monitoring usage, centralizing procurement, automating license management, consolidating tools, and negotiating smarter vendor contracts—form a framework for long-term success. Each practice builds on the last, creating a cycle of continuous improvement where SaaS investments are transparent, efficient, and aligned with business goals.
Companies that adopt these practices often discover they can reduce SaaS costs by 20–30% annually, while also improving employee productivity and strengthening compliance. More importantly, they transform SaaS management from a reactive chore into a proactive strategy that supports growth.
As the SaaS landscape continues to evolve, one thing remains clear: the organizations that treat spend optimization as a strategic discipline will be the ones best positioned to maximize value, minimize waste, and stay competitive in a digital-first world.

