
The rapid adoption of SaaS applications has transformed how businesses operate, offering unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, this cloud-centric approach introduces a critical concern that many organizations overlook until it’s too late: data portability. The ability to seamlessly extract, migrate, and utilize your data when switching between SaaS solutions can mean the difference between smooth business continuity and costly operational disruptions.
In today’s competitive business environment, organizations increasingly rely on multiple SaaS management platforms to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and reduce IT overhead. Yet, the convenience of software subscriptions often masks a fundamental challenge: what happens when you need to change providers, consolidate platforms, or exit a service entirely?
This comprehensive guide explores the critical aspects of SaaS data portability and provides actionable strategies for developing robust exit plans. Whether you’re managing a growing SaaS stack or implementing cloud cost optimization strategies, understanding data portability principles will protect your organization from vendor lock-in and ensure business continuity regardless of changing circumstances.
What is SaaS Data Portability?
SaaS data portability refers to the ability to extract, transfer, and utilize data stored within a Software as a Service application in a format that can be easily imported into another system or platform. This concept encompasses not only the technical capability to export data but also the practical feasibility of migrating information without losing functionality, formatting, or critical business context.
Unlike traditional on-premises software where organizations maintain direct control over their data storage and access, cloud computing introduces dependencies on external vendors for data access and extraction capabilities. This dependency creates unique challenges when organizations need to migrate between platforms, consolidate SaaS applications, or discontinue services.
Effective data portability encompasses several key dimensions:
Technical Portability involves the ability to export data in standard, machine-readable formats that preserve data integrity and structure. This includes ensuring that exported data maintains proper relationships, metadata, and formatting necessary for successful migration to alternative platforms.
Functional Portability extends beyond raw data export to include the preservation of workflows, configurations, and business logic that enable continued operations. This aspect is particularly crucial for complex SaaS platforms that integrate multiple business functions.
Temporal Portability addresses the timing and scheduling aspects of data migration, ensuring that transitions can occur within acceptable business continuity windows without disrupting critical operations or violating regulatory requirements.
Why Data Portability Matters in SaaS Management
Data portability has emerged as a fundamental consideration in modern SaaS spend management strategies. Organizations that fail to prioritize portability planning often find themselves trapped in expensive, inefficient vendor relationships that hinder growth and innovation.
Strategic Flexibility and Competitive Advantage
The ability to migrate data seamlessly between platforms provides organizations with crucial negotiating leverage when renewing contracts or evaluating alternatives. Companies with well-planned exit strategies can more effectively negotiate pricing, features, and service levels, knowing they retain the option to switch providers if agreements become unfavorable.
This flexibility becomes particularly valuable during SaaS procurement processes, where organizations can confidently evaluate new solutions without fear of being permanently locked into suboptimal platforms. Strategic portability planning enables businesses to pursue best-of-breed solutions and adapt their technology stack as market conditions and business requirements evolve.
Risk Mitigation and Business Continuity
Data portability planning serves as a critical risk management strategy, protecting organizations from various scenarios that could disrupt operations. These include vendor acquisition or merger situations that alter service offerings, sudden price increases that make continued usage economically unfeasible, or service discontinuation announcements that force immediate migration.
Organizations with robust portability strategies can respond quickly to market changes, regulatory requirements, or internal restructuring needs without compromising data integrity or operational continuity. This preparedness is particularly crucial for businesses operating in regulated industries where data handling and retention requirements must be maintained regardless of platform changes.
Cost Optimization and Resource Allocation
Effective portability planning directly supports cloud cost optimization initiatives by enabling organizations to pursue more cost-effective alternatives when current solutions become expensive or inefficient. Companies that can easily migrate between platforms are better positioned to take advantage of competitive pricing, promotional offers, or emerging solutions that provide superior value.
Furthermore, portability planning helps organizations avoid the hidden costs associated with vendor lock-in, including escalating licensing fees, forced upgrades to premium tiers, and expensive custom integration requirements that accumulate over time.
The Hidden Costs of Vendor Lock-in
Vendor lock-in represents one of the most significant and often underestimated risks in SaaS management. While the initial appeal of comprehensive, integrated platforms can seem attractive, organizations that become overly dependent on single vendors often face substantial financial and operational penalties when circumstances require change.
Financial Impact of Lock-in Scenarios
The financial implications of vendor lock-in extend far beyond obvious switching costs. Organizations trapped in lock-in situations frequently experience gradual price increases that compound over time, as vendors recognize their customers’ limited ability to migrate to alternatives. These price escalations can significantly impact SaaS spending budgets and force difficult decisions between accepting higher costs or undertaking expensive migration projects.
Lock-in scenarios also create opportunity costs by preventing organizations from adopting innovative solutions that could provide better functionality or cost efficiency. Companies constrained by difficult-to-migrate platforms often miss opportunities to consolidate overlapping services, implement more specialized tools, or take advantage of competitive pricing from alternative vendors.
Operational Constraints and Innovation Barriers
Beyond financial considerations, vendor lock-in creates operational constraints that can limit business agility and growth potential. Organizations dependent on proprietary data formats, custom integrations, or vendor-specific workflows may find it increasingly difficult to adapt their operations to changing market conditions or business requirements.
These constraints become particularly problematic when organizations need to integrate with new business partners, comply with evolving regulatory requirements, or implement digital transformation initiatives that require data sharing across multiple platforms and systems.
Technical Debt Accumulation
Long-term vendor relationships without adequate portability planning often result in the accumulation of technical debt through custom configurations, workarounds, and integrations that become increasingly difficult to replicate or migrate. This technical debt can significantly complicate future migration efforts and increase the cost and complexity of switching to alternative solutions.
Organizations should regularly assess their technical debt accumulation and implement strategies to minimize dependencies on vendor-specific features or proprietary formats that could complicate future migration efforts.
Common Data Portability Challenges
Understanding common data portability challenges enables organizations to develop more effective migration strategies and avoid potential pitfalls that could compromise business operations during transitions between SaaS solutions.
Data Format Incompatibilities
One of the most fundamental challenges in SaaS data portability involves incompatible data formats between source and destination platforms. Many SaaS providers use proprietary formats optimized for their specific architecture, making direct migration to alternative platforms difficult or impossible without significant data transformation efforts.
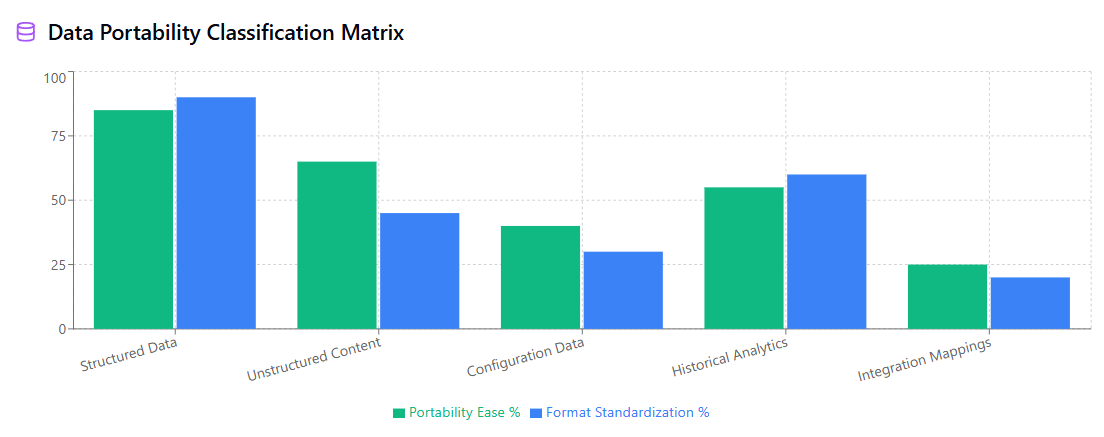
These format incompatibilities can affect various types of information, including structured data like customer records and financial transactions, unstructured content such as documents and multimedia files, and configuration data that defines workflows, user permissions, and system settings.
Organizations should prioritize platforms that support industry-standard data formats and provide robust export capabilities that preserve data structure and relationships during migration processes.
Incomplete Data Export Capabilities
Many SaaS platforms provide limited export functionality that may not include all data types, historical information, or metadata necessary for complete migration to alternative solutions. Common limitations include restrictions on historical data export, missing metadata and configuration information, and incomplete relationship data that defines connections between different data entities.
These limitations can force organizations to accept partial data migrations that compromise operational continuity or require expensive custom development efforts to extract complete information from source platforms.
Integration Dependencies and Custom Configurations
Complex SaaS applications often include extensive customizations, integrations, and workflow configurations that cannot be easily replicated in alternative platforms. These dependencies create additional migration challenges that extend beyond simple data export and import processes.
Organizations should document and regularly review their custom configurations, integrations, and dependencies to understand the full scope of migration requirements and identify potential complications that could arise during platform transitions.
Data Validation and Quality Assurance
Ensuring data integrity and quality during migration processes represents a critical challenge that requires comprehensive validation and testing procedures. Migration processes can introduce data corruption, formatting errors, or relationship breaks that may not be immediately apparent but could compromise business operations over time.
Effective portability planning includes developing robust data validation procedures, establishing quality assurance checkpoints, and implementing rollback strategies that can quickly restore operations if migration issues arise.
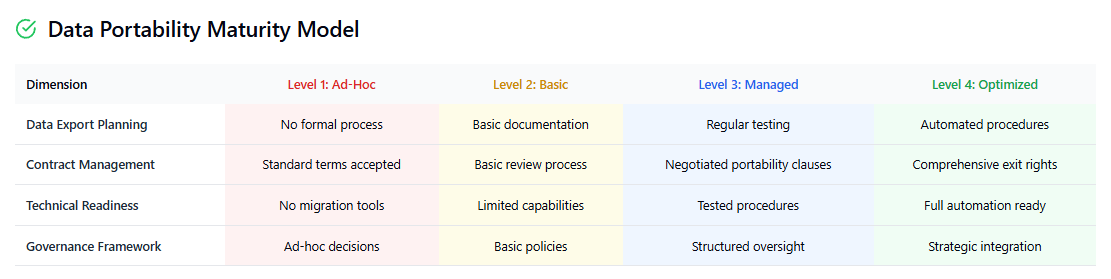
Key Components of a SaaS Exit Strategy
Developing a comprehensive SaaS exit strategy requires careful planning across multiple dimensions, from technical data extraction procedures to business continuity planning that ensures minimal operational disruption during transitions.
Data Inventory and Classification
The foundation of any effective exit strategy begins with a comprehensive inventory and classification of all data stored within SaaS platforms. This inventory should categorize information based on business criticality, regulatory requirements, and technical complexity to prioritize migration efforts and resource allocation.
Critical data categories typically include customer information, financial records, operational data, configuration settings, user accounts and permissions, integration specifications, and historical analytics and reporting data.
Organizations should maintain current data inventories that include information about data volumes, update frequencies, dependencies, and retention requirements to facilitate rapid decision-making during exit scenarios.
Technical Migration Planning
Technical migration planning encompasses the detailed procedures and resources required to extract, transform, and load data from source platforms to alternative solutions. This planning should address data extraction methods and timing, format conversion requirements, validation and quality assurance procedures, integration reconfiguration needs, and testing and rollback strategies.
Effective technical planning includes developing standardized procedures that can be quickly implemented across multiple platforms and maintaining current documentation that enables rapid execution when migration becomes necessary.
Business Continuity Considerations
SaaS exit strategies must address business continuity requirements that ensure minimal disruption to operations during migration processes. This includes identifying critical business functions that depend on specific platforms, developing temporary workaround procedures, establishing communication plans for stakeholders, and defining acceptable downtime windows and service level requirements.
Business continuity planning should also address training requirements for staff who may need to work with new platforms and procedures for maintaining customer service levels during transition periods.
Legal and Contractual Preparation
Exit strategies must account for legal and contractual obligations that could affect migration timing, data access rights, or post-termination support requirements. Organizations should regularly review contract terms related to data ownership, export rights, termination notice requirements, and post-contract data access or support availability.
Legal preparation should also address intellectual property considerations, regulatory compliance requirements, and potential liability issues that could arise during migration processes.
Data Portability Standards and Formats
Understanding industry standards and common data formats enables organizations to make informed decisions about platform selection and migration planning that support long-term portability objectives.
Industry Standards for Data Portability
Several industry initiatives have developed standards and frameworks designed to improve data portability across different platforms and vendors. The Data Transfer Project, supported by major technology companies, provides frameworks for secure, direct data transfers between online platforms.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) includes specific provisions for data portability that require organizations to provide personal data in machine-readable formats, establishing important precedents for broader portability rights and capabilities.
Organizations should prioritize platforms that support recognized industry standards and actively participate in portability initiatives that promote interoperability and reduce vendor lock-in risks.
Common Data Export Formats
Different data types require different export formats to preserve functionality and enable successful migration to alternative platforms. Structured data like customer records and financial transactions typically export well in formats such as CSV, JSON, XML, and SQL database dumps that preserve relationships and data types.
Unstructured content including documents, images, and multimedia files may require specialized formats that maintain metadata and formatting information necessary for proper display and functionality in destination platforms.
Configuration data representing workflows, user permissions, and system settings often requires custom formats that may need significant transformation to work with alternative platforms.
Evaluating Platform Export Capabilities
When selecting SaaS management tools, organizations should systematically evaluate export capabilities to ensure adequate portability support. Key evaluation criteria include completeness of data export functionality, supported formats and standards, historical data access and retention, metadata and relationship preservation, and automation and scheduling capabilities.
Regular assessment of platform export capabilities helps organizations identify potential portability limitations before they become critical obstacles during migration scenarios.
Best Practices for SaaS Data Management
Implementing proactive data management practices significantly improves portability outcomes and reduces migration complexity when platform transitions become necessary.
Standardization and Documentation
Maintaining consistent data standards and comprehensive documentation across all SaaS applications simplifies migration planning and execution. Organizations should establish data naming conventions, format standards, classification systems, and integration documentation that remains current and accessible to migration teams.
Regular documentation reviews and updates ensure that information remains accurate and useful for migration planning and execution.
Regular Data Backup and Validation
Independent data backup strategies provide additional security and migration options beyond vendor-provided export capabilities. Organizations should implement regular backup procedures that capture complete data sets, including metadata and relationship information, and conduct periodic validation tests to ensure backup integrity and completeness.
These backup strategies serve dual purposes of disaster recovery protection and migration preparation, providing organizations with multiple options for data extraction during exit scenarios.
Monitoring and Governance Frameworks
Implementing comprehensive SaaS governance frameworks helps organizations maintain visibility into their data portfolios and identify potential portability risks before they become critical issues. Effective governance includes regular platform assessments, contract review procedures, data audit processes, and risk evaluation frameworks.
Monitoring frameworks should track changes in platform capabilities, contract terms, and business requirements that could affect portability planning and execution.
Planning Your Exit Strategy: Step-by-Step Guide
Developing and maintaining effective exit strategies requires systematic planning and regular updates to address changing business requirements and technology landscapes.
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning
The initial phase involves comprehensive assessment of current SaaS portfolios and identification of potential migration requirements. This includes cataloging all current platforms and data types, evaluating existing export capabilities and limitations, identifying critical dependencies and integration points, and assessing business continuity requirements and constraints.
Assessment activities should produce detailed migration requirements documents that serve as the foundation for subsequent planning and execution phases.
Phase 2: Technical Preparation
Technical preparation involves developing specific procedures and resources for data extraction and migration. This includes creating data extraction procedures and schedules, developing format conversion and validation tools, establishing testing and quality assurance protocols, and preparing integration reconfiguration procedures.
Technical preparation should also include identifying and procuring necessary tools, resources, and expertise required for successful migration execution.
Phase 3: Testing and Validation
Regular testing of migration procedures ensures that exit strategies remain viable and effective as business requirements and platform capabilities evolve. Testing should include data extraction and validation exercises, format conversion and quality assurance testing, integration reconfiguration verification, and business continuity procedure validation.
Testing activities should be documented and reviewed to identify areas for improvement and ensure that procedures remain current and effective.
Phase 4: Documentation and Maintenance
Maintaining current and comprehensive documentation ensures that exit strategies can be quickly implemented when migration becomes necessary. Documentation should include detailed migration procedures, contact information for key personnel and vendors, current contract terms and obligations, and business continuity procedures and contact information.
Regular documentation reviews and updates ensure that information remains accurate and useful for rapid deployment during exit scenarios.

Legal and Compliance Considerations
SaaS exit strategies must address various legal and compliance requirements that could affect migration timing, data handling procedures, or post-migration obligations.
Data Ownership and Access Rights
Understanding data ownership rights and access obligations forms the foundation of legal exit planning. Organizations should clearly establish their rights to extract and use data stored in SaaS platforms and understand any limitations or restrictions that vendors may impose during or after contract termination.
Contract reviews should specifically address data export rights, post-termination access periods, and any restrictions on data use or transfer that could affect migration planning and execution.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Many industries have specific regulatory requirements for data handling, retention, and transfer that must be maintained during migration processes. Organizations should identify applicable regulations and compliance requirements that affect their data portability planning and ensure that migration procedures meet all necessary standards.
Compliance planning should also address notification requirements, audit trail maintenance, and documentation standards that may apply during migration processes.
Intellectual Property and Confidentiality
Migration processes may involve sharing sensitive information with new vendors, integration partners, or migration service providers, creating potential intellectual property and confidentiality concerns. Organizations should develop appropriate confidentiality agreements, data handling procedures, and security protocols that protect sensitive information during migration processes.
These protections should extend to all parties involved in migration activities, including internal staff, external consultants, and new platform vendors.
Tools and Technologies for Data Migration
Selecting appropriate tools and technologies significantly impacts migration success and can reduce both complexity and cost of platform transitions.
Migration Platform Categories
Various categories of migration tools address different aspects of SaaS data portability challenges. Enterprise data integration platforms provide comprehensive capabilities for large-scale migrations involving complex data transformations and multiple source and destination systems.
Specialized SaaS migration tools focus on specific platform combinations or data types, offering streamlined procedures for common migration scenarios.
Cloud-native migration services leverage cloud computing infrastructure to provide scalable, cost-effective migration capabilities that can handle large data volumes and complex transformation requirements.
Evaluation Criteria for Migration Tools
When selecting migration tools, organizations should evaluate capabilities based on their specific requirements and constraints. Key evaluation criteria include data source and destination support, transformation and validation capabilities, scalability and performance characteristics, security and compliance features, and cost and licensing considerations.
Tool evaluation should also consider integration requirements, training needs, and ongoing support availability that may affect migration success and total cost of ownership.
Custom Development Considerations
Some migration scenarios may require custom development efforts to address unique data formats, complex transformations, or specific business requirements that cannot be handled by standard migration tools.
Organizations should carefully evaluate the cost-benefit trade-offs of custom development versus standard tools, considering factors such as development time and cost, ongoing maintenance requirements, and the likelihood of future migration needs that could justify custom tool investment.
How Binadox Helps with SaaS Portfolio Management
Effective SaaS data portability planning requires comprehensive visibility into your organization’s software portfolio, usage patterns, and vendor relationships. Binadox provides integrated SaaS management tools that support both day-to-day optimization and strategic portability planning.
Portfolio Visibility and Documentation
Binadox provides centralized visibility into your entire SaaS portfolio, including application inventories, usage analytics, cost tracking, contract management, and integration mapping that forms the foundation of effective exit strategy planning.
This comprehensive visibility enables organizations to understand their data distribution, identify critical dependencies, and prioritize portability planning efforts based on business impact and migration complexity.
Contract and Renewal Management
The platform’s contract management capabilities help organizations track important terms and conditions that affect data portability, including export rights, termination clauses, data retention policies, and vendor obligations that could impact migration planning and execution.
Automated renewal tracking and alerts provide advance notice of contract decisions, enabling organizations to negotiate better portability terms or plan strategic migrations before contract renewals lock them into extended commitments.
Cost Optimization and Alternative Evaluation
Binadox’s cost analysis and optimization features help organizations identify opportunities for platform consolidation or migration to more cost-effective alternatives. The platform provides detailed spending analytics, usage optimization recommendations, and vendor comparison capabilities that support informed decision-making about platform changes.
These capabilities enable organizations to proactively plan migrations based on cost optimization opportunities rather than reactive responses to vendor lock-in situations.
Integration and Dependency Mapping
Understanding integration dependencies is crucial for successful migration planning. Binadox helps organizations map connections between applications, identify critical data flows, and assess the complexity of potential migration scenarios.
This integration visibility enables more accurate migration planning, helps identify potential complications before they occur, and supports better resource allocation for complex transition projects.
Conclusion
SaaS data portability represents a critical strategic capability that organizations can no longer afford to overlook in their digital transformation initiatives. As businesses become increasingly dependent on cloud-based solutions for core operations, the ability to maintain control over data and preserve migration flexibility becomes essential for long-term success and competitive advantage.
Effective portability planning requires proactive strategies that address technical, legal, and operational dimensions of data migration. Organizations that invest in comprehensive exit strategy development, maintain robust data management practices, and regularly assess their portability capabilities are better positioned to avoid vendor lock-in, optimize costs, and adapt quickly to changing business requirements.
The key to successful SaaS data portability lies in treating it as an ongoing strategic initiative rather than a reactive response to crisis situations. By implementing systematic assessment procedures, maintaining current documentation, and regularly testing migration capabilities, organizations can ensure that they retain the flexibility needed to pursue optimal technology solutions regardless of changing market conditions or vendor relationships.
Furthermore, leveraging comprehensive SaaS management platforms like Binadox enables organizations to maintain the visibility, documentation, and strategic oversight necessary for effective portability planning while optimizing day-to-day operations and costs.
As the SaaS ecosystem continues to evolve, organizations that prioritize data portability and maintain robust exit strategies will be best positioned to capitalize on innovation opportunities, negotiate favorable vendor relationships, and maintain operational resilience in an increasingly complex technological landscape. The investment in portability planning today provides the foundation for strategic flexibility and competitive advantage tomorrow.
By following the strategies and best practices outlined in this guide, organizations can develop comprehensive data portability capabilities that protect against vendor lock-in, support cost optimization initiatives, and ensure business continuity regardless of future platform transitions or market changes.

