The digital transformation accelerated by the pandemic has fundamentally changed how organizations acquire and deploy software solutions. What began as a necessary shift to support remote work has evolved into a complex web of Software as a Service (SaaS) applications that span across departments, teams, and individual users. This phenomenon, known as SaaS sprawl, has become one of the most pressing challenges facing IT departments and financial teams today.
At the heart of this challenge lies decentralized purchasing—the practice of allowing individual departments, teams, or employees to independently acquire SaaS solutions without centralized oversight. While this approach initially seemed to enhance agility and productivity, it has created a perfect storm of redundant subscriptions, security vulnerabilities, and escalating costs that many organizations struggle to control.
This comprehensive guide examines how decentralized purchasing has contributed to the explosive growth of SaaS sprawl and provides actionable strategies for organizations to regain control over their software ecosystems. From implementing centralized governance policies to leveraging sophisticated SaaS management platforms, we’ll explore the tools and techniques necessary to optimize SaaS spending while maintaining operational efficiency.
What is SaaS Sprawl?
SaaS sprawl refers to the uncontrolled proliferation of Software as a Service applications within an organization. This phenomenon occurs when multiple SaaS solutions are adopted across different departments without centralized oversight, leading to a complex ecosystem of overlapping tools, duplicate functionalities, and fragmented data.
Unlike traditional software deployments that required IT approval and installation, SaaS applications can be purchased and deployed instantly with just a credit card and an email address. This ease of adoption, while beneficial for productivity, has created an environment where organizations often discover they’re paying for dozens or even hundreds of SaaS subscriptions they weren’t aware of.
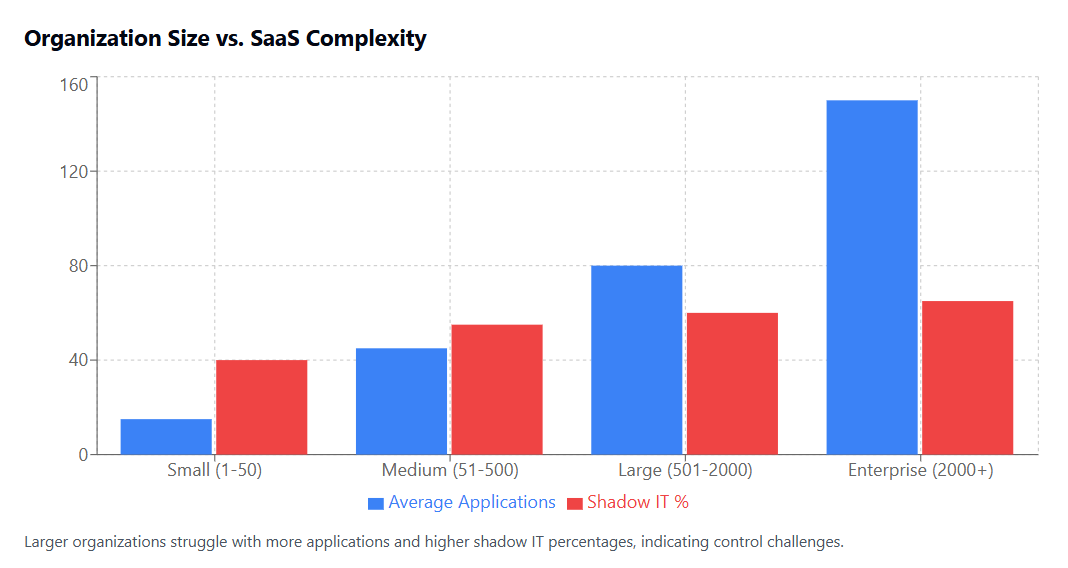
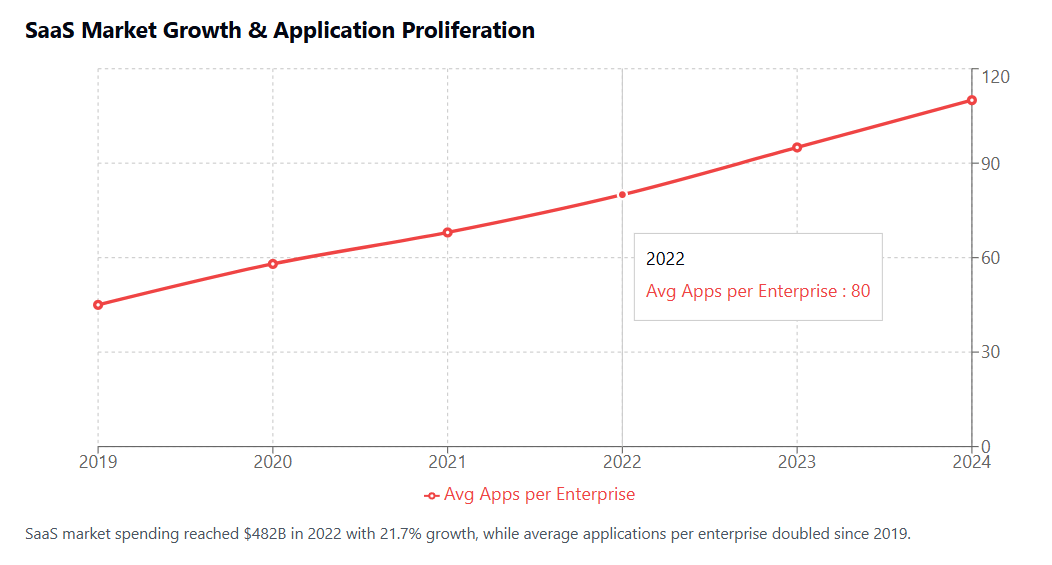
The typical enterprise today uses an average of 80 SaaS applications, according to recent studies. However, many organizations report having little to no visibility into the full scope of their SaaS portfolio. This lack of visibility extends beyond simple inventory management to encompass usage patterns, security compliance, data integration, and cost optimization opportunities.
SaaS sprawl manifests in several ways: duplicate applications serving similar functions across different teams, unused or underutilized licenses consuming budget, shadow IT implementations that bypass security protocols, and integration challenges that create data silos. The cumulative effect is a fragmented technology landscape that increases operational complexity while diminishing the potential return on software investments.
The Rise of Decentralized Purchasing
The shift toward decentralized purchasing didn’t happen overnight. It evolved gradually as organizations sought to become more agile and responsive to changing business needs. Traditional IT procurement processes, characterized by lengthy approval cycles and bureaucratic overhead, became increasingly incompatible with the fast-paced demands of modern business operations.
Several factors contributed to the rise of decentralized purchasing in the SaaS era. The consumerization of enterprise software made business applications as easy to purchase and deploy as consumer apps. Credit card-based pricing models eliminated the need for purchase orders and complex vendor negotiations. Free trials and freemium offerings allowed teams to test solutions before committing to paid subscriptions.
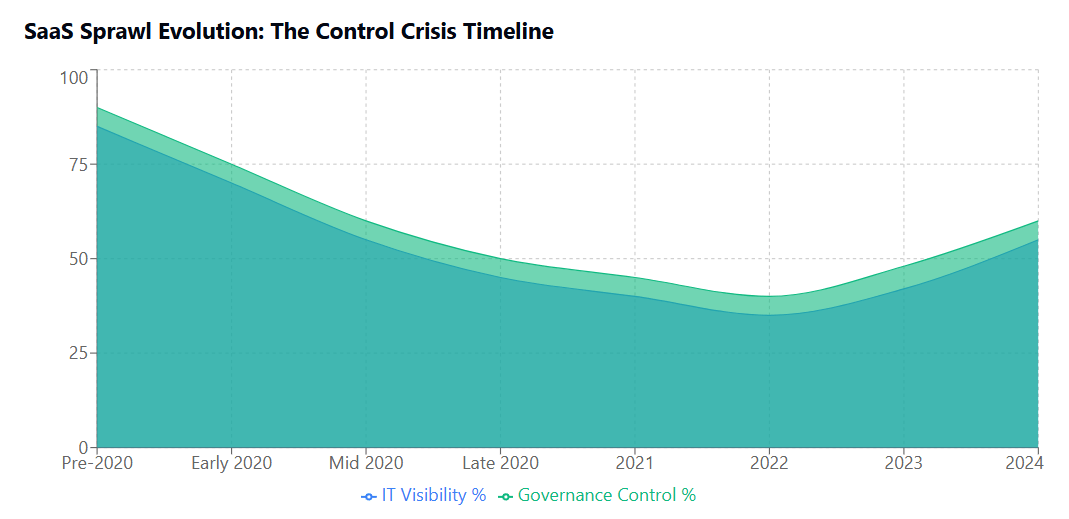
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this trend dramatically. As organizations scrambled to enable remote work, traditional procurement gatekeeping mechanisms were temporarily relaxed or bypassed entirely. Teams needed collaboration tools, project management platforms, and communication solutions immediately, not after weeks of IT evaluation and approval processes.
Cloud computing infrastructure made it possible for any employee to spin up new services without involving IT departments. Self-service marketplaces like the Salesforce AppExchange, Google Workspace Marketplace, and Microsoft AppSource further democratized software procurement by making it easy for end users to discover and install applications directly.
Departmental budgets also played a role in this decentralization. As organizations allocated more technology spending directly to business units, department heads gained the autonomy to make software purchasing decisions based on their specific needs and priorities. This distributed approach to technology investment initially seemed to improve efficiency by reducing bottlenecks and enabling faster innovation.
How Decentralized Purchasing Fueled SaaS Sprawl
Decentralized purchasing created the perfect conditions for SaaS sprawl to flourish. Without centralized oversight, individual teams began acquiring solutions that addressed their immediate needs without considering broader organizational implications or existing capabilities.
The low barrier to entry for SaaS applications encouraged experimentation and rapid adoption. Teams could sign up for new tools during lunch breaks, test solutions over weekends, and begin full implementation without formal approval processes. While this agility initially boosted productivity, it also led to a proliferation of point solutions that often overlapped in functionality.
Different departments frequently ended up purchasing similar tools to solve comparable problems. Marketing teams might adopt one project management platform while engineering teams selected another, despite both solutions offering nearly identical capabilities. Sales teams could implement their own customer communication tools while customer service maintained separate systems for similar purposes.
The subscription model inherent to SaaS applications compounded the sprawl problem. Unlike traditional software purchases that involved significant upfront investments and careful evaluation, SaaS subscriptions often started with low monthly fees that seemed insignificant in isolation. Teams rationalized these “small” expenses without considering their cumulative impact on organizational spending.
Integration challenges further accelerated sprawl as teams discovered that their newly adopted tools didn’t connect well with existing systems. Rather than addressing integration issues or consolidating platforms, organizations often acquired additional middleware solutions or maintained parallel systems, adding layers of complexity to their technology stack.
The auto-renewal nature of SaaS subscriptions meant that once applications were deployed, they tended to persist even when usage declined or needs changed. Unlike traditional software that required active renewal decisions, SaaS applications continued billing automatically, creating a gradually expanding portfolio of subscriptions that often went unnoticed until budget reviews.
The Hidden Costs of Uncontrolled SaaS Adoption
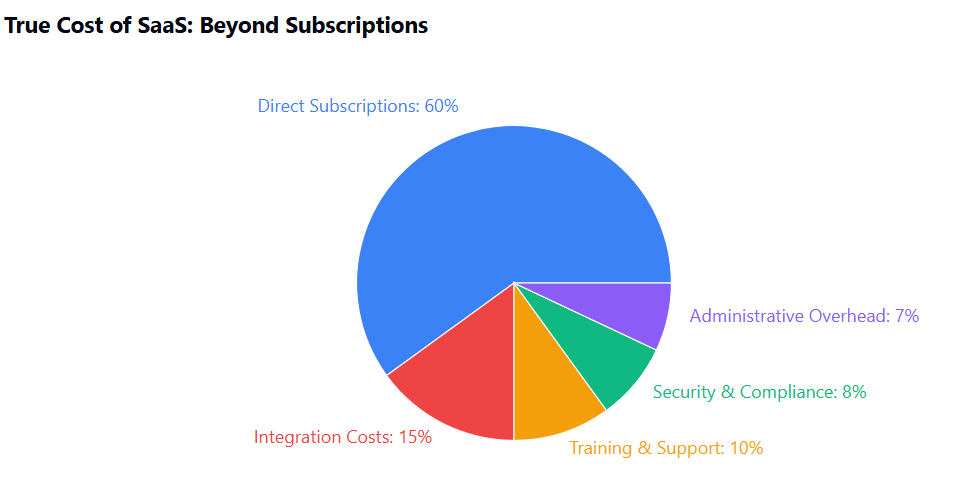
The financial impact of SaaS sprawl extends far beyond the obvious subscription costs. While organizations typically focus on the monthly or annual fees associated with each application, the hidden costs of uncontrolled SaaS adoption can be significantly more substantial.
Duplicate licensing represents one of the most common sources of waste in sprawling SaaS environments. Organizations frequently discover they’re paying for multiple solutions that serve identical functions, sometimes with different teams using competing platforms for the same basic tasks. This redundancy not only increases direct costs but also creates inefficiencies in training, support, and data management.
Underutilized licenses constitute another major source of expense. Many SaaS platforms charge based on the number of user seats, regardless of actual usage levels. Organizations often purchase more licenses than needed or fail to remove licenses for departed employees, resulting in ongoing payments for unused access. Studies suggest that up to 30% of SaaS licenses in typical organizations are underutilized or completely unused.
Integration costs multiply rapidly in sprawling environments. Each new SaaS application potentially requires integration with existing systems, data migration, custom development, and ongoing maintenance. These integration projects often consume significant IT resources and budget, sometimes exceeding the cost of the SaaS subscriptions themselves.
Security and compliance risks translate into both direct and indirect costs. Sprawling SaaS environments create multiple attack vectors and compliance challenges that require additional security tools, monitoring systems, and specialized personnel. Data governance becomes increasingly complex when information is scattered across numerous platforms with varying security standards and access controls.
Training and productivity costs accumulate as employees must learn and maintain proficiency across multiple platforms. Context switching between different applications reduces efficiency, while the cognitive overhead of managing numerous tools can impact overall productivity. Additionally, organizations often need to provide training for each new SaaS application, multiplying education costs.
Administrative overhead grows exponentially with the number of SaaS applications. Each platform requires ongoing management for user provisioning, access controls, billing oversight, vendor relationships, and compliance monitoring. These administrative tasks consume valuable IT and business resources that could be allocated to more strategic initiatives.
Current State of SaaS Sprawl in Organizations
Recent research reveals the staggering scope of SaaS sprawl across organizations of all sizes. The average enterprise now manages subscriptions to over 80 SaaS applications, with some large organizations reporting portfolios exceeding 300 different platforms. However, these numbers likely underestimate the true extent of sprawl, as many organizations lack comprehensive visibility into their complete SaaS ecosystem.
Shadow IT deployments represent a significant portion of untracked SaaS adoption. Studies suggest that IT departments are typically aware of only 40-60% of the SaaS applications actually being used within their organizations. The remaining applications exist in shadow IT environments, purchased and deployed by business units without formal IT involvement or oversight.
Financial impact data demonstrates the substantial costs associated with uncontrolled SaaS adoption. Organizations report that SaaS spending has increased by an average of 15-25% annually over the past three years, with much of this growth attributed to sprawl rather than strategic expansion. Waste levels are equally concerning, with typical organizations identifying 20-40% of their SaaS spending as unnecessary or underutilized when they conduct comprehensive audits.
Industry-specific patterns are emerging in SaaS sprawl trends. Technology companies tend to have the highest number of SaaS applications per employee, averaging over 150 different platforms. Financial services organizations, while more controlled due to regulatory requirements, still report significant sprawl in non-regulated business functions. Healthcare organizations face unique challenges balancing compliance requirements with operational efficiency needs.
Geographic variations also influence sprawl patterns. Organizations with global operations often discover regional teams have independently adopted local solutions that duplicate functionality available in corporate-approved platforms. These geographic duplications create additional complexity in data consolidation, reporting, and governance.
The remote work trend has accelerated SaaS adoption across all sectors. Organizations report that remote work necessitated rapid deployment of collaboration, communication, and productivity tools, often without time for proper evaluation or integration planning. While these deployments supported business continuity during crisis periods, many organizations now struggle to rationalize the resulting sprawl.
Strategies to Reclaim Control Over SaaS Sprawl
Regaining control over SaaS sprawl requires a comprehensive approach that balances operational flexibility with financial discipline and security requirements. Successful organizations implement multi-faceted strategies that address both immediate sprawl challenges and long-term governance needs.
Discovery and Inventory Management
The first step in controlling SaaS sprawl involves gaining complete visibility into existing applications. Organizations must conduct comprehensive discovery exercises that go beyond IT-managed systems to identify shadow IT deployments, departmental purchases, and individual subscriptions that may be expensed or paid through personal accounts.
Modern discovery approaches leverage multiple data sources including network traffic analysis, expense report mining, browser extension monitoring, and credit card transaction analysis. Cloud access security brokers (CASBs) and SaaS management platforms can automatically identify applications being accessed by employees, providing more comprehensive visibility than traditional IT inventory systems.
Financial Analysis and Optimization
Once organizations understand their complete SaaS portfolio, detailed financial analysis becomes possible. This analysis should identify duplicate applications, underutilized licenses, and optimization opportunities. Organizations should calculate total cost of ownership for each application, including subscription fees, integration costs, training expenses, and administrative overhead.
License rightsizing represents one of the most immediate opportunities for cost reduction. Organizations frequently discover they can eliminate 20-30% of their SaaS spending simply by removing unused licenses, downgrading overprovisioned accounts, and consolidating duplicate subscriptions.
Risk Assessment and Prioritization
Not all SaaS applications pose equal risks or offer equal value. Organizations should develop risk assessment frameworks that evaluate each application based on data sensitivity, business criticality, compliance requirements, and security posture. This assessment enables prioritized remediation efforts focused on the highest-impact opportunities.
Applications handling sensitive data or supporting critical business processes require immediate attention and often need to migrate to approved platforms. Lower-risk applications might be grandfathered temporarily while organizations develop long-term consolidation plans.
Implementing Centralized SaaS Governance
Effective SaaS governance requires establishing clear policies, processes, and accountability structures that prevent future sprawl while maintaining organizational agility. Successful governance programs balance control with flexibility, ensuring that legitimate business needs can be met without sacrificing security or cost effectiveness.
Governance Framework Development
Organizations should establish formal SaaS governance frameworks that define roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes for software acquisition. These frameworks typically include procurement policies, security requirements, integration standards, and approval workflows that scale with organizational size and complexity.
Governance frameworks should distinguish between different categories of SaaS applications based on risk levels, business impact, and complexity. Low-risk productivity tools might have streamlined approval processes, while applications handling sensitive data require comprehensive security reviews and formal contracts.
Procurement Standardization
Centralized procurement processes help prevent duplicate purchases and ensure that all SaaS acquisitions meet organizational standards. However, these processes must be designed for speed and efficiency to avoid driving teams toward shadow IT solutions.
Modern procurement approaches often include pre-approved catalogs of SaaS applications that have already been evaluated for security, integration, and cost-effectiveness. Teams can select from these approved options without lengthy review cycles, while requests for non-catalog applications trigger more detailed evaluation processes.
Vendor Management and Contracts
Effective SaaS governance includes comprehensive vendor management practices that optimize contract terms, pricing, and service levels. Organizations should consolidate vendor relationships where possible, negotiating enterprise agreements that provide better pricing and terms than individual departmental contracts.
Regular vendor reviews should assess performance, security posture, and alignment with organizational needs. Organizations should maintain vendor scorecards that track key metrics and inform renewal decisions.
Tools and Technologies for SaaS Management
Managing complex SaaS environments requires sophisticated tools that provide visibility, control, and optimization capabilities. The SaaS management platform market has evolved rapidly to address sprawl challenges, offering solutions that range from simple discovery tools to comprehensive governance platforms.
SaaS Management Platforms
Dedicated SaaS management platforms like Binadox provide comprehensive capabilities for discovering, managing, and optimizing SaaS portfolios. These platforms typically offer automated discovery, spend analysis, usage monitoring, and optimization recommendations that help organizations gain control over sprawling environments.
Key capabilities to evaluate in SaaS management platforms include integration breadth, automated discovery accuracy, financial reporting flexibility, and governance workflow support. Leading platforms can connect to hundreds of SaaS applications, providing detailed usage and spending analytics that inform optimization decisions.
Financial Management Integration
SaaS management tools should integrate with existing financial management systems to provide comprehensive spend visibility and budget control. This integration enables organizations to track SaaS spending alongside other technology investments and implement charge-back models that encourage responsible consumption.
Advanced financial management features include budget alerts, spend forecasting, and automated cost allocation across departments or projects. These capabilities help organizations implement accountability measures that reduce unnecessary spending.
Security and Compliance Tools
Given the security risks associated with SaaS sprawl, management platforms should include security assessment and monitoring capabilities. These tools can identify applications with weak security postures, monitor for compliance violations, and provide alerts for suspicious activities.
Integration with existing security infrastructure, including identity management systems and security information and event management (SIEM) platforms, enables comprehensive security monitoring across the entire SaaS portfolio.
Best Practices for Sustainable SaaS Control
Maintaining control over SaaS environments requires ongoing attention and continuous improvement processes. Organizations that successfully manage SaaS sprawl implement systematic approaches that evolve with changing business needs and technology landscapes.
Regular Audits and Reviews
Quarterly or semi-annual SaaS audits help organizations maintain visibility and control over their portfolios. These audits should assess usage patterns, identify optimization opportunities, and ensure compliance with governance policies. Regular reviews also provide opportunities to evaluate new applications and retire obsolete solutions.
Audit processes should be automated where possible, using management platforms to generate reports and identify anomalies that require human attention. Automated alerting can notify administrators of unusual spending patterns, new application deployments, or compliance violations.
User Education and Training
Employee education plays a crucial role in preventing SaaS sprawl. Organizations should provide training on approved applications, procurement processes, and security requirements. This education helps employees understand why governance policies exist and how to navigate them effectively.
Self-service resources, including application catalogs and procurement guidelines, can reduce the friction associated with acquiring approved solutions. Clear communication about available alternatives can prevent teams from independently seeking external solutions.
Continuous Optimization
SaaS optimization is not a one-time activity but requires ongoing attention to changing business needs, usage patterns, and market conditions. Organizations should regularly evaluate their portfolios for consolidation opportunities, negotiate better terms with vendors, and retire applications that no longer provide value.
Optimization efforts should be data-driven, using analytics from management platforms to identify specific improvement opportunities. Organizations should track key metrics including cost per user, utilization rates, and business value delivered to inform optimization decisions.
How Binadox Helps Organizations Manage SaaS Sprawl
Binadox addresses the complex challenges of SaaS sprawl through a comprehensive platform that provides visibility, control, and optimization capabilities for organizations of all sizes. The platform’s approach to SaaS management combines automated discovery with intelligent analytics to help organizations regain control over their software portfolios.
Comprehensive Discovery and Inventory
Binadox automatically discovers SaaS applications across the organization, including shadow IT deployments that might not be visible through traditional IT management systems. The platform monitors network traffic, integrates with financial systems, and analyzes user behavior to build complete inventories of SaaS usage.
This discovery capability extends beyond simple application identification to include detailed usage analytics, license allocation, and cost analysis. Organizations gain visibility into which applications are actively used, who is using them, and how much value they’re delivering relative to their cost.
Financial Optimization and Control
The platform provides sophisticated financial management capabilities that help organizations optimize their SaaS spending. Binadox tracks costs across all applications, identifies duplicate or underutilized licenses, and provides recommendations for consolidation and rightsizing.
Automated renewal management ensures that organizations don’t miss important contract dates or auto-renew applications that are no longer needed. The platform can alert administrators to upcoming renewals and provide usage data to inform renewal decisions.
Security and Compliance Monitoring
Binadox includes security assessment capabilities that evaluate the security posture of SaaS applications and identify potential risks. The platform can monitor for compliance violations, track data access patterns, and provide alerts for suspicious activities.
Integration with existing security infrastructure enables comprehensive monitoring across the entire SaaS portfolio, helping organizations maintain security standards while supporting business agility.
Governance and Policy Enforcement
The platform supports governance workflows that enforce organizational policies while maintaining operational flexibility. Binadox can implement approval processes, spending limits, and security requirements that prevent unauthorized deployments while enabling legitimate business needs.
Reporting and analytics capabilities provide leadership with visibility into SaaS spending patterns, usage trends, and optimization progress. These insights support strategic decision-making and help organizations continuously improve their SaaS management practices.
Conclusion
The explosion of SaaS sprawl driven by decentralized purchasing represents one of the most significant challenges facing modern organizations. While the flexibility and agility enabled by direct SaaS procurement initially seemed beneficial, the long-term costs and complexity have proven substantial. Organizations now face the dual challenge of optimizing existing sprawling environments while implementing governance structures that prevent future uncontrolled growth.
Successfully reclaiming control over SaaS sprawl requires a comprehensive approach that combines technology solutions with process improvements and organizational change management. Organizations must invest in discovery and management tools while simultaneously implementing governance frameworks that balance control with business agility.
The most successful organizations recognize that SaaS management is not a one-time project but an ongoing capability that requires dedicated resources and continuous attention. By implementing proper governance, leveraging management platforms like Binadox, and maintaining focus on optimization opportunities, organizations can harness the benefits of SaaS while avoiding the pitfalls of uncontrolled sprawl.
As the SaaS ecosystem continues to evolve and expand, organizations that establish strong management foundations now will be better positioned to adapt to future changes while maintaining cost effectiveness and operational efficiency. The investment in SaaS control and governance pays dividends through reduced costs, improved security, and enhanced organizational agility that supports long-term business success.

