Enterprise organizations today operate in an increasingly complex digital ecosystem where multi-cloud architectures have become the standard rather than the exception. As Fortune 500 companies navigate the challenges of 2025, the strategic management of multi-cloud costs has emerged as a critical competitive differentiator that directly impacts bottom-line performance and operational agility. The landscape of enterprise cloud computing has evolved dramatically, with organizations now leveraging an average of 2.6 cloud providers alongside dozens of SaaS applications. This distributed approach offers unprecedented flexibility and resilience but introduces significant complexity in cost management, governance, and optimization. The most successful enterprises have developed sophisticated strategies that treat cloud cost management not as a reactive cost-cutting exercise, but as a proactive driver of business value and innovation.
Modern enterprise multi-cloud cost management encompasses far more than traditional expense tracking. It involves sophisticated financial operations practices, advanced analytics, automated governance policies, and strategic alignment between technology investments and business outcomes. Organizations that master these capabilities consistently achieve 25-40% cost reductions while simultaneously improving performance and accelerating innovation cycles.
This comprehensive analysis explores the cutting-edge strategies, tools, and frameworks that Fortune 500 companies are employing to optimize their multi-cloud investments in 2025. From advanced SaaS spend management techniques to emerging AI-driven cost optimization platforms, we examine the practical approaches that drive measurable results in large-scale enterprise environments.
The Multi-Cloud Enterprise Landscape in 2025
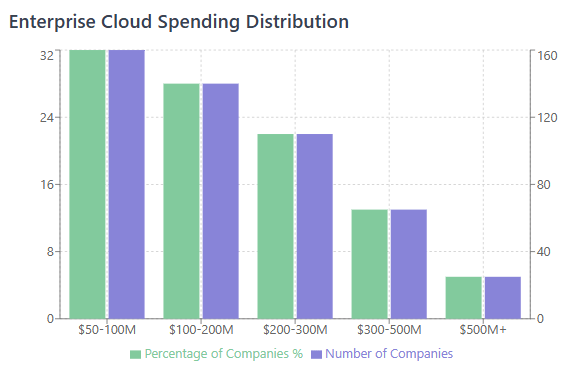
The enterprise cloud landscape has reached unprecedented complexity, with organizations managing hybrid environments spanning multiple public clouds, private infrastructure, and hundreds of SaaS applications. According to recent enterprise surveys, 89% of Fortune 500 companies now operate multi-cloud strategies, with the average organization utilizing 3.4 cloud providers and 127 SaaS applications across their technology stack.
This architectural complexity creates both opportunities and challenges for enterprise cost management. On one hand, multi-cloud strategies enable organizations to optimize workload placement, leverage best-of-breed services, and avoid vendor lock-in. On the other hand, this distributed approach significantly complicates cost visibility, governance, and optimization efforts across the enterprise.
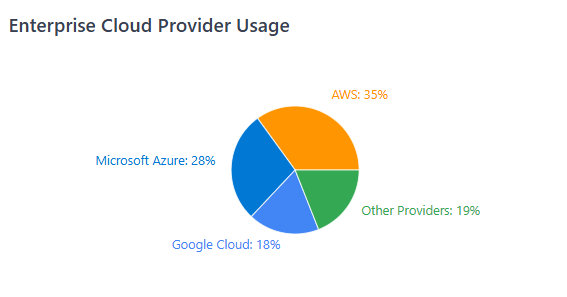
Modern enterprise multi-cloud environments typically include primary relationships with major providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform, complemented by specialized services from vendors like Salesforce, ServiceNow, and Snowflake. Each provider brings unique pricing models, billing structures, and optimization opportunities that require sophisticated management approaches.
The financial impact of effective multi-cloud cost management has never been more significant. Enterprise organizations report average annual cloud spending ranging from $50 million to $500 million, with SaaS expenditures representing an additional 20-30% of total technology budgets. Organizations that implement comprehensive cost management strategies consistently achieve savings of $10-50 million annually while improving operational efficiency and innovation velocity.
Leading enterprises recognize that multi-cloud cost management requires fundamental changes to organizational structures, processes, and capabilities. The most successful companies have established dedicated Cloud Financial Management (FinOps) teams that combine financial expertise with deep technical knowledge of cloud architectures and pricing models.
Fortune 500 Multi-Cloud Cost Management Strategies
Fortune 500 companies have developed sophisticated approaches to multi-cloud cost management that go far beyond basic monitoring and reporting. These strategies encompass comprehensive frameworks for cost visibility, optimization, governance, and strategic planning that enable consistent results across complex enterprise environments.
Centralized Cost Visibility and Analytics
The foundation of effective enterprise multi-cloud cost management lies in achieving comprehensive visibility across all cloud providers and SaaS applications. Leading organizations implement unified cost management platforms that aggregate billing data from multiple sources, normalize pricing information, and provide real-time analytics across the entire technology portfolio.
Advanced enterprises leverage sophisticated tagging strategies and cost allocation methodologies that enable precise tracking of expenses by business unit, project, application, and cost center. These approaches typically involve automated tagging policies enforced through infrastructure-as-code practices and governance controls that ensure consistency across all cloud resources.
Modern cost visibility platforms provide multi-dimensional analytics that enable enterprise leaders to understand spending patterns, identify optimization opportunities, and make data-driven decisions about resource allocation. These systems integrate with existing enterprise financial systems to provide seamless budget tracking and variance analysis capabilities.
Strategic Workload Optimization
Fortune 500 companies implement sophisticated workload optimization strategies that continuously evaluate the most cost-effective placement of applications and services across their multi-cloud environments. These approaches combine technical performance requirements with detailed cost modeling to optimize both financial and operational outcomes.
Advanced organizations utilize automated rightsizing tools that continuously monitor resource utilization and recommend optimal instance types, storage configurations, and service tiers based on actual usage patterns. These recommendations are typically integrated with change management processes that ensure optimization activities align with business requirements and risk management policies.
Leading enterprises also implement sophisticated reserved capacity strategies that leverage long-term commitments across multiple cloud providers to achieve significant cost reductions. These strategies typically involve detailed demand forecasting, risk assessment, and financial modeling to optimize the balance between cost savings and operational flexibility.
SaaS Portfolio Optimization
Enterprise SaaS spend management has become increasingly sophisticated as organizations manage hundreds of applications across diverse functional areas. Leading companies implement comprehensive SaaS governance frameworks that encompass procurement, utilization monitoring, license optimization, and vendor management processes.
Advanced SaaS optimization strategies involve continuous monitoring of user adoption, feature utilization, and license allocation to identify opportunities for consolidation and rightsizing. These approaches typically achieve 20-35% cost reductions through elimination of unused licenses, optimization of subscription tiers, and consolidation of overlapping applications.
Modern enterprises also leverage automated renewal management processes that proactively negotiate contract terms, evaluate alternative solutions, and optimize license quantities based on actual usage patterns. These capabilities are particularly critical given the average enterprise manages 127 SaaS applications with annual renewal values exceeding $25 million.
Advanced SaaS Spend Management for Enterprises
Enterprise SaaS spend management has evolved into a sophisticated discipline that requires specialized tools, processes, and expertise to optimize the complex portfolio of applications that power modern business operations. Organizations that excel in this area implement comprehensive frameworks that address procurement, utilization, optimization, and governance across their entire SaaS ecosystem.
Comprehensive SaaS Discovery and Inventory Management
The first challenge in enterprise SaaS management involves achieving complete visibility into the applications being used across the organization. Many enterprises discover that shadow IT and decentralized procurement processes have resulted in significantly more SaaS applications than officially recognized, often doubling or tripling the known application count.
Leading organizations implement automated discovery tools that monitor network traffic, analyze financial transactions, and integrate with identity management systems to identify all SaaS applications in use across the enterprise. These comprehensive discovery processes typically reveal 40-60% more applications than traditional IT asset management approaches.
Modern SaaS inventory management systems provide detailed tracking of subscription details, user assignments, feature utilization, and renewal dates across the entire application portfolio. This comprehensive visibility enables proactive management decisions and optimization opportunities that would otherwise remain hidden in the complexity of enterprise operations.
Advanced License Optimization and Utilization Analytics
Enterprise organizations implement sophisticated analytics platforms that continuously monitor SaaS application usage patterns to identify optimization opportunities across user licenses, feature sets, and subscription tiers. These systems typically integrate with application APIs to gather detailed utilization data that enables precise optimization recommendations.
Advanced utilization analytics reveal significant optimization opportunities in most enterprise environments. Common findings include 25-40% of licenses showing minimal or no usage, over-provisioning of premium features that remain unused, and opportunities to consolidate similar applications across different business units.
Leading enterprises implement automated license optimization processes that continuously adjust subscription levels based on actual usage patterns, seasonal variations, and business growth projections. These dynamic optimization approaches typically achieve ongoing cost reductions of 20-30% compared to static license management approaches.
Strategic Vendor Management and Procurement Optimization
Fortune 500 companies leverage their scale and negotiating power to achieve significant cost reductions through strategic vendor management and procurement optimization. These approaches involve sophisticated contract negotiation, bulk purchasing strategies, and long-term partnership development that extends beyond simple cost reduction.
Advanced procurement strategies involve detailed market analysis, alternative solution evaluation, and competitive benchmarking that enables enterprises to negotiate optimal contract terms. Leading organizations typically achieve 15-25% cost reductions through strategic procurement practices compared to standard list pricing.
Modern vendor management approaches also emphasize partnership development and value-based contracting that aligns vendor incentives with enterprise business outcomes. These strategic relationships often enable access to advanced features, priority support, and collaborative product development opportunities that provide value beyond cost optimization.
Multi-Cloud Governance and Financial Operations
Enterprise multi-cloud governance has evolved into a comprehensive discipline that encompasses financial operations, security compliance, operational efficiency, and strategic alignment across complex cloud environments. Organizations that excel in this area implement sophisticated frameworks that balance cost optimization with operational requirements and business objectives.
FinOps Implementation and Organizational Structure
Leading enterprises establish dedicated Cloud Financial Operations (FinOps) teams that combine financial expertise with deep technical knowledge of cloud architectures and pricing models. These teams typically report to enterprise finance organizations while maintaining close collaboration with IT and business stakeholders.
Successful FinOps implementations involve comprehensive organizational change management that establishes clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability frameworks across engineering, finance, and business teams. These structures enable collaborative decision-making and shared responsibility for cost optimization outcomes.
Modern FinOps practices leverage automated workflows and analytics platforms that provide real-time cost visibility, predictive modeling, and optimization recommendations that enable proactive financial management. These capabilities are essential for managing the complexity and scale of enterprise multi-cloud environments.
Policy-Driven Cost Controls and Automation
Enterprise organizations implement sophisticated policy frameworks that automatically enforce cost controls, resource limits, and governance requirements across their multi-cloud environments. These automated controls prevent cost overruns while enabling developer productivity and operational agility.
Advanced policy frameworks typically include automated resource provisioning controls, spending limits by business unit or project, and approval workflows for high-cost resources or significant infrastructure changes. These policies are enforced through infrastructure-as-code practices and integrated development environments.
Leading enterprises also implement predictive analytics and anomaly detection systems that proactively identify unusual spending patterns, potential security issues, or operational inefficiencies before they impact business operations or budgets.
Cross-Cloud Cost Allocation and Chargeback Systems
Fortune 500 companies implement sophisticated cost allocation and chargeback systems that enable accurate tracking of cloud costs by business unit, project, application, and cost center. These systems provide the financial transparency necessary for effective decision-making and accountability in large enterprise environments.
Advanced chargeback systems integrate with existing enterprise financial systems to provide seamless budget tracking, variance analysis, and financial reporting capabilities. These integrations enable finance teams to treat cloud costs as standard operational expenses within existing financial management processes.
Modern cost allocation approaches leverage automated tagging, resource grouping, and utilization analytics to provide precise cost attribution even in complex shared infrastructure environments. These capabilities are essential for effective financial management in enterprise multi-cloud architectures.
Emerging Technologies Reshaping Enterprise Cloud Costs
The enterprise cloud landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with emerging technologies creating new opportunities and challenges for cost management. Organizations that stay ahead of these trends position themselves to achieve significant competitive advantages through early adoption and strategic implementation of next-generation cost optimization approaches.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cost Optimization
Advanced AI and machine learning technologies are revolutionizing enterprise cloud cost management by enabling predictive analytics, automated optimization, and intelligent resource management capabilities that far exceed traditional rule-based approaches.
Modern AI-driven cost optimization platforms analyze historical usage patterns, business seasonality, and application behavior to predict future resource requirements with remarkable accuracy. These predictive capabilities enable proactive scaling decisions and optimized resource provisioning that minimizes costs while maintaining performance.
Machine learning algorithms also enable sophisticated anomaly detection and root cause analysis that helps enterprises quickly identify and resolve cost spikes, security issues, or operational inefficiencies. These capabilities are particularly valuable in complex multi-cloud environments where manual monitoring approaches become impractical.
Container and Serverless Cost Management
The growing adoption of container platforms and serverless computing architectures creates new challenges and opportunities for enterprise cost management. These technologies enable more granular resource utilization and cost allocation but require sophisticated monitoring and optimization approaches.
Container cost management involves detailed tracking of resource consumption by individual workloads, namespaces, and applications within shared infrastructure environments. Leading enterprises implement specialized monitoring tools that provide precise cost attribution and optimization recommendations for containerized applications.
Serverless computing platforms offer unique cost optimization opportunities through fine-grained usage-based pricing models, but require different optimization strategies focused on function efficiency, memory allocation, and execution patterns rather than traditional infrastructure metrics.
Edge Computing and Distributed Infrastructure Costs
The expansion of edge computing and distributed infrastructure architectures creates new complexities for enterprise cost management as organizations deploy workloads across geographically distributed locations with varying cost structures and performance requirements.
Edge cost management requires sophisticated modeling of data transfer costs, latency requirements, and regional pricing variations to optimize workload placement across distributed infrastructure. These decisions often involve complex tradeoffs between cost, performance, and compliance requirements.
Advanced enterprises implement dynamic workload orchestration systems that automatically optimize placement decisions based on real-time cost and performance metrics across their distributed infrastructure environments.
Case Studies: Fortune 500 Success Stories
Global Manufacturing Company: 42% Multi-Cloud Cost Reduction
A Fortune 100 manufacturing company achieved remarkable results through implementation of a comprehensive multi-cloud cost management program that addressed both technical optimization and organizational change management challenges.
The organization began with annual cloud spending of $180 million across AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, managing 847 applications and serving 125,000 employees globally. Initial assessment revealed significant optimization opportunities including unused resources, oversized instances, and lack of reserved capacity utilization.
Implementation involved establishing a centralized FinOps team, deploying unified cost management platforms, and implementing automated governance policies across all cloud environments. The program achieved $76 million in annual cost savings while improving application performance and developer productivity.
Key success factors included executive sponsorship, comprehensive training programs, and integration with existing enterprise financial systems. The organization continues to achieve ongoing optimization through continuous monitoring and automated optimization processes.
Financial Services Enterprise: SaaS Portfolio Consolidation
A major financial services company transformed its SaaS management approach, reducing costs by 38% while improving user experience and security compliance across its technology portfolio.
The organization discovered 312 SaaS applications in use across the enterprise, compared to 87 applications in their official IT asset inventory. Detailed analysis revealed significant redundancies, underutilized licenses, and security compliance gaps across the application portfolio.
The optimization program involved comprehensive application rationalization, license rightsizing, and vendor consolidation that eliminated 127 redundant applications while improving functionality and user satisfaction. Strategic vendor negotiations achieved additional cost reductions through volume discounts and multi-year commitments.
Results included $12 million in annual cost savings, improved security compliance, and enhanced user productivity through consolidation of overlapping applications and improved integration capabilities.
Implementation Framework for Enterprise Multi-Cloud Cost Management
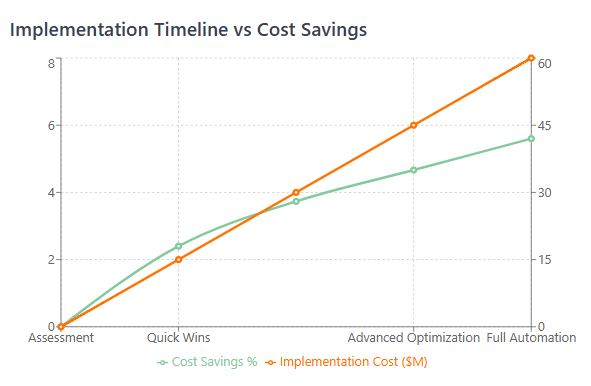
Phase 1: Assessment and Foundation Building (Months 1-3)
Successful enterprise multi-cloud cost management implementations begin with comprehensive assessment of current state architecture, spending patterns, and organizational capabilities. This foundation phase establishes baseline metrics and identifies immediate optimization opportunities while building the organizational capabilities necessary for long-term success.
Initial assessment activities include complete inventory of cloud resources and SaaS applications, analysis of spending patterns and cost drivers, evaluation of existing governance and optimization processes, and identification of key stakeholders and success metrics.
Foundation building involves establishing FinOps team structures, implementing unified cost visibility platforms, developing tagging and cost allocation strategies, and creating initial governance policies and approval workflows.
Phase 2: Quick Wins and Process Implementation (Months 4-6)
The second phase focuses on achieving immediate cost reductions through obvious optimization opportunities while implementing the processes and tools necessary for sustainable cost management.
Quick win activities typically include eliminating unused resources, rightsizing oversized instances, implementing basic reserved capacity strategies, and consolidating redundant SaaS applications. These activities often achieve 15-25% cost reductions within the first six months.
Process implementation involves deploying automated monitoring and alerting systems, establishing regular optimization review cycles, implementing approval workflows for new resources, and training teams on cost optimization best practices.
Phase 3: Advanced Optimization and Automation (Months 7-12)
The final implementation phase focuses on sophisticated optimization strategies and automation capabilities that enable sustainable long-term cost management and continuous improvement.
Advanced optimization activities include implementing predictive analytics and machine learning-driven optimization, developing sophisticated reserved capacity and committed use strategies, optimizing application architectures for cost efficiency, and implementing dynamic resource scaling and optimization.
Automation capabilities include policy-driven cost controls, automated optimization workflows, integration with CI/CD pipelines for cost-aware deployment processes, and continuous monitoring and adjustment of optimization strategies.
Future-Proofing Your Multi-Cloud Cost Strategy
Emerging Technology Considerations
Enterprise organizations must consider the cost implications of emerging technologies including quantum computing, advanced AI platforms, augmented reality applications, and next-generation networking technologies. These technologies will create new cost management challenges and opportunities that require proactive planning and capability development.
Quantum computing platforms are beginning to emerge with unique pricing models based on quantum processing unit consumption rather than traditional compute metrics. Early adopters must develop new cost modeling approaches and optimization strategies for these revolutionary computing platforms.
Advanced AI and machine learning platforms require sophisticated cost management approaches that consider training costs, inference costs, data storage and transfer costs, and specialized hardware requirements. These technologies often involve significant upfront investments with variable ongoing costs based on usage patterns.
Regulatory and Compliance Evolution
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve with new requirements for data privacy, security, and financial reporting that impact multi-cloud cost management strategies. Organizations must ensure their cost management approaches remain compliant with emerging regulatory requirements while maintaining operational efficiency.
Data sovereignty requirements increasingly impact cloud architecture decisions and cost optimization strategies as organizations must balance compliance requirements with cost efficiency and operational flexibility. These considerations often require sophisticated modeling of regional deployment strategies and data management approaches.
Environmental sustainability regulations are beginning to impact cloud cost management as organizations face requirements to track and report carbon emissions associated with their technology infrastructure. Leading cloud providers are developing carbon accounting capabilities that will become integrated with cost management platforms.
Strategic Technology Partnerships
Future-oriented enterprises are developing strategic partnerships with cloud providers, SaaS vendors, and technology innovators that extend beyond traditional vendor relationships. These partnerships enable access to emerging technologies, preferential pricing, and collaborative development opportunities that provide competitive advantages.
Strategic vendor partnerships often involve multi-year commitments, volume discounts, and collaborative innovation programs that require sophisticated financial modeling and risk assessment. These relationships can provide significant cost advantages while enabling early access to breakthrough technologies.
Innovation partnerships with emerging technology companies enable enterprises to participate in the development of next-generation solutions while gaining cost advantages through early adoption and strategic investment opportunities.
Conclusion
Enterprise multi-cloud cost management has evolved from a reactive cost control function into a strategic capability that drives business value, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage. Fortune 500 companies that excel in this discipline consistently achieve 25-40% cost reductions while improving performance and accelerating innovation.
The most successful organizations treat multi-cloud cost management as a comprehensive program that encompasses technology, processes, organizational capabilities, and strategic planning. These programs require executive sponsorship, cross-functional collaboration, and sustained investment in tools, training, and capability development.
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, enterprise multi-cloud cost management will continue to evolve with emerging technologies, changing regulatory requirements, and new business models. Organizations that invest in building sophisticated cost management capabilities today will be well-positioned to capitalize on future opportunities while maintaining operational efficiency and financial discipline.
The key to success lies in viewing multi-cloud cost management not as a cost center, but as a value driver that enables strategic technology investments, accelerated innovation, and sustainable competitive advantage in an increasingly digital business environment. Organizations that embrace this perspective and invest in comprehensive cost management capabilities will thrive in the complex multi-cloud landscape of the future.

