
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) fundamentally reshape how organizations approach their technology infrastructure, particularly their Software as a Service (SaaS) portfolios. As companies combine forces, they often discover overlapping subscriptions, redundant licenses, and fragmented SaaS spend management practices that can significantly impact their bottom line. Understanding how to navigate these complexities while optimizing SaaS costs becomes crucial for successful post-merger integration.
The modern enterprise landscape has witnessed unprecedented M&A activity, with organizations constantly seeking growth through strategic acquisitions. However, the technology integration aspect, specifically SaaS consolidation, often receives insufficient attention during the due diligence process. This oversight can lead to substantial financial inefficiencies and operational challenges that persist long after the merger completion.
The Current State of Enterprise SaaS Portfolios
Today’s enterprises typically manage an average of 130 SaaS applications across their organization, with some large corporations utilizing over 300 different SaaS solutions. This proliferation of SaaS tools creates a complex ecosystem that becomes exponentially more challenging to manage when two or more organizations merge. Each company brings its own set of subscriptions, licensing agreements, and usage patterns that must be reconciled and optimized.
The complexity intensifies when considering that most organizations lack comprehensive visibility into their complete SaaS portfolio. Shadow IT practices, where departments independently procure SaaS solutions without IT oversight, contribute to this challenge. During M&A activities, discovering these hidden subscriptions becomes critical for accurate cost assessment and effective consolidation planning.
Furthermore, the subscription-based nature of SaaS creates ongoing financial commitments that extend beyond the merger timeline. Unlike traditional software purchases, SaaS subscriptions represent recurring expenses that require careful evaluation and potential renegotiation during the integration process.
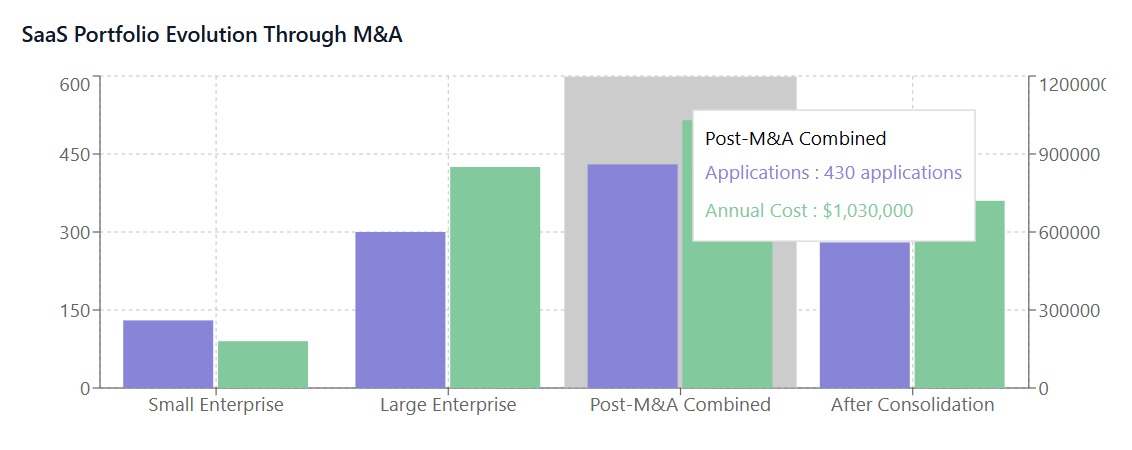
M&A Impact on SaaS Spend Management
When organizations merge, their SaaS spend management strategies must evolve to accommodate new realities. The immediate impact typically manifests in several key areas that require strategic attention and careful planning.
Subscription Overlap and Redundancy
The most obvious challenge emerges from subscription overlap, where merged entities maintain multiple licenses for identical or similar SaaS solutions. For example, if Company A uses Slack for communication while Company B relies on Microsoft Teams, the merged organization must decide which platform to standardize on, potentially eliminating unnecessary subscriptions worth thousands of dollars annually.
This redundancy extends beyond obvious duplications to include functional overlap between different applications. A comprehensive audit often reveals that seemingly different SaaS tools provide similar capabilities, presenting opportunities for SaaS cost optimization through strategic consolidation.
Licensing Agreement Complications
M&A activities frequently complicate existing licensing agreements, as most SaaS vendors structure their contracts based on specific organizational parameters such as employee count, revenue, or usage metrics. When these parameters change due to merger activity, organizations may find themselves either overpaying for unused capacity or requiring additional licenses to accommodate the expanded user base.
Enterprise licensing agreements often include specific terms regarding organizational changes, acquisitions, and user transfers. Understanding these contractual nuances becomes essential for avoiding unexpected costs or compliance issues during the integration process.
Procurement Process Integration
Merged organizations must reconcile different procurement processes, approval workflows, and vendor relationships. Each company typically has established relationships with specific SaaS vendors, negotiated pricing structures, and internal processes for evaluating and purchasing new software solutions.
The integration of these diverse procurement approaches requires careful consideration of existing vendor relationships, contract terms, and organizational preferences. This process often presents opportunities to leverage increased buying power for better pricing negotiations while standardizing on more efficient procurement procedures.
Consolidation Strategies and Challenges
Successful SaaS consolidation during M&A requires a systematic approach that balances cost savings with operational efficiency. Organizations must develop comprehensive strategies that address both immediate integration needs and long-term optimization goals.
Assessment and Inventory
The first step involves conducting a thorough assessment of both organizations’ SaaS portfolios. This inventory process should catalog all applications, associated costs, user counts, contract terms, and renewal dates. Many organizations are surprised to discover the true extent of their SaaS usage during this assessment phase.
Effective inventory management requires collaboration between IT departments, finance teams, and business units from both organizations. Each stakeholder group provides unique insights into application usage, business criticality, and cost considerations that inform consolidation decisions.
Advanced SaaS management platforms can significantly streamline this assessment process by automatically discovering applications, tracking usage patterns, and providing comprehensive spend analytics across the merged organization.
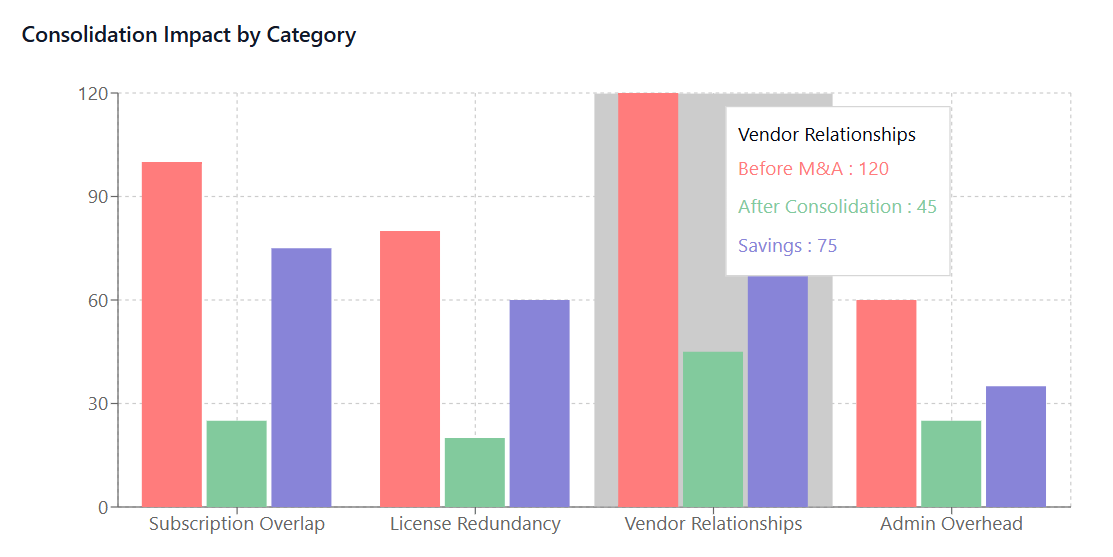
Prioritization Framework
Not all SaaS applications warrant immediate consolidation attention. Organizations need a structured framework for prioritizing consolidation efforts based on factors such as cost impact, user adoption, business criticality, and integration complexity.
High-impact, low-complexity consolidations should typically receive immediate attention, while mission-critical applications with complex integrations may require longer-term planning and gradual migration strategies. This prioritized approach ensures that consolidation efforts deliver maximum value while minimizing operational disruption.
Change Management Considerations
SaaS consolidation inevitably involves change for end users who must adapt to new applications or modified workflows. Effective change management becomes crucial for maintaining productivity and user satisfaction during the transition period.
Organizations should develop comprehensive training programs, communication strategies, and support resources to facilitate smooth transitions. User feedback and adoption metrics provide valuable insights for refining consolidation approaches and identifying potential issues before they impact business operations.
Financial Optimization Opportunities
M&A activities create unique opportunities for financial optimization that extend beyond simple subscription elimination. Organizations can leverage their increased scale and negotiating power to achieve better pricing, terms, and service levels across their consolidated SaaS portfolio.
Volume Discounting and Enterprise Agreements
Merged organizations often qualify for enterprise pricing tiers and volume discounts that were previously unavailable to the individual companies. SaaS vendors typically offer significant price reductions for larger deployments, making consolidation financially attractive even when maintaining multiple solutions temporarily.
These negotiations should consider not only immediate cost savings but also long-term strategic relationships with key vendors. Establishing preferred vendor relationships can provide ongoing benefits through priority support, early access to new features, and favorable terms for future expansions.
Contract Restructuring
M&A activities provide natural opportunities to renegotiate existing contracts and restructure agreements to better align with the merged organization’s needs. This process may involve combining separate contracts, adjusting user counts, modifying service levels, or updating payment terms.
Contract restructuring conversations should address future growth plans, integration timelines, and potential further consolidation activities. Forward-thinking agreements can provide flexibility for ongoing optimization efforts while securing favorable terms for the combined organization.
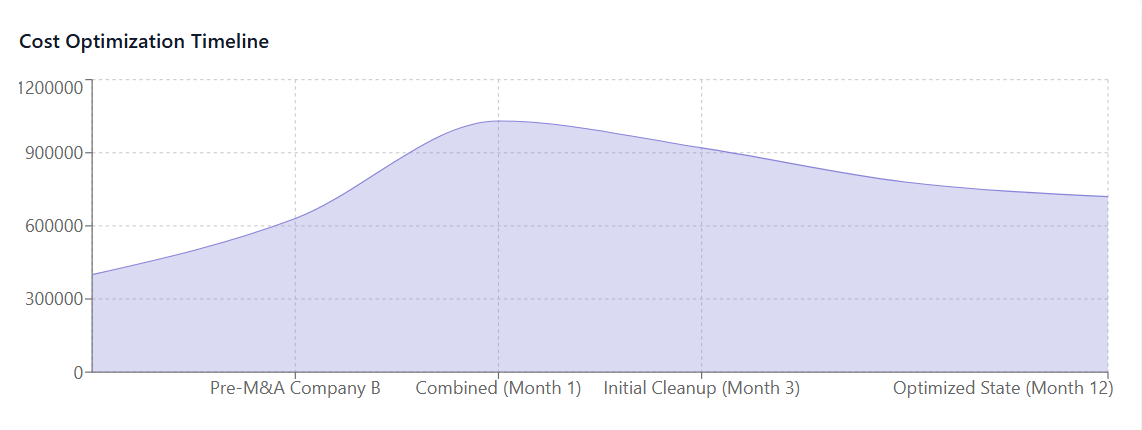
Vendor Relationship Optimization
Consolidating vendor relationships can reduce administrative overhead while improving service quality through simplified support channels and clearer accountability structures. Rather than maintaining separate relationships with dozens of vendors, organizations can focus on building stronger partnerships with a smaller number of strategic providers.
This optimization extends to payment processes, where consolidating multiple subscriptions under unified billing arrangements can reduce administrative complexity and improve cash flow management.
Governance and Compliance Integration
Post-merger SaaS governance requires integrating different organizational cultures, policies, and compliance requirements into a unified framework that supports both operational efficiency and regulatory adherence.
Policy Harmonization
Each organization typically brings its own set of policies regarding SaaS procurement, usage, and management. Harmonizing these policies requires careful consideration of regulatory requirements, security standards, and operational preferences from both entities.
The resulting unified policies should address approval processes, security requirements, data handling procedures, and vendor evaluation criteria. These policies must be comprehensive enough to ensure compliance while remaining practical for day-to-day operations.
Security and Compliance Alignment
SaaS consolidation often involves migrating data between applications and potentially exposing sensitive information to new systems or vendors. Organizations must ensure that consolidated solutions meet the highest security and compliance standards required across all business units and jurisdictions.
This alignment process should include thorough security assessments of retained applications, data migration planning, and compliance verification for all consolidated solutions. Regular audits and monitoring help maintain security standards throughout the integration process.
Access Control and Identity Management
Merging organizations typically operate separate identity management systems and access control frameworks. Consolidating these systems while maintaining appropriate security controls requires careful planning and execution.
Single sign-on (SSO) implementations can significantly simplify access management across consolidated SaaS portfolios while improving user experience and security posture. However, these implementations require coordination with existing identity providers and may necessitate application modifications or vendor negotiations.
Technology Integration Challenges
The technical aspects of SaaS consolidation often prove more complex than initially anticipated, particularly when dealing with data migration, integration requirements, and system dependencies.
Data Migration and Synchronization
Moving data between SaaS applications requires careful planning to ensure data integrity, minimize downtime, and maintain business continuity. Different applications may use incompatible data formats, have varying export/import capabilities, or include proprietary data structures that complicate migration efforts.
Organizations should develop comprehensive data migration strategies that include backup procedures, validation processes, and rollback plans. Testing migration procedures with non-critical data helps identify potential issues before full-scale implementation.
Integration Architecture
Many SaaS applications integrate with other systems through APIs, webhooks, or third-party integration platforms. Consolidation efforts must account for these dependencies and potentially rebuild integrations when switching between applications.
Mapping existing integrations and their business impact helps prioritize consolidation activities while ensuring that critical business processes remain functional throughout the transition period. Some organizations may need to maintain parallel systems temporarily while rebuilding essential integrations.
Performance and Reliability Considerations
Consolidated SaaS solutions must meet or exceed the performance and reliability standards of the applications they replace. Organizations should evaluate capacity requirements, performance benchmarks, and service level agreements before finalizing consolidation decisions.
Load testing and performance monitoring become particularly important when migrating from multiple smaller applications to fewer, larger solutions that must handle increased user loads and data volumes.
Cost Management Best Practices
Effective cost management during SaaS consolidation requires ongoing attention to spending patterns, usage optimization, and vendor relationships. Organizations should implement systematic approaches to maintain cost discipline throughout the integration process.
Spend Visibility and Analytics
Comprehensive spend visibility becomes crucial for managing costs across a consolidated SaaS portfolio. Organizations need real-time insights into subscription costs, usage patterns, and optimization opportunities to make informed decisions about their software investments.
Advanced analytics can identify underutilized subscriptions, predict future capacity needs, and highlight opportunities for further consolidation. These insights support data-driven decision-making and help justify consolidation investments through quantifiable cost savings.
Budget Planning and Allocation
Post-merger budget planning must account for one-time consolidation costs while projecting ongoing savings from optimized subscriptions. Organizations should develop comprehensive financial models that include migration costs, training expenses, and potential productivity impacts during transition periods.
Budget allocation strategies should consider both centralized IT costs and departmental software expenses, ensuring that cost savings are appropriately distributed across the organization while maintaining accountability for software spending.
Renewal Management
Consolidated organizations often face complex renewal schedules inherited from multiple entities. Effective renewal management requires coordinating dozens or hundreds of subscription renewals while optimizing terms and identifying consolidation opportunities.
Automated renewal tracking and early notification systems help prevent unexpected renewals while providing sufficient lead time for renegotiation or consolidation activities. Regular renewal reviews should evaluate continued business need, usage patterns, and alternative solutions.
Emerging Trends and Future Considerations
The SaaS consolidation landscape continues evolving as new technologies, vendor strategies, and organizational approaches emerge. Understanding these trends helps organizations prepare for future consolidation challenges and opportunities.
AI-Powered Optimization
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies increasingly support SaaS portfolio optimization by analyzing usage patterns, predicting future needs, and identifying consolidation opportunities. These tools can process vast amounts of data to provide insights that would be impossible to achieve through manual analysis.
AI-powered recommendations can help organizations optimize their SaaS portfolios continuously rather than only during major organizational changes like M&A activities. This ongoing optimization approach helps maintain cost discipline and operational efficiency over time.
Vendor Consolidation Trends
SaaS vendors themselves are consolidating through acquisitions and platform expansions, creating opportunities for customers to reduce vendor relationships while maintaining functionality. Organizations should monitor vendor roadmaps and acquisition activities to identify consolidation opportunities.
Platform approaches that combine multiple previously separate solutions can significantly simplify vendor management while potentially reducing costs through bundled pricing structures.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
As organizations adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies, SaaS consolidation must consider integration with cloud infrastructure and platform services. These considerations may influence application selection and consolidation priorities based on cloud provider relationships and integration capabilities.
Implementation Roadmap
Successful SaaS consolidation requires a structured implementation approach that balances speed with thoroughness while minimizing operational disruption.
Phase 1: Discovery and Assessment
The initial phase focuses on comprehensive discovery and assessment of existing SaaS portfolios across both organizations. This phase should establish baseline metrics, identify immediate consolidation opportunities, and develop preliminary cost-benefit analyses.
Key activities include application inventory, spend analysis, contract review, and stakeholder interviews to understand business requirements and constraints.
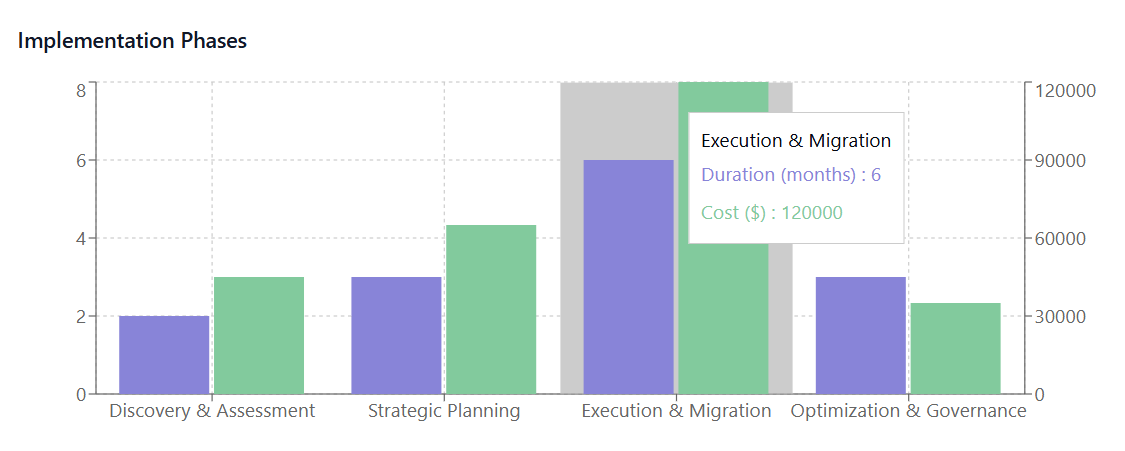
Phase 2: Strategic Planning
Strategic planning involves developing comprehensive consolidation strategies based on assessment findings. This phase should prioritize consolidation activities, establish implementation timelines, and secure necessary resources and approvals.
Strategic planning should also address change management requirements, training needs, and communication strategies to ensure successful adoption of consolidated solutions.
Phase 3: Execution and Migration
The execution phase implements consolidation plans through systematic migration activities, user training, and performance monitoring. This phase requires careful coordination to minimize business disruption while achieving consolidation objectives.
Migration activities should follow established procedures with appropriate testing, validation, and rollback capabilities to ensure business continuity throughout the transition process.
Phase 4: Optimization and Governance
The final phase focuses on ongoing optimization and governance to maintain the benefits achieved through consolidation while preventing future fragmentation. This phase should establish monitoring systems, governance procedures, and continuous improvement processes.
Regular reviews and optimization activities help maintain cost discipline and operational efficiency while adapting to changing business requirements and new technology opportunities.
Measuring Success and ROI
Organizations must establish clear metrics and measurement frameworks to evaluate the success of their SaaS consolidation efforts and demonstrate return on investment.
Financial Metrics
Financial success metrics should include subscription cost reductions, administrative cost savings, and avoided costs through elimination of redundant applications. These metrics should account for both immediate savings and ongoing operational benefits.
Total cost of ownership calculations should consider migration costs, training expenses, and productivity impacts to provide comprehensive financial assessments of consolidation activities.
Operational Metrics
Operational success metrics might include user satisfaction scores, system performance improvements, and reduced complexity indicators such as decreased vendor relationships or simplified support processes.
These metrics help demonstrate the broader organizational benefits of consolidation beyond simple cost savings, supporting continued investment in optimization activities.
Strategic Alignment
Success measurement should also evaluate strategic alignment between consolidated SaaS portfolios and organizational objectives. This alignment includes support for business growth, operational flexibility, and technology innovation capabilities.
Regular strategic reviews ensure that consolidated SaaS portfolios continue supporting organizational goals as business requirements evolve and new opportunities emerge.
Conclusion
M&A activities present both significant challenges and substantial opportunities for enterprise SaaS spend optimization. Organizations that approach consolidation strategically can achieve meaningful cost savings while improving operational efficiency and user satisfaction. However, success requires comprehensive planning, systematic execution, and ongoing attention to optimization opportunities.
The key to successful SaaS consolidation lies in balancing immediate cost reduction opportunities with long-term strategic objectives while maintaining operational continuity throughout the transition process. Organizations should leverage specialized SaaS spend management tools and best practices to navigate the complexities of post-merger integration while maximizing the value of their software investments.
As the SaaS ecosystem continues evolving, organizations must remain adaptable and proactive in their approach to portfolio management. Those that develop strong consolidation capabilities and governance frameworks will be better positioned to capitalize on future M&A opportunities while maintaining optimal SaaS spend efficiency. The investment in proper consolidation strategies and tools pays dividends not only during major organizational changes but also through ongoing operational optimization and cost management.
Improve SaaS Cost Management with Binadox
Managing SaaS consolidation during M&A activities requires comprehensive visibility and control over your software portfolio. Binadox provides the platform and tools necessary to navigate complex consolidation challenges while optimizing costs and maintaining operational efficiency. With Binadox, organizations can discover all SaaS applications, analyze spending patterns, and implement data-driven consolidation strategies that deliver measurable results.

