The modern workplace runs on software. From collaboration tools to project management platforms, customer relationship management systems to cloud infrastructure services, organizations today rely on an ever-expanding stack of SaaS solutions to drive productivity and growth. However, this digital transformation comes with a hefty price tag that many businesses are only beginning to fully understand.
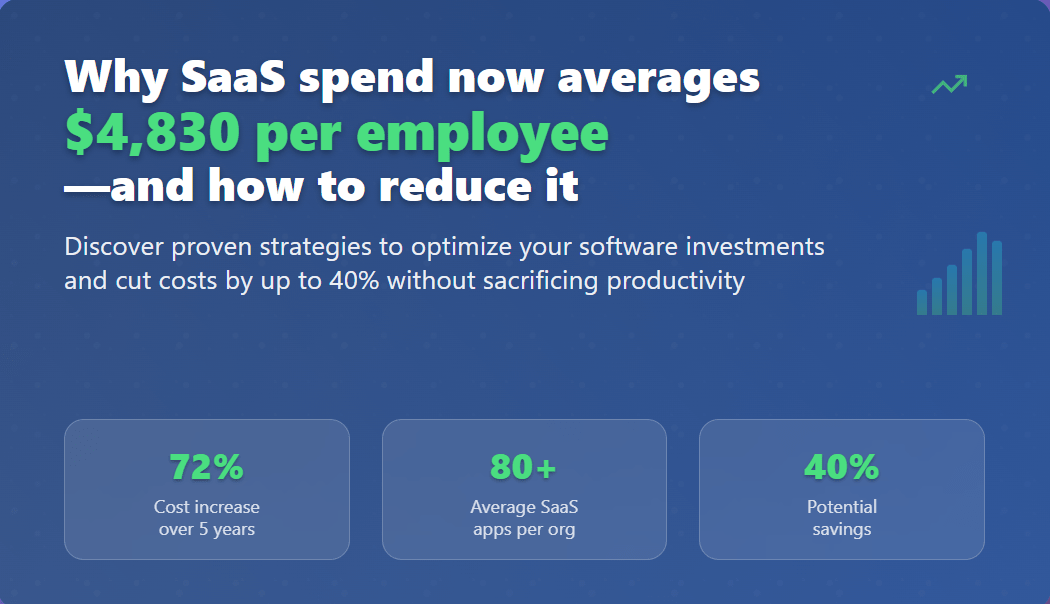
Recent industry analysis reveals a startling reality: the average organization now spends $4,830 per employee annually on SaaS applications. This figure represents a significant increase from just a few years ago and shows no signs of slowing down. For a company with 100 employees, this translates to nearly half a million dollars in annual software costs alone.
This comprehensive guide examines the factors driving this explosive growth in SaaS spending, explores the hidden costs that many organizations overlook, and provides actionable strategies to help businesses optimize their software investments without sacrificing operational efficiency.
The Rising Cost of SaaS: Understanding the $4,830 Reality
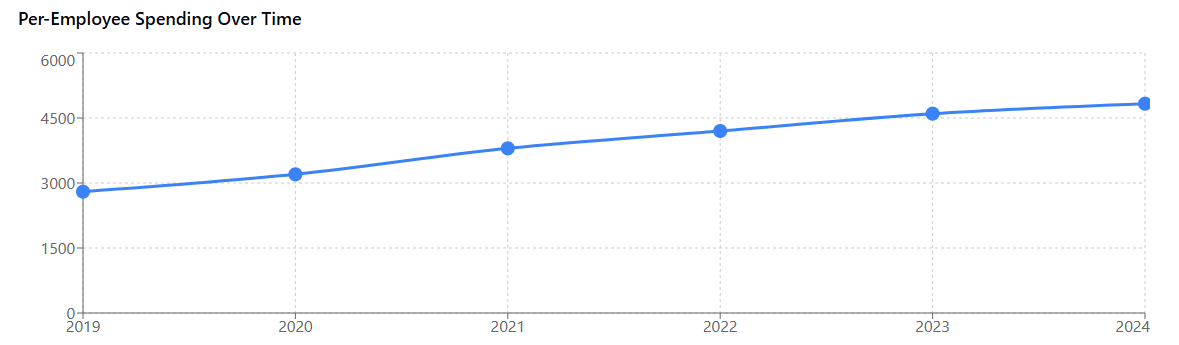
The $4,830 per-employee figure isn’t just a number pulled from thin air—it reflects a fundamental shift in how businesses operate and scale in the digital age. This spending encompasses everything from basic productivity suites like Microsoft Office 365 and Google Workspace to specialized industry-specific applications, cloud infrastructure costs, and the numerous point solutions that teams adopt to solve specific problems.
To put this in perspective, consider that the average knowledge worker now uses between 9-11 different SaaS applications daily, while organizations typically maintain subscriptions to 80+ different software services. This proliferation of SaaS platforms has created both opportunities and challenges for modern businesses.
The growth trajectory is particularly concerning when viewed against historical context. Just five years ago, the average per-employee SaaS spend hovered around $2,800 annually. The 72% increase over this period far outpaces most other business expense categories, making SaaS cost optimization a critical priority for financial leaders.
This trend is driven by several converging factors: the acceleration of digital transformation initiatives, the shift to remote and hybrid work models, the increasing sophistication of SaaS solutions, and the ease with which individual teams can adopt new tools without centralized oversight.
What’s Driving the Explosion in SaaS Spending?
Understanding the root causes behind escalating SaaS costs is essential for developing effective mitigation strategies. Several key factors contribute to this phenomenon:
Shadow IT and Decentralized Purchasing
One of the primary drivers of SaaS spend inflation is the democratization of software purchasing. Unlike traditional enterprise software that required lengthy procurement processes and IT approval, modern SaaS solutions can be purchased with a credit card and deployed immediately. This ease of adoption has led to widespread shadow IT practices, where individual departments and teams subscribe to applications without central visibility or control.
Research indicates that the average organization discovers they have 30-40% more software subscriptions than initially estimated when they conduct their first comprehensive SaaS audit. This shadow IT phenomenon creates redundancies, security risks, and significant cost overruns.
Feature Creep and Over-Provisioning
As SaaS solutions evolve, vendors continuously add new features and capabilities, often bundling them into higher-tier plans. Organizations frequently find themselves paying for premium features they don’t use or need, simply because the vendor’s pricing structure makes it difficult to maintain basic functionality without upgrading.
Additionally, many businesses over-provision user licenses as a safety measure, paying for seats that remain unused for months or even years. This “better safe than sorry” approach can add thousands of dollars to annual software costs.
Integration Complexity and Vendor Lock-in
Modern SaaS ecosystems are highly interconnected, with applications sharing data and workflows across platforms. While this integration capability is valuable, it also creates dependencies that make it difficult to switch providers or eliminate redundant tools. Organizations often maintain multiple overlapping solutions because the cost and complexity of migration outweigh the potential savings.
Remote Work Acceleration
The shift to remote and hybrid work models has accelerated SaaS adoption across virtually every business function. Companies have invested heavily in collaboration tools, project management platforms, virtual meeting solutions, and cloud-based productivity suites to support distributed teams. While these investments were necessary, many organizations haven’t optimized their tool stack as work patterns have stabilized.
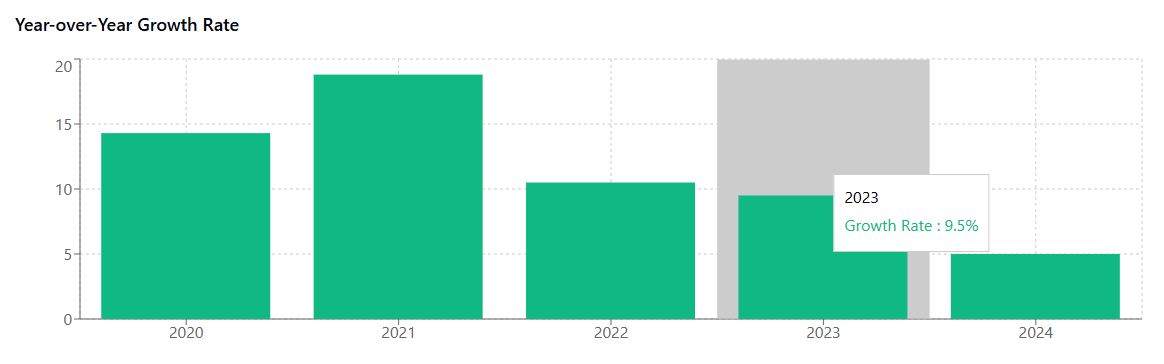
The Hidden Costs Behind SaaS Platforms
Beyond the obvious subscription fees, SaaS deployments carry several hidden costs that contribute to the $4,830 per-employee average:
Training and Onboarding Expenses
Each new SaaS platform requires employee training and onboarding. While vendors often provide basic training materials, the time investment required for teams to become proficient with new tools represents a significant indirect cost. Studies suggest that it takes an average of 3-6 months for teams to reach full productivity with new software solutions.
Integration and Customization Costs
Most SaaS platforms require some degree of customization and integration with existing systems. These services, whether provided by the vendor or third-party consultants, can easily add 20-30% to the total cost of ownership for enterprise deployments.
Data Storage and Bandwidth Charges
As organizations generate and store more data within SaaS platforms, additional charges for storage, bandwidth, and data processing can accumulate quickly. Cloud cost optimization becomes crucial as data volumes grow.
Compliance and Security Overhead
Maintaining compliance across multiple SaaS platforms requires additional tools, processes, and often specialized personnel. The complexity of managing security policies, data governance, and regulatory compliance across dozens of different platforms adds substantial overhead costs.
Industry Analysis: How Different Sectors Stack Up
SaaS spending patterns vary significantly across industries, with some sectors showing dramatically higher per-employee costs:
Technology and Software Companies
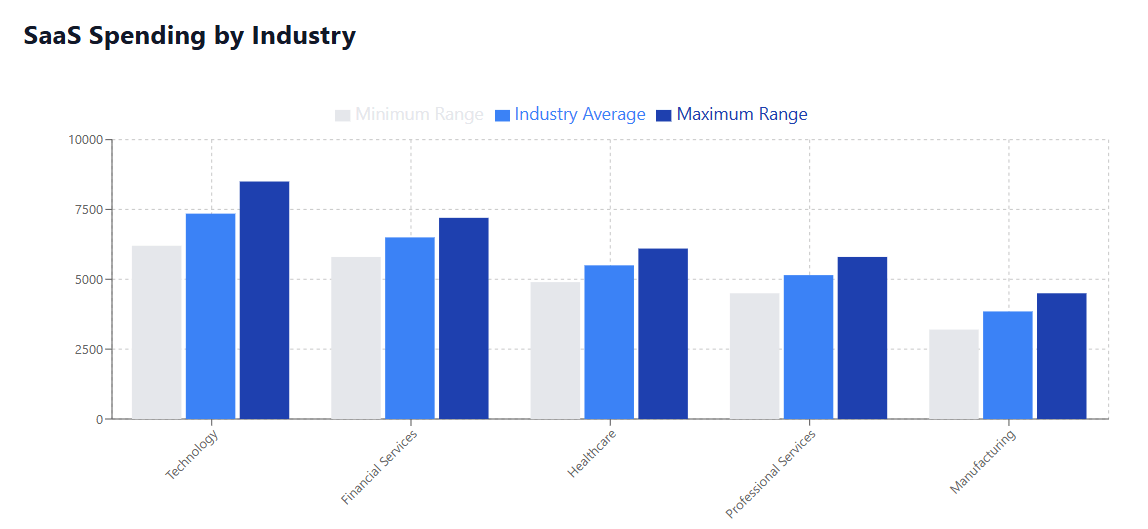
Technology companies lead in SaaS spending, averaging $6,200-8,500 per employee annually. These organizations typically maintain extensive development toolchains, multiple cloud infrastructure environments, and sophisticated analytics platforms that drive up costs.
Financial Services
The financial sector averages $5,800-7,200 per employee, driven by regulatory compliance requirements, security tools, and specialized financial analysis software. The need for redundant systems and extensive audit trails contributes to higher costs.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
Healthcare organizations spend approximately $4,900-6,100 per employee on SaaS solutions, with electronic health records systems, telemedicine platforms, and regulatory compliance tools driving expenses.
Manufacturing and Industrial
Traditional manufacturing companies typically have lower SaaS costs, averaging $3,200-4,500 per employee, though this is rapidly increasing as these industries embrace digital transformation initiatives.
Professional Services
Consulting, legal, and accounting firms average $4,500-5,800 per employee, with project management tools, document management systems, and specialized industry software contributing to costs.
The True Impact of Unmanaged SaaS Spend
Uncontrolled SaaS spending creates several cascading problems beyond the immediate financial impact:
Budget Unpredictability
Without proper SaaS spend management tools, organizations struggle to predict and plan for software costs. Automatic renewals, usage-based pricing tiers, and mid-contract upgrades can cause budget overruns that impact other business initiatives.
Security and Compliance Risks
Shadow IT practices create security vulnerabilities and compliance gaps. When IT departments lack visibility into all software applications in use, they cannot properly assess risks, implement security policies, or ensure regulatory compliance.
Operational Inefficiencies
Redundant and overlapping tools create confusion and inefficiency. Employees may struggle to determine which application to use for specific tasks, leading to inconsistent processes and reduced productivity.
Vendor Management Complexity
Managing relationships with dozens of different software vendors becomes a significant administrative burden. Contract negotiations, renewal management, and support coordination require dedicated resources that could be better utilized elsewhere.
Proven Strategies to Reduce SaaS Costs
Organizations can implement several proven strategies to reduce their SaaS spending while maintaining operational effectiveness:
Conduct Comprehensive SaaS Audits
The first step in cost optimization is gaining complete visibility into all software subscriptions. This involves discovering shadow IT applications, cataloging all active subscriptions, and analyzing usage patterns across the organization. Many companies are surprised to find they’re paying for 30-50% more applications than they realized.
Implement Centralized Procurement Processes
Establishing centralized approval processes for new SaaS purchases helps prevent redundant subscriptions and ensures that new tools align with organizational standards and existing investments. This doesn’t mean stifling innovation—rather, it means creating a framework for evaluating and approving new tools based on business need, security requirements, and integration capabilities.
Rightsizing and License Optimization
Regularly review user access and activity levels to identify opportunities for license optimization. This includes downgrading unused premium licenses, eliminating inactive user accounts, and negotiating more appropriate pricing tiers based on actual usage patterns.
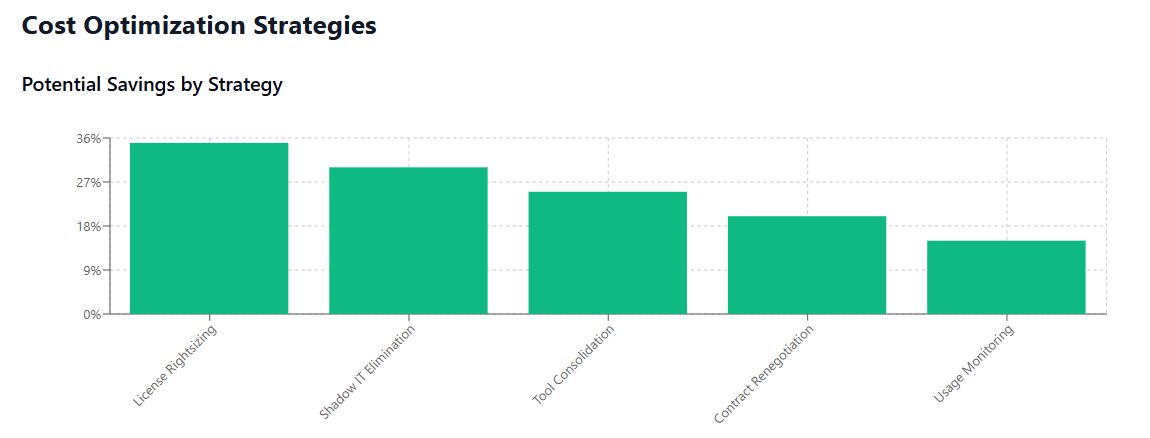
Consolidate Overlapping Tools
Identify and eliminate redundant applications that serve similar functions. For example, many organizations maintain multiple project management tools, communication platforms, or document storage solutions that could be consolidated without impacting productivity.
Negotiate Better Contract Terms
Leverage purchasing power to negotiate better pricing, especially for enterprise-wide deployments. This includes seeking volume discounts, longer-term contract incentives, and more favorable terms for contract modifications and cancellations.
Implement Usage Monitoring and Governance
Deploy SaaS management tools that provide ongoing visibility into application usage, user activity, and cost trends. This enables proactive management rather than reactive cost control.
SaaS Spend Management Tools: Your Arsenal Against Waste
Modern SaaS spend management platforms provide the visibility and control necessary to optimize software investments. These tools typically offer several key capabilities:
Discovery and Inventory Management
Advanced discovery tools can identify SaaS applications through multiple channels, including network traffic analysis, expense report mining, and integration with corporate credit card systems. This comprehensive approach ensures that shadow IT applications are discovered and cataloged.
Usage Analytics and Optimization Recommendations
Sophisticated analytics engines analyze user activity patterns to identify underutilized applications, redundant tools, and optimization opportunities. These platforms can automatically generate recommendations for license rightsizing and application consolidation.
Automated Renewal Management
Automated renewal tracking and alert systems help prevent surprise renewals and provide advance notice for contract renegotiation opportunities. This is particularly valuable for preventing automatic upgrades and ensuring that renewals align with current business needs.
Cost Allocation and Chargeback
Advanced platforms provide detailed cost allocation capabilities, enabling organizations to understand spending by department, project, or business unit. This transparency helps drive accountability and more informed decision-making about software investments.
Security and Compliance Monitoring
Integrated security assessment capabilities help identify potential risks associated with SaaS applications, including data access permissions, security configurations, and compliance status.
Integration with Financial Systems
Seamless integration with existing financial and procurement systems enables automated expense tracking, budget monitoring, and procurement workflow integration.
Cloud Cost Optimization: The Bigger Picture
SaaS spending is often closely tied to cloud infrastructure costs, making cloud cost optimization an essential component of overall software cost management. Key strategies include:
Resource Rightsizing
Regularly analyze cloud resource utilization to identify opportunities for rightsizing instances, storage allocations, and network configurations. Many organizations over-provision cloud resources as a safety measure, leading to unnecessary costs.
Reserved Instance and Commitment Optimization
Take advantage of reserved instance pricing and long-term commitments for predictable workloads. This can provide significant cost savings compared to on-demand pricing models.
Multi-Cloud Strategy
Consider a strategic multi-cloud approach that leverages the strengths and pricing advantages of different cloud providers for different workloads and use cases.
Automated Cost Management
Implement automated policies for resource scheduling, scaling, and cost optimization. This includes automatically shutting down development environments during off-hours and implementing cost alerts for unusual spending patterns.
Real-World Examples: Companies That Cut SaaS Costs Successfully
Several organizations have successfully implemented comprehensive SaaS cost optimization initiatives:
TechCorp Case Study
A 500-employee technology company discovered they were spending $2.8 million annually on SaaS applications—nearly double their budgeted amount. Through a comprehensive audit and optimization program, they:
- Eliminated 40% of redundant applications
- Rightsized licenses across their entire software stack
- Negotiated enterprise agreements with key vendors
- Implemented automated renewal management
The result was a 35% reduction in annual SaaS spending, saving over $980,000 while actually improving operational efficiency through better tool consolidation.
Manufacturing Giant Success
A large manufacturing company with 15,000 employees reduced their per-employee SaaS costs from $4,200 to $2,800 through:
- Centralizing procurement processes
- Implementing usage-based chargeback systems
- Consolidating multiple communication and collaboration platforms
- Negotiating enterprise-wide volume discounts
Professional Services Optimization
A 200-person consulting firm cut their SaaS costs by 42% through a systematic approach that included:
- Comprehensive discovery of shadow IT applications
- Implementation of approval workflows for new software purchases
- Regular quarterly reviews of usage and utilization
- Strategic vendor consolidation initiatives
Building a Sustainable SaaS Cost Management Strategy
Long-term success in SaaS cost optimization requires a systematic, ongoing approach rather than one-time cost-cutting initiatives:
Establish Clear Governance Policies
Develop comprehensive policies that define approval processes, security requirements, and integration standards for new SaaS applications. These policies should balance the need for innovation and agility with cost control and risk management.
Create Cross-Functional Teams
Form teams that include representatives from IT, finance, procurement, and business units to ensure that SaaS management decisions consider all relevant perspectives and requirements.
Implement Regular Review Cycles
Establish quarterly or semi-annual reviews of SaaS spending, usage patterns, and optimization opportunities. This proactive approach helps identify issues before they become costly problems.
Invest in Training and Change Management
Ensure that teams understand the financial impact of their software choices and provide training on approved tools and processes. Change management is crucial for gaining adoption of new governance processes.
Leverage Data for Decision Making
Use data-driven insights to guide decisions about software investments, renewals, and eliminations. Metrics such as cost per user, utilization rates, and business value should inform all SaaS-related decisions.
Develop Vendor Relationships
Build strategic relationships with key software vendors to ensure favorable pricing, early access to new features, and responsive support. These relationships can also provide insights into product roadmaps and optimization opportunities.
Conclusion
The reality of $4,830 per-employee annual SaaS spending represents both a challenge and an opportunity for modern organizations. While this level of investment reflects the critical role that software plays in driving business success, it also highlights the urgent need for more sophisticated approaches to SaaS cost optimization and management.
Organizations that take a proactive, systematic approach to SaaS spend management can achieve significant cost reductions—often 25-40%—while actually improving operational efficiency and security posture. The key lies in implementing comprehensive visibility tools, establishing effective governance processes, and maintaining ongoing optimization practices.
The most successful organizations treat SaaS spend management not as a one-time cost-cutting exercise, but as an ongoing strategic capability that enables them to maximize the value of their software investments while maintaining fiscal discipline. By leveraging modern SaaS management tools, implementing data-driven decision-making processes, and fostering a culture of cost consciousness, businesses can harness the power of SaaS solutions without falling victim to runaway software costs.
As the SaaS ecosystem continues to evolve and mature, organizations that master these cost optimization strategies will find themselves better positioned to invest in innovation, scale efficiently, and maintain competitive advantages in an increasingly software-driven business landscape. The $4,830 per-employee benchmark need not be a ceiling—with the right approach, it can become a starting point for building more efficient, cost-effective, and strategically aligned software portfolios.
Through careful planning, systematic implementation, and ongoing optimization, organizations can ensure that their SaaS investments drive genuine business value while maintaining financial sustainability in an era of digital transformation.

