
The global shift to remote work has fundamentally transformed organizational cloud spending patterns. What began as an emergency pandemic response has evolved into permanent business operations, creating unprecedented demand for cloud-based solutions.
Organizations have moved from hybrid on-premises environments to distributed cloud-first approaches. This shift hasn’t just increased spending—it has completely restructured technology investments, resource allocation, and optimization strategies. Traditional centralized IT infrastructure has given way to distributed systems requiring new frameworks for cloud cost optimization and operational efficiency.
Key Areas Where Remote Work Has Changed Cloud Spending
Collaboration and Communication Tools
Remote work has driven explosive growth in collaboration platform spending. Organizations shifted from in-person meetings to heavy investments in video conferencing, document collaboration, and team communication tools.
Video conferencing platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet experienced unprecedented usage spikes, requiring immediate upgrades from basic to enterprise subscriptions. Costs extend beyond subscriptions to include bandwidth requirements, meeting storage, and enhanced security features.
Document collaboration tools such as Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Slack saw similar adoption. Organizations needed extensive cloud storage, real-time editing capabilities, and comprehensive project management solutions almost overnight.
Cloud Infrastructure Scaling
Remote work created new infrastructure demands beyond traditional applications:
- Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI): Companies invested heavily in cloud-based virtual desktops for secure remote access, representing a significant departure from traditional desktop management with substantial compute and storage costs.
- Network Solutions: Secure connections for remote workers drove investments in cloud-based VPN solutions, SD-WAN, and networking technologies previously managed through on-premises hardware.
- Application Hosting: Applications once hosted locally now require cloud hosting for remote accessibility, increasing costs for compute resources, data transfer, and performance optimization.
The SaaS Explosion in Remote Work Environments
Remote work has created unprecedented “SaaS sprawl”—rapid, often uncontrolled adoption of software-as-a-service applications across organizations.
Productivity and Collaboration SaaS
Remote work necessitated investments in numerous previously unnecessary SaaS applications:
- Project Management: Platforms like Asana, Trello, Monday.com, and Notion became essential for coordinating distributed teams
- Time Tracking: Tools for monitoring remote productivity and managing time across time zones
- Digital Collaboration: Applications like Miro, Mural, and Conceptboard for virtual brainstorming sessions
- Enhanced Storage: Enterprise-grade cloud storage with security and compliance features
Industry-Specific Applications
Different sectors saw unique SaaS adoption patterns:
- Healthcare: Telemedicine platforms, remote patient monitoring, and cloud-based practice management systems experienced massive growth.
- Education: Learning management systems, virtual classrooms, and student engagement tools became critical infrastructure.
- Financial Services: Enhanced cybersecurity tools, remote trading platform access, and cloud-based compliance monitoring drove significant spending increases.
Hidden Costs of SaaS Proliferation
While individual subscriptions seem cost-effective, aggregate adoption creates new challenges:
- Subscription Overlap: Organizations often pay for multiple tools providing similar functionality, creating redundant spending.
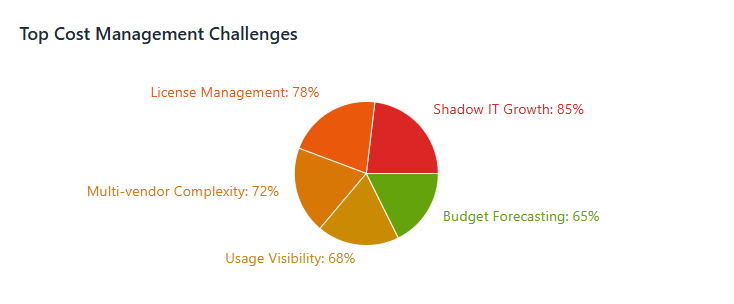
- License Management: Managing licenses across numerous platforms becomes complex, resulting in unused or underutilized subscriptions.
- Integration Expenses: Connecting multiple SaaS applications often requires additional middleware or integration platform investments.
Infrastructure Changes and Cloud Resource Demands
Remote work has fundamentally altered cloud infrastructure requirements, creating new cost patterns and resource demands.
Compute Resource Scaling
Remote work created unique scaling challenges for cloud compute resources. Unlike predictable office environments, distributed workforces create variable and geographically dispersed resource needs.
Organizations provision cloud resources across multiple regions for optimal remote worker performance. This geographic distribution increases costs through data transfer fees and redundant infrastructure requirements.
Resource utilization patterns changed from traditional 9-to-5 usage to distributed patterns across time zones, requiring higher baseline resource levels to accommodate varying work schedules.
Storage and Data Management
Remote work dramatically increased data storage requirements:
Distributed Data Creation: Remote workers create and store data across various locations, increasing needs for centralized cloud storage and synchronization services.
Backup and Recovery: Distributed work complicated backup strategies, requiring more comprehensive and expensive cloud-based solutions.
Data Transfer Costs: Increased data movement between remote locations and cloud services resulted in higher transfer costs.
Network and Connectivity Infrastructure
Supporting remote workforces required substantial networking investments:
Secure Access: Traditional VPN solutions were supplemented with cloud-based SASE solutions and zero-trust network access platforms.
Content Delivery: Organizations increased CDN and edge computing usage to ensure optimal global performance for remote workers.
Performance Optimization: Cloud-based network optimization tools became necessary for adequate distributed team performance.
Security and Compliance Cost Implications
Remote work security implications created entirely new cloud spending categories many organizations hadn’t previously budgeted for.
Enhanced Security Tooling
Remote work necessitated significant cloud-based security investments:
Endpoint Security: With employees using various devices from different locations, organizations invested heavily in cloud-based endpoint detection and response solutions.
Identity Management: Managing user access across distributed environments drove adoption of sophisticated cloud-based identity and access management platforms.
Security Monitoring: Monitoring security events across distributed environments increased demand for cloud-based SIEM solutions.
Compliance and Governance
Remote work complicated compliance requirements, particularly for regulated industries:
Data Loss Prevention: Cloud-based DLP solutions became essential for monitoring sensitive data across distributed environments.
Compliance Monitoring: Automated compliance tools hosted in the cloud became necessary for regulatory adherence across distributed teams.
Audit Tools: Enhanced logging and reporting capabilities for demonstrating compliance drove additional cloud service investments.
Current State of Remote Work Cloud Spending
Recent industry reports provide insight into the current remote work cloud spending landscape and trajectory.
Market Growth and Spending Patterns
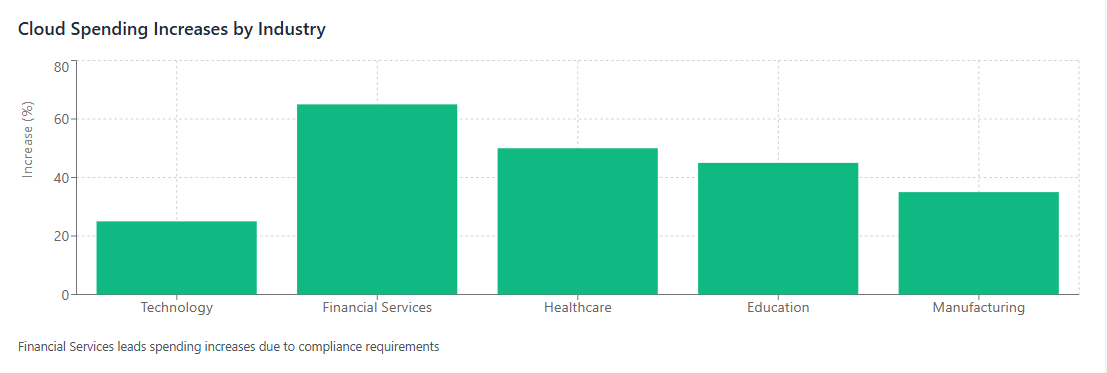
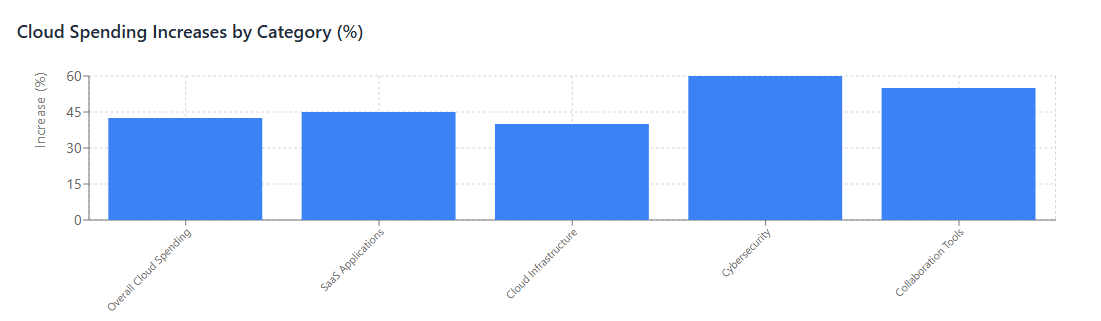
Organizations have increased cloud spending by 35-50% to support remote work initiatives, with some sectors seeing higher increases.
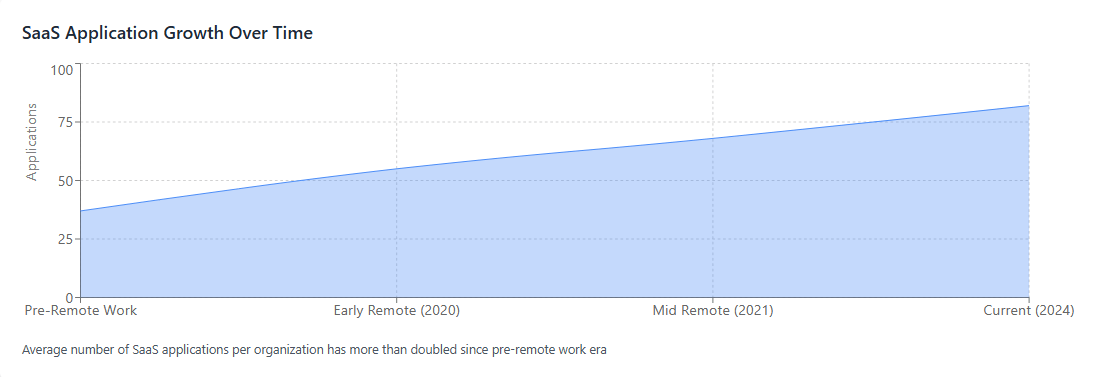
SaaS Growth: The average organization now uses 80+ SaaS applications, compared to 35-40 before remote work adoption—more than doubling usage in just a few years.
Infrastructure Spending: Cloud infrastructure spending for remote work support grew by an average of 40% across industries, particularly in compute, storage, and networking services.
Security Investment: Cybersecurity cloud spending increased by 60% as organizations invested in tools to secure distributed workforces.
Industry Variations
Different industries experienced varying cloud spending impacts:
Technology Companies: Saw smaller relative increases as they were already cloud-native, but experienced growth in collaboration and productivity tools.
Financial Services: Experienced the largest increases due to strict security and compliance requirements for remote access.
Healthcare: Saw dramatic increases in telemedicine platforms and cloud-based patient management systems.
Education: Invested heavily in learning management systems and virtual classroom technologies.
Challenges in Managing Remote Work Cloud Costs
Remote work has created new cloud cost management challenges requiring different approaches than traditional IT cost management.
Visibility and Tracking
Organizations face significant challenges gaining visibility into distributed cloud spending:
Shadow IT Growth: Remote work accelerated shadow IT adoption as teams independently signed up for services without central IT approval.
Multi-vendor Complexity: Organizations now deal with hundreds of cloud service providers and SaaS vendors, making centralized cost tracking extremely challenging.
Usage Pattern Changes: Traditional cost models based on predictable usage are less effective in remote environments with highly variable, distributed usage.
Budget Planning and Forecasting
Remote work made cloud cost forecasting significantly more complex:
Variable Demand: Office-based computing predictability was replaced by variable demand patterns harder to forecast.
Rapid Scaling: The need to quickly scale based on changing remote work requirements makes budget planning challenging.
New Cost Categories: Organizations must budget for entirely new cloud service categories that weren’t previously necessary.
Governance and Control
Maintaining governance over cloud spending in distributed environments presents unique challenges:
Distributed Decisions: Remote work often requires faster tool adoption decisions, sometimes bypassing traditional procurement processes.
Cost Allocation: Attributing costs to specific departments becomes complex when teams use shared collaboration platforms.
Policy Enforcement: Enforcing spending policies is more challenging when teams work independently and are distributed.
Best Practices for Optimizing Remote Work Cloud Spending
Successfully managing cloud costs in remote work environments requires new best practices and strategies designed for distributed operations.
Implementing Centralized SaaS Management
Effective SaaS spend management begins with gaining centralized visibility into all cloud subscriptions and services.
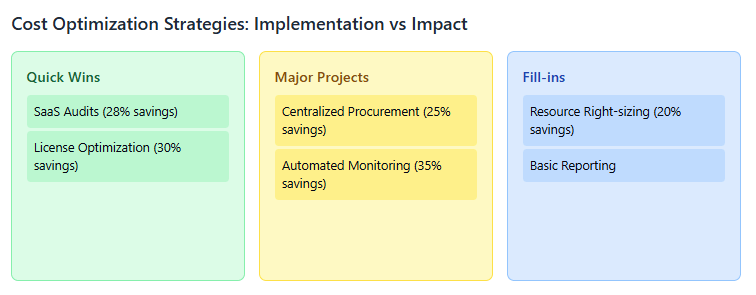
Centralized Procurement: Establish clear processes for evaluating and approving new SaaS applications while maintaining speed for remote work requirements.
Regular Audits: Conduct frequent SaaS subscription audits to identify unused licenses, redundant applications, and optimization opportunities.
License Optimization: Implement processes to regularly review user access and usage patterns to ensure organizations aren’t paying for unused licenses.
Cloud Resource Optimization
Optimizing cloud infrastructure for remote work requires different approaches:
Right-sizing Resources: Regularly review cloud resource allocations to match actual usage patterns that may have changed significantly with remote work.
Geographic Optimization: Optimize resource placement based on actual user locations rather than assuming centralized usage.
Auto-scaling Configuration: Implement intelligent auto-scaling policies accounting for different remote work usage patterns.
Cost Allocation and Chargeback
Implementing effective cost allocation strategies helps organizations understand spending patterns:
Tagging Strategies: Use comprehensive tagging to track costs by department, team, or project, even when using shared platforms.
Usage-based Allocation: Develop models for allocating shared service costs based on actual usage rather than headcount-based allocation.
Transparency and Reporting: Provide regular, detailed reports to department heads about their cloud spending to encourage responsible usage.
Tools and Strategies for Cost Management
Effective remote work cloud cost management requires specialized tools and strategies designed for distributed, multi-vendor environments.
Cloud Cost Management Platforms
Organizations need sophisticated tools to manage remote work cloud spending complexity:
Multi-cloud Management: Platforms that track and optimize costs across multiple cloud providers and SaaS vendors are essential for comprehensive cost management.
Real-time Monitoring: Tools providing real-time cloud spending visibility help organizations quickly identify and address cost spikes or unusual usage patterns.
Automated Optimization: Platforms that automatically implement cost optimization recommendations reduce manual effort required for efficient cloud spending.
SaaS Management Solutions
Specialized SaaS management platforms have become essential for organizations supporting remote workforces:
Application Discovery: Tools that automatically discover and catalog all SaaS applications in use, including shadow IT adoptions.
Usage Analytics: Platforms providing detailed analytics about actual SaaS application usage, helping identify optimization opportunities.
Renewal Management: Automated tracking of renewal dates and contract terms to prevent unexpected charges and enable proactive negotiation.
Binadox exemplifies comprehensive cloud cost management platforms organizations need to effectively manage remote work cloud spending. Such platforms provide unified visibility into both traditional cloud infrastructure costs and SaaS application spending, enabling organizations to optimize their entire cloud portfolio from a single interface.
Financial Management Integration
Integrating cloud cost management with broader financial processes is crucial:
Budget Integration: Connecting cloud cost management tools with existing budgeting systems provides better organizational oversight.
Invoice Processing: Automated cloud service invoice processing reduces administrative overhead and improves cost tracking accuracy.
Financial Reporting: Integration with financial systems ensures cloud costs are properly reflected in departmental and organizational statements.
Future Trends and Predictions
The intersection of remote work and cloud spending continues evolving, with several key trends shaping the future landscape.
Hybrid Work Model Optimization
As organizations settle into permanent hybrid work models, cloud spending patterns become more sophisticated:
Dynamic Resource Allocation: Organizations are developing sophisticated models for dynamically allocating cloud resources based on actual remote vs. in-office work patterns.
Location-based Optimization: Cloud resource placement strategies are becoming more location-aware, accounting for where employees actually work.
Flexible Licensing: Software vendors are developing more flexible licensing models accounting for variable hybrid work environments.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly applied to remote work cloud cost management:
Predictive Cost Management: AI-powered tools predict cloud spending patterns based on work patterns, seasonal variations, and business cycles.
Automated Optimization: Machine learning algorithms are becoming more sophisticated at automatically optimizing cloud resource allocation and SaaS license management.
Anomaly Detection: AI-powered anomaly detection is more effective at identifying unusual spending patterns or potential security incidents.
Edge Computing and Distributed Infrastructure
Edge computing growth creates new considerations for remote work cloud spending:
Edge Resource Management: As computing moves to edge locations closer to remote workers, organizations need new strategies for managing distributed infrastructure costs.
Bandwidth Optimization: Edge computing solutions reduce bandwidth costs by processing data closer to where it’s consumed.
Hybrid Models: New architectures combining edge computing with traditional cloud services create more complex but potentially cost-effective remote work solutions.
Conclusion
The shift to remote work has fundamentally transformed organizational cloud spending beyond simple collaboration tool subscription increases. This transformation created new cost categories, changed usage patterns, and introduced complexity requiring new approaches to cost management and optimization.
Organizations successfully navigating this landscape share common characteristics: they’ve invested in comprehensive visibility tools, established governance frameworks for distributed operations, and developed optimization strategies accounting for remote work challenges.
Success lies in recognizing that remote work cloud cost management isn’t simply an extension of traditional IT cost management—it requires new tools, processes, and thinking about technology spending. Effective cloud management strategies must account for distributed remote work nature, SaaS application proliferation, and needs for more agile cost optimization.
Looking forward, organizations developing sophisticated remote work cloud cost management capabilities will be better positioned to support flexible work arrangements while maintaining financial efficiency. The most successful organizations will view cloud cost optimization not as a constraint on remote work capabilities, but as an enabler providing better tools and experiences for distributed workforces while maintaining financial sustainability.
The remote work revolution has permanently changed how organizations think about technology infrastructure and spending. By adopting best practices for cloud cost optimization, implementing comprehensive SaaS management processes, and leveraging specialized tools for multi-vendor cost tracking, organizations can successfully navigate this new landscape and optimize their cloud investments for long-term success.

