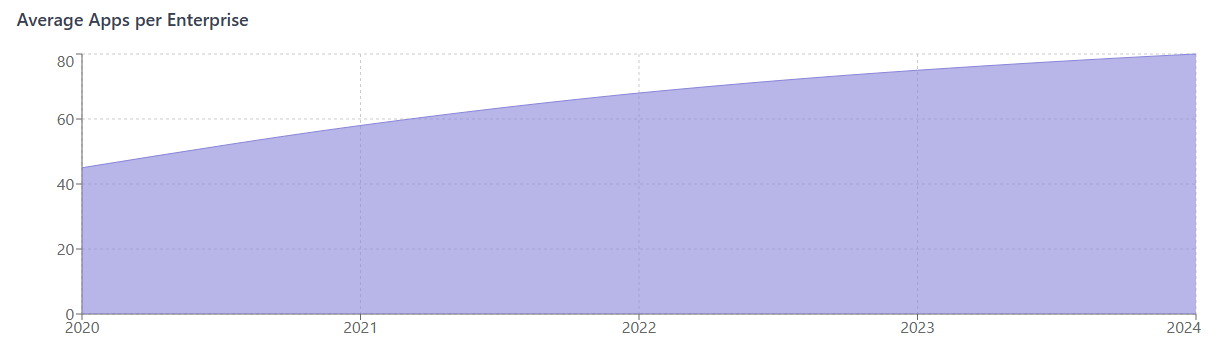
The modern business landscape has witnessed an unprecedented surge in Software as a Service (SaaS) adoption, fundamentally transforming how organizations operate and manage their technology stack. According to recent industry reports, the average enterprise now uses over 80 different SaaS applications, creating a complex web of subscriptions, licenses, and recurring payments that traditional management methods simply cannot handle effectively.
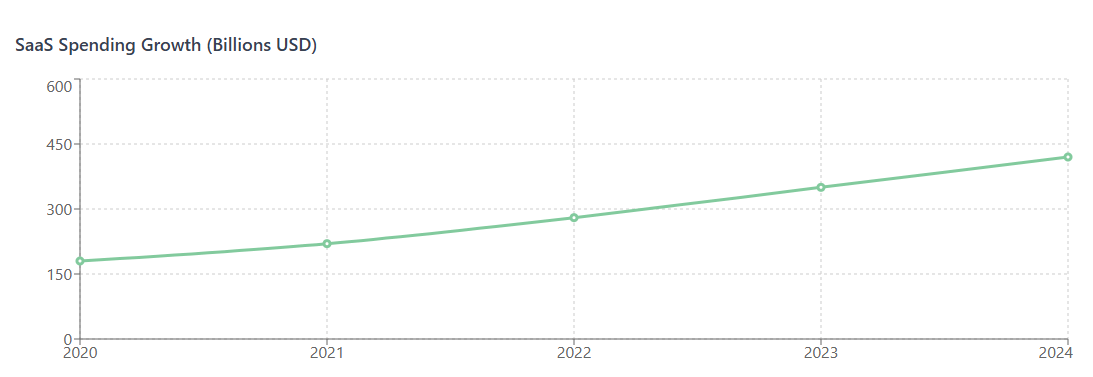
Gone are the days when businesses could rely on simple spreadsheets or manual tracking systems to manage their software subscriptions. The explosive growth of SaaS spend management has created new challenges that demand sophisticated, automated solutions. Organizations are discovering that without proper automation, they’re not just losing money—they’re losing competitive advantage.
The Problem with Manual SaaS Management
Spreadsheet Limitations in the Modern SaaS Era
Traditional spreadsheet-based approaches to subscription management have become increasingly inadequate in today’s fast-paced business environment. While spreadsheets served their purpose in simpler times, they now represent significant bottlenecks and sources of error in SaaS governance.
Manual tracking systems typically suffer from several critical flaws. First, they require constant human intervention to remain accurate, making them prone to human error and oversight. Second, they lack real-time visibility into subscription usage and costs, often resulting in delayed reactions to budget overruns or license waste. Third, they provide no automated alerts for renewal dates or usage anomalies, leading to surprise charges and missed optimization opportunities.
Consider a mid-sized company managing subscriptions for tools like Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, Zoom, Slack, Adobe Creative Suite, and dozens of other applications. Each application has different billing cycles, user tiers, feature sets, and renewal dates. Tracking this manually across departments, teams, and geographical locations becomes a full-time job that’s still prone to costly mistakes.
The Hidden Costs of Poor SaaS Management
The financial impact of inadequate SaaS subscription management extends far beyond obvious waste. Organizations frequently discover they’re paying for unused licenses, duplicate services, or feature tiers that exceed their actual needs. Industry studies suggest that businesses waste approximately 30% of their SaaS spending due to poor visibility and management practices.
Hidden costs manifest in various ways. Abandoned licenses continue generating charges long after employees leave or change roles. Duplicate subscriptions occur when different departments independently purchase similar tools. Feature bloat happens when organizations pay for premium tiers but only use basic functionality. License sprawl emerges as teams sign up for new tools without central oversight.
These issues compound over time, creating what experts call “SaaS sprawl”—an uncontrolled proliferation of software subscriptions that drains budgets and complicates IT governance. Without automation, organizations lack the visibility needed to identify and address these inefficiencies before they become significant financial burdens.
The Rise of SaaS Automation Tools
Understanding Modern SaaS Management Platforms
The evolution of SaaS automation tools represents a direct response to the limitations of manual management approaches. Modern platforms leverage sophisticated technologies including artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics to provide comprehensive subscription oversight and optimization.
These platforms operate on the principle of centralized visibility and automated control. They connect directly to your organization’s financial systems, SaaS applications, and cloud infrastructure to create a unified view of all software spending and usage. Through application programming interfaces (APIs) and secure integrations, they continuously monitor subscription activity, user behavior, and spending patterns.
Advanced SaaS management platforms offer features that were impossible with manual systems. Real-time usage monitoring tracks how employees actually use software applications, identifying underutilized licenses and optimization opportunities. Automated spend tracking consolidates expenses across multiple payment methods and currencies, providing accurate cost attribution by team, department, or project. Predictive analytics use historical data to forecast future spending and identify potential budget overruns before they occur.
Key Features That Drive Automation Success
Successful SaaS automation relies on several critical capabilities that distinguish modern platforms from traditional management approaches. These features work together to create a comprehensive management ecosystem that reduces manual effort while improving control and visibility.
License optimization represents one of the most valuable automation features. Intelligent algorithms analyze usage patterns to recommend optimal license distributions, suggesting when to upgrade, downgrade, or cancel subscriptions based on actual needs rather than initial estimates. This dynamic optimization ensures organizations pay only for the software capacity they truly require.
Automated renewal management eliminates the surprise charges and missed optimization opportunities that plague manual systems. Platforms monitor upcoming renewal dates, analyze usage trends, and provide recommendations for each subscription well before renewal deadlines. Some systems can even negotiate renewals automatically or pause subscriptions for seasonal businesses.
Integration capabilities enable seamless data flow between SaaS management platforms and existing business systems. Modern solutions integrate with financial software, human resources systems, and identity management platforms to provide context-rich insights and automated workflows. For example, when an employee leaves the company, the platform can automatically identify and cancel their software licenses while ensuring knowledge transfer and data security.
Core Components of Automated SaaS Management
Discovery and Inventory Automation
The foundation of effective SaaS management lies in comprehensive discovery and inventory automation. Traditional methods require manual cataloging of every software subscription, a process that’s both time-consuming and inevitably incomplete. Automated discovery changes this paradigm entirely.
Modern discovery tools employ multiple detection methods to identify SaaS usage across an organization. Network traffic analysis reveals software applications communicating with external services, identifying both sanctioned and shadow IT deployments. Financial integration discovers subscriptions through payment processing systems, credit card statements, and expense reports. Browser-based detection identifies web applications accessed by employees, providing insights into actual software usage patterns.
The inventory automation process creates detailed profiles for each discovered application, including subscription details, user assignments, feature utilization, and cost attribution. This automated cataloging provides the foundation for all subsequent optimization activities, ensuring no subscription escapes management oversight.
Usage Monitoring and Analytics
Automated usage monitoring transforms raw application data into actionable insights about software utilization and optimization opportunities. Unlike manual surveys or periodic reviews, automated monitoring provides continuous, objective measurement of how employees actually use software applications.
Advanced analytics platforms track multiple usage dimensions simultaneously. User engagement metrics reveal how frequently employees access applications and which features they use most. Time-based analysis identifies seasonal usage patterns that might warrant temporary subscription adjustments. Behavioral analytics detect when users consistently access only basic features of premium applications, suggesting opportunities for downgrading.
The insights generated through automated monitoring enable data-driven decision making about subscription optimization. Rather than relying on user surveys or manager estimates, organizations can make confident decisions based on objective usage data and clear return-on-investment calculations.
Financial Integration and Spend Tracking
Comprehensive financial integration represents a critical component of successful SaaS automation, providing the data foundation needed for accurate cost attribution and optimization analysis. Modern platforms integrate with multiple financial systems to create a complete picture of SaaS spending across an organization.
Automated spend tracking consolidates expenses from various sources including corporate credit cards, procurement systems, departmental budgets, and direct vendor relationships. Multi-currency support ensures accurate reporting for organizations with global operations, while automated categorization organizes expenses by department, project, or cost center.
Real-time spend monitoring enables proactive budget management rather than reactive cost control. Organizations can set spending thresholds and receive automated alerts when approaching budget limits, preventing unexpected overages and enabling timely corrective action.
Implementation Strategies for SaaS Automation
Assessment and Planning Phase
Successful SaaS automation implementation begins with a comprehensive assessment of current subscription management practices and organizational requirements. This planning phase establishes the foundation for effective platform selection and deployment.
The assessment process should inventory all existing SaaS subscriptions, regardless of how they’re currently managed or paid for. This includes applications purchased through central procurement, departmental subscriptions, and individual employee accounts. Understanding the full scope of current SaaS usage provides crucial context for automation platform selection and configuration.
Stakeholder interviews across IT, finance, and business departments reveal specific pain points and optimization opportunities. These conversations help identify the most valuable automation features and establish success metrics for the implementation. Common objectives include reducing overall SaaS spending, improving license utilization, enhancing security and compliance, and streamlining renewal management.
Budget analysis examines current SaaS spending patterns and identifies areas of waste or inefficiency. This analysis helps establish baseline metrics for measuring automation success and provides insights into potential cost savings that can justify platform investment.
Platform Selection Criteria
Choosing the right SaaS automation platform requires careful evaluation of organizational needs against available solution capabilities. The complexity of modern SaaS environments demands platforms that can handle diverse requirements while providing room for future growth.
Integration capabilities represent the most critical selection criterion. The chosen platform must integrate seamlessly with existing financial systems, identity management platforms, and major SaaS applications used within the organization. Poor integration capabilities limit the platform’s effectiveness and create additional manual work rather than reducing it.
Scalability considerations ensure the platform can grow with organizational needs. This includes support for increasing numbers of applications and users, as well as advanced features that may become valuable as SaaS management maturity increases. Cloud cost optimization capabilities are particularly important for organizations using cloud infrastructure alongside SaaS applications.
Security and compliance features must align with organizational requirements and industry regulations. This includes data encryption, access controls, audit trails, and compliance reporting capabilities. Organizations in regulated industries may require additional security certifications and compliance frameworks.
Change Management and User Adoption
Successful SaaS automation implementation depends heavily on effective change management and user adoption strategies. Even the most sophisticated platform will fail if users don’t understand its value or resist changing established workflows.
Communication strategies should emphasize the benefits automation provides to different stakeholder groups. IT teams gain visibility and control over software deployments. Finance departments receive accurate spending data and budget control tools. Business users benefit from streamlined access to approved applications and reduced administrative overhead.
Training programs must address different user types and their specific needs. Platform administrators require comprehensive technical training on configuration and optimization features. Department managers need understanding of reporting capabilities and approval workflows. End users benefit from simple guidance on how automation improves their software access and usage experience.
Gradual rollout approaches reduce implementation risk and allow for iterative improvement. Starting with a subset of applications or departments provides opportunities to refine processes and address challenges before full-scale deployment. Success stories from early implementation phases help build momentum for broader adoption.
Advanced Automation Capabilities
AI-Powered Optimization
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are revolutionizing SaaS subscription management by enabling predictive optimization and intelligent decision-making. These advanced capabilities go beyond simple monitoring and reporting to provide proactive recommendations and automated actions.
Machine learning algorithms analyze usage patterns, spending trends, and organizational behavior to identify optimization opportunities that might not be apparent through traditional analysis. For example, AI can predict when teams will need additional software capacity based on project timelines and historical usage patterns, enabling proactive license scaling.
Predictive analytics help organizations anticipate future SaaS needs and budget requirements. By analyzing factors such as employee growth, seasonal business patterns, and project pipeline data, AI-powered platforms can forecast software demand and recommend optimal subscription planning strategies.
Automated optimization actions represent the next evolution in SaaS management, where platforms can automatically implement approved optimization strategies without manual intervention. This might include automatically adjusting license quantities based on usage patterns, pausing subscriptions during slow periods, or upgrading accounts when usage approaches tier limits.
Integration with Enterprise Systems
Advanced SaaS automation platforms integrate deeply with enterprise systems to provide seamless workflows and comprehensive organizational visibility. These integrations eliminate data silos and enable sophisticated automation scenarios that improve both efficiency and control.
Human resources system integration enables automatic license provisioning and deprovisioning based on employee lifecycle events. When new employees join the organization, the platform can automatically assign appropriate software licenses based on their role and department. Similarly, when employees leave, the system can immediately revoke access and cancel unnecessary licenses.
Financial system integration provides real-time budget tracking and automated approval workflows. Purchase requests can be automatically routed through appropriate approval chains based on cost thresholds and departmental budgets. Integration with procurement systems ensures contract compliance and enables bulk purchasing optimization.
Identity and access management integration enhances security while simplifying user experience. Single sign-on capabilities reduce password complexity while providing detailed audit trails. Automated access reviews ensure employees maintain appropriate permissions as their roles change over time.
Governance and Compliance Automation
Automated governance capabilities help organizations maintain control over SaaS deployments while ensuring compliance with internal policies and external regulations. These features are particularly valuable for larger organizations with complex approval processes and regulatory requirements.
Policy enforcement automation ensures SaaS deployments comply with organizational standards and security requirements. Platforms can automatically block or flag applications that don’t meet security criteria, data residency requirements, or integration standards. This prevents shadow IT deployments while still enabling business agility.
Compliance reporting automation generates required documentation for audits and regulatory reviews. Platforms maintain detailed records of software usage, access controls, and data handling practices, automatically formatting this information for various compliance frameworks including SOX, GDPR, and industry-specific regulations.
Contract management automation tracks subscription terms, renewal dates, and compliance obligations across all SaaS applications. Automated alerts ensure organizations meet contractual obligations while identifying opportunities for better terms during renewal negotiations.
Measuring Success and ROI
Key Performance Indicators
Establishing appropriate key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for measuring the success of SaaS automation initiatives and demonstrating their value to organizational stakeholders. These metrics should align with the original objectives established during the planning phase while providing ongoing visibility into optimization opportunities.
Cost-related KPIs focus on the primary financial benefits of automation. Total SaaS spending trends show whether automation is successfully controlling costs over time. Cost per user metrics help organizations understand their software efficiency and identify opportunities for improvement. License utilization rates reveal how effectively the organization is using purchased software capacity.
Operational efficiency metrics demonstrate how automation improves business processes and reduces administrative burden. Time to provision new software access shows whether automation is accelerating business capabilities. The number of unused licenses identified and eliminated demonstrates ongoing optimization effectiveness. Renewal cycle efficiency measures how automation improves contract management processes.
Risk and compliance metrics ensure automation is enhancing rather than compromising organizational security and governance. The percentage of software deployments following approved processes shows governance effectiveness. Security incident reduction demonstrates whether automated controls are improving risk management. Audit readiness metrics measure how quickly organizations can respond to compliance requirements.
Calculating Return on Investment
Calculating return on investment (ROI) for SaaS automation requires comprehensive analysis of both costs and benefits over appropriate time periods. This analysis should include direct financial impacts as well as indirect benefits that may be more difficult to quantify but equally valuable.
Direct cost savings typically represent the most significant ROI contributors. These include eliminated waste from unused licenses, avoided duplicate subscriptions, and optimized contract terms achieved through better visibility and negotiation capabilities. Organizations commonly achieve 20-30% reduction in SaaS spending through effective automation, providing clear financial justification for platform investment.
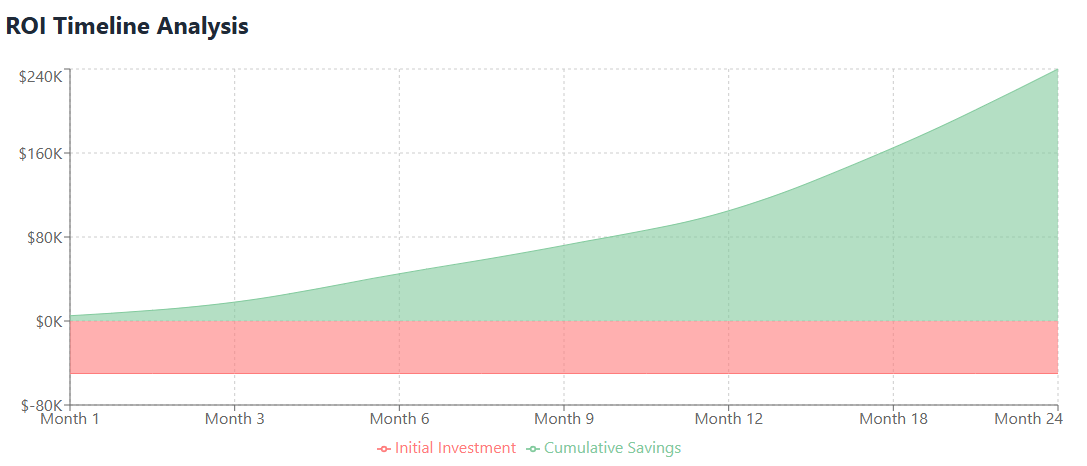
Indirect benefits often provide substantial value that may not be immediately apparent in financial statements. Reduced administrative time allows staff to focus on higher-value activities. Improved security and compliance reduce risk exposure and potential penalty costs. Enhanced business agility through faster software provisioning enables revenue opportunities that might otherwise be missed.
The calculation should also consider implementation costs including platform licensing, integration development, training expenses, and ongoing operational overhead. However, most organizations find that comprehensive SaaS automation pays for itself within the first year through direct cost savings alone, with additional benefits providing ongoing value.
Future Trends in SaaS Automation
Emerging Technologies and Capabilities
The future of SaaS automation is being shaped by emerging technologies that promise to further enhance optimization capabilities and reduce manual management requirements. Organizations planning long-term automation strategies should consider how these trends might impact their platform selection and implementation approaches.
Advanced AI capabilities are evolving beyond simple pattern recognition to provide sophisticated decision-making support. Natural language processing enables conversational interfaces for SaaS management, allowing users to query spending data and optimization recommendations using plain English. Computer vision technologies can analyze user interface interactions to provide detailed insights into feature utilization and user experience optimization.
Blockchain technology may revolutionize SaaS contract management by providing immutable records of license agreements and usage rights. Smart contracts could automate renewal negotiations and payment processing while ensuring transparent and auditable transaction records.
Internet of Things (IoT) integration expands SaaS automation beyond traditional software applications to include connected devices and embedded systems. This broader integration provides comprehensive visibility into all technology spending and usage across modern digital organizations.
The Evolution of SaaS Management
The SaaS management landscape continues evolving as organizations become more sophisticated in their automation approaches and vendors respond with increasingly powerful capabilities. Understanding these evolutionary trends helps organizations make strategic decisions about their automation investments.
Industry-specific SaaS management solutions are emerging to address the unique requirements of different business sectors. Healthcare organizations require specialized compliance features and integration with medical systems. Financial services companies need advanced security controls and regulatory reporting capabilities. Manufacturing organizations benefit from integration with operational technology and supply chain systems.
The integration of SaaS management with broader cloud cost optimization strategies reflects the reality that modern organizations use hybrid technology environments. Platforms that can optimize both software subscriptions and cloud infrastructure spending provide more comprehensive value and simplified management approaches.
Collaborative optimization features enable organizations to share insights and best practices across industry communities. Anonymized benchmarking data helps organizations understand how their SaaS usage and spending compare to similar companies, identifying additional optimization opportunities.
Conclusion: Embracing the Automated Future
The transition from spreadsheet-based SaaS management to comprehensive automation represents more than a technological upgrade—it’s a strategic imperative for organizations seeking to thrive in an increasingly software-dependent business environment. The complexity and scale of modern SaaS environments have made manual management approaches not just inefficient, but dangerously inadequate.
Organizations that embrace SaaS automation gain significant competitive advantages through improved cost control, enhanced operational efficiency, and reduced risk exposure. The ability to make data-driven decisions about software investments, optimize license utilization in real-time, and maintain comprehensive visibility across complex subscription portfolios becomes a source of sustainable competitive advantage.
The implementation journey requires careful planning, appropriate platform selection, and effective change management, but the benefits justify the investment for virtually all organizations using more than a handful of SaaS applications. The question is not whether to automate SaaS management, but how quickly and comprehensively to implement automation capabilities.
As the SaaS ecosystem continues evolving and growing, organizations with sophisticated automation capabilities will be better positioned to capitalize on new opportunities while avoiding the pitfalls that trap those relying on outdated management approaches. The future belongs to organizations that can effectively harness the power of automated SaaS management to drive business success in an increasingly digital world.
The transformation beyond spreadsheets isn’t just about technology—it’s about empowering organizations to focus on their core business objectives while ensuring their software investments deliver maximum value. With the right automation platform and implementation strategy, organizations can turn SaaS management from a source of complexity and cost into a driver of efficiency and competitive advantage.

