
Startups face a unique challenge in today’s digital landscape: they need powerful software tools to compete effectively, but they must do so within extremely tight budget constraints. Software as a Service (SaaS) solutions offer the perfect answer to this dilemma, providing enterprise-grade functionality without massive upfront investments. However, without proper management, SaaS subscriptions can quickly spiral out of control, consuming precious resources that growing companies desperately need for other priorities.
This comprehensive guide explores how startups can master SaaS spend management while building scalable, efficient operations on lean budgets. By implementing smart strategies for affordable SaaS solutions and establishing robust budget management practices from day one, startups can harness the full potential of cloud-based tools without compromising their financial runway.
The Startup SaaS Challenge
Modern startups operate in an environment where software tools are essential for virtually every business function. From customer relationship management and project coordination to marketing automation and financial tracking, SaaS applications have become the backbone of startup operations. According to recent industry data, the average organization uses approximately 80 different SaaS applications, and this number continues to grow rapidly.
For startups, this presents both tremendous opportunities and significant risks. On one hand, SaaS solutions provide access to sophisticated capabilities that would have been prohibitively expensive just a few years ago. On the other hand, the ease of signing up for new services can lead to subscription sprawl, where costs accumulate faster than value delivery.
The challenge becomes particularly acute during rapid growth phases. As teams expand and new departments form, each group naturally gravitates toward tools that solve their specific problems. Without centralized oversight, startups often discover they’re paying for multiple solutions that provide overlapping functionality, or worse, paying for licenses that aren’t being used at all.
Furthermore, many startups operate with limited financial expertise in their early stages. Founders and early employees typically focus on product development and customer acquisition, leaving financial optimization as a secondary concern. This approach, while understandable, can result in inefficient spending patterns that become increasingly difficult to correct as the organization grows.
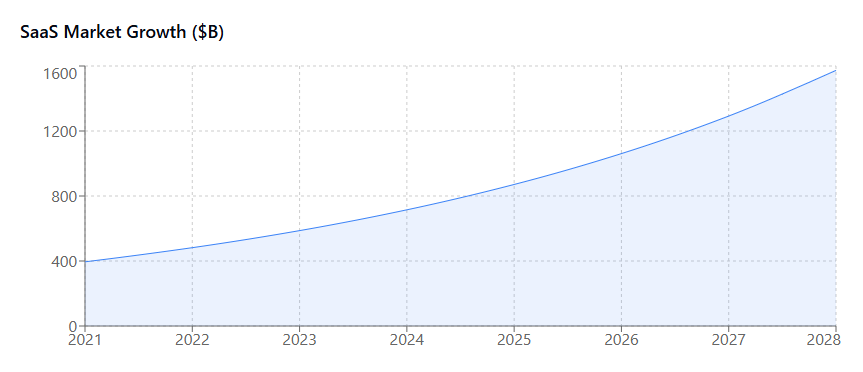
Understanding SaaS Spend Management for Startups
SaaS spend management for startups involves more than simply tracking monthly subscription costs. It encompasses a holistic approach to software procurement, utilization monitoring, and strategic planning that aligns with the company’s growth trajectory and financial constraints.
Effective SaaS spend management begins with visibility. Startups need comprehensive insight into all software subscriptions across the organization, including who initiated each subscription, how extensively each tool is being used, and what value each application delivers to the business. This visibility forms the foundation for all subsequent optimization efforts.
The subscription model inherent in SaaS solutions creates both advantages and complexities for startups. Unlike traditional software purchases, SaaS subscriptions provide flexibility to scale up or down based on changing needs. However, this flexibility requires active management to ensure that subscription levels remain aligned with actual usage patterns and business requirements.
Budget management for startups must also account for the predictable nature of SaaS expenses. Monthly or annual subscription fees create consistent cash flow requirements that must be factored into financial planning. Smart startups use this predictability to their advantage, negotiating annual contracts for better rates while ensuring they have adequate cash reserves to meet these commitments.
Another critical aspect involves understanding the total cost of ownership for each SaaS solution. Beyond the basic subscription fee, startups must consider implementation costs, training requirements, integration expenses, and potential switching costs if they need to change platforms later. These factors significantly impact the true value proposition of any software investment.
The Real Cost of Poor SaaS Management
The financial impact of inadequate SaaS spend management extends far beyond obvious waste from unused subscriptions. Poor management practices create cascading effects that can seriously undermine a startup’s competitive position and growth potential.
Shadow IT proliferation represents one of the most significant risks for growing startups. When employees can easily sign up for software tools using personal credit cards or departmental budgets, the organization loses visibility into its total software spend. This shadow IT often results in duplicate functionality across teams, security vulnerabilities from unvetted applications, and integration challenges when attempting to create cohesive workflows.
Scaling inefficiencies become apparent as startups grow beyond their initial team size. Without proper planning, organizations often find themselves locked into pricing tiers that made sense for a five-person team but become prohibitively expensive for a fifty-person company. Similarly, startups may discover they’re paying for premium features that only a small percentage of users actually need.
Cash flow implications can be particularly severe for early-stage companies. SaaS vendors typically offer significant discounts for annual payments, but startups must balance these savings against their need to preserve working capital. Poor timing of renewals can create unexpected cash flow crunches during critical periods.
Opportunity costs perhaps represent the most substantial hidden expense. Money spent on redundant or underutilized software represents resources that could have been invested in product development, marketing, or talent acquisition. For startups where every dollar counts, these opportunity costs can significantly impact growth trajectories.
Integration complexity grows exponentially as the number of disconnected tools increases. Startups often underestimate the time and resources required to create seamless workflows across multiple platforms. The hidden costs of manual data transfer, duplicate data entry, and system maintenance can quickly outweigh the benefits of specialized tools.
Essential SaaS Spend Management Strategies for Startups
Successful SaaS spend management for startups requires implementing systematic approaches that scale with the organization. These strategies must balance cost control with the need for tools that enable growth and productivity.
Centralized procurement processes form the cornerstone of effective SaaS management. Even small startups benefit from establishing clear approval workflows for new software purchases. This doesn’t mean creating bureaucratic bottlenecks, but rather ensuring that decision-makers understand the full implications of each software investment. Centralized procurement enables better negotiation with vendors, prevents duplicate purchases, and maintains visibility into total spending.
Regular subscription audits should become a standard practice, conducted at least quarterly. These audits involve reviewing all active subscriptions, analyzing usage data, and evaluating whether each tool continues to deliver appropriate value. During these reviews, startups should identify opportunities for downgrades, cancellations, or consolidations. The goal isn’t necessarily to minimize the number of tools, but to ensure that every subscription contributes meaningfully to business objectives.
Usage monitoring and optimization requires establishing metrics for software utilization. Most SaaS platforms provide analytics showing login frequencies, feature usage, and user activity levels. Startups should leverage this data to identify underutilized licenses that could be reassigned or cancelled. Additionally, usage patterns often reveal opportunities to adjust subscription tiers or negotiate custom pricing arrangements.
Strategic vendor relationships become increasingly important as SaaS spend grows. Rather than treating software vendors purely as service providers, startups should view them as strategic partners. This approach often leads to better pricing, early access to new features, and more flexible contract terms. Many vendors offer startup-specific programs with significant discounts or deferred payment options.
Budget forecasting and planning must account for the predictable nature of SaaS expenses while building in flexibility for growth. Startups should model their software costs under different growth scenarios, identifying which tools will require scaling and at what points cost increases will occur. This planning enables proactive decision-making rather than reactive budget management.
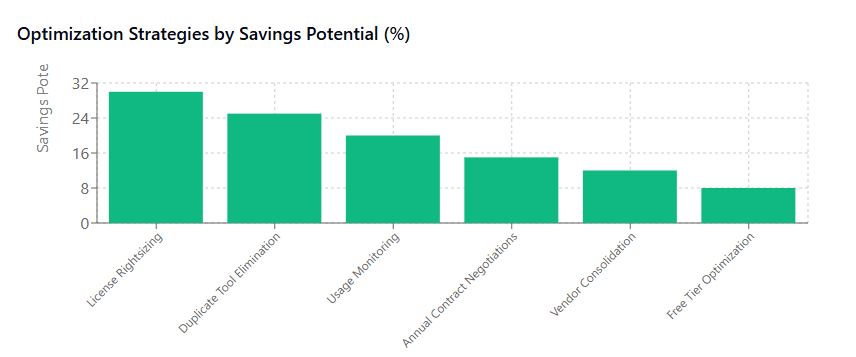
Building Your Startup’s SaaS Stack: Smart Selection Criteria
The process of selecting SaaS solutions requires balancing immediate needs with long-term scalability considerations. Startups must be particularly thoughtful about their technology choices since switching costs can be substantial once systems become deeply integrated into business processes.
Scalability assessment should be a primary consideration for any SaaS selection. Tools that work well for a ten-person team may become inadequate or prohibitively expensive as the organization grows. Startups should evaluate not just current pricing tiers, but how costs will evolve as user counts and data volumes increase. The most affordable option today may not be the most cost-effective choice over a two or three-year period.
Integration capabilities become crucial as the number of tools in the stack increases. Startups should prioritize solutions that offer robust APIs, pre-built integrations with commonly used platforms, and compatibility with their existing technology infrastructure. The ability to create seamless workflows across tools often provides more value than individual feature sets.
Vendor stability and roadmap alignment present unique considerations for startups. While established vendors offer stability, they may not innovate as quickly as startups need. Conversely, newer vendors may provide cutting-edge features but carry higher risks of service disruption or business failure. Startups should evaluate vendor financial health, customer base diversity, and product development trajectories.
Free tier and trial optimization can significantly impact early-stage costs. Many SaaS providers offer generous free tiers or extended trial periods specifically to attract startup customers. Smart utilization of these programs can defer costs during crucial early months while providing full access to needed functionality. However, startups should plan transition strategies to avoid service disruptions when free periods expire.
Total cost of ownership analysis must consider factors beyond subscription fees. Implementation time, training requirements, data migration costs, and ongoing maintenance all contribute to the true expense of any software investment. Startups should create comprehensive cost models that account for these factors when comparing alternatives.
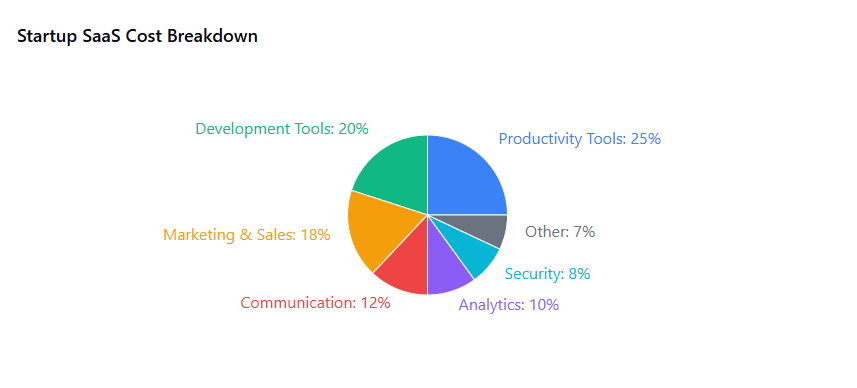
Budget Management Techniques for Growing Teams
As startups evolve from small teams to larger organizations, their budget management approaches must mature accordingly. Effective techniques must provide financial control while enabling the agility that growing companies require.
Departmental budget allocation helps distribute spending responsibility while maintaining overall visibility. Rather than managing all SaaS spend centrally, startups can allocate specific budgets to different departments or functions. This approach empowers teams to select tools that best meet their needs while creating natural spending limits. However, coordination mechanisms must ensure that departmental decisions align with overall technology strategy.
Cost center tracking enables detailed analysis of software expenses by business function. This granular view helps identify which areas of the business generate the highest software costs relative to their value contribution. Startups can use this information to optimize resource allocation and identify opportunities for shared services or tool consolidation.
Renewal calendar management becomes critical as the number of subscriptions grows. Startups should maintain comprehensive calendars showing all renewal dates, contract terms, and cancellation deadlines. This planning enables proactive vendor negotiations and prevents unwanted auto-renewals. Many successful startups negotiate renewal cycles to align with their financial planning periods.
Performance-based budgeting ties software spending to business outcomes rather than simply allocating fixed amounts. Under this approach, increases in SaaS budgets must be justified by corresponding improvements in productivity, revenue generation, or cost savings in other areas. This methodology helps ensure that software investments contribute meaningfully to business growth.
Contingency planning must account for both growth scenarios and potential downturns. Startups should identify which subscriptions are absolutely essential versus those that could be temporarily suspended during challenging periods. This planning provides flexibility to adjust spending quickly when circumstances change.
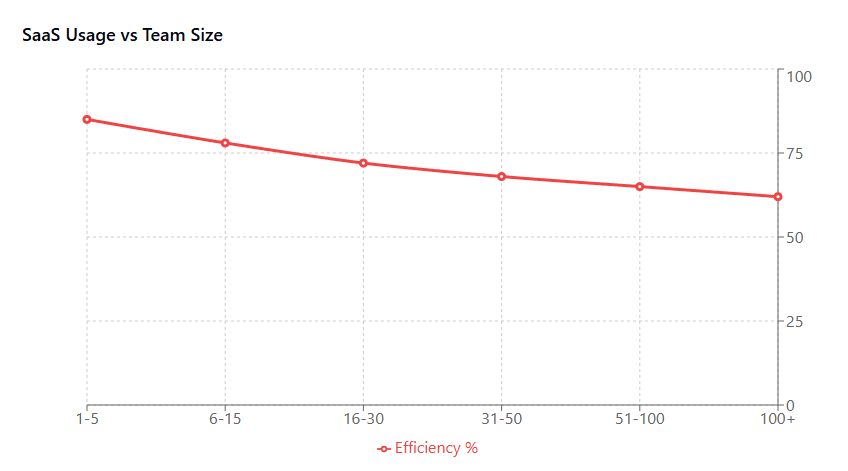
Affordable SaaS Solutions Every Startup Should Consider
While specific tool recommendations can quickly become outdated, certain categories of affordable SaaS solutions consistently provide strong value propositions for startups across industries.
All-in-one productivity platforms often provide better value than specialized point solutions for early-stage companies. Platforms that combine project management, communication, document collaboration, and basic CRM functionality can meet most of a startup’s initial needs at a fraction of the cost of purchasing separate tools for each function.
Open-source alternatives deserve serious consideration for startups with technical capabilities. Many commercial SaaS solutions have open-source equivalents that provide similar functionality at dramatically lower costs. While these solutions may require more technical expertise to implement and maintain, the cost savings can be substantial for resource-constrained startups.
Freemium models can provide significant value when used strategically. Many established vendors offer generous free tiers that can support startups through their early growth phases. The key is understanding the limitations of free plans and planning upgrade paths that align with business milestones rather than arbitrary user count thresholds.
Startup-specific programs offered by major vendors can provide substantial discounts and extended payment terms. Programs like AWS Activate, Google for Startups, and Microsoft for Startups can reduce software costs by thousands of dollars annually. These programs often include additional benefits like technical support and networking opportunities.
Industry-specific solutions may provide better value than generic tools for startups in specialized sectors. While these solutions may have higher per-user costs, they often include industry-specific features that would require multiple generic tools to replicate.
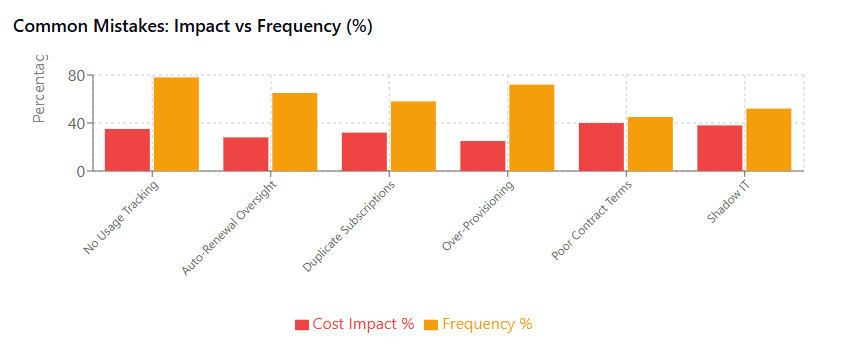
Common SaaS Spending Mistakes Startups Make
Understanding common pitfalls helps startups avoid expensive mistakes that can drain precious resources and complicate future optimization efforts.
Premature scaling represents one of the most frequent and costly mistakes. Startups often purchase enterprise-level subscriptions based on optimistic growth projections rather than current needs. While planning for growth is important, paying for unused capacity provides no immediate value and ties up capital that could be invested in growth-driving activities.
Ignoring contract terms beyond pricing can create significant future costs. Auto-renewal clauses, data export restrictions, and termination fees can make it difficult or expensive to change vendors later. Startups should carefully review all contract terms and negotiate modifications when necessary.
Lack of stakeholder involvement in software selection often leads to poor adoption and wasted investments. Tools selected without input from actual users frequently fail to meet practical needs, resulting in shadow IT adoption or outright abandonment. Successful startups involve end users in evaluation processes while maintaining budget oversight.
Security oversight can create substantial hidden costs through data breaches or compliance failures. While security features often come at premium pricing tiers, the cost of inadequate security can far exceed subscription savings. Startups should prioritize security requirements and factor these costs into their selection criteria.
Poor vendor relationship management misses opportunities for better pricing and support. Many startups treat vendor relationships as purely transactional, failing to leverage opportunities for strategic partnerships that could provide significant value beyond the basic software functionality.
Scaling Your SaaS Spend Management as You Grow
As startups mature into larger organizations, their SaaS management approaches must evolve to handle increased complexity while maintaining cost efficiency.
Governance framework development becomes essential as teams and tool counts grow. This framework should define approval processes, usage monitoring requirements, and renewal procedures that scale with organizational complexity. The goal is creating systematic approaches that don’t become bureaucratic obstacles to necessary software adoption.
Advanced analytics implementation enables more sophisticated optimization strategies. As data volumes increase, startups can leverage analytics tools to identify usage patterns, predict future needs, and optimize license allocation. These insights become particularly valuable for organizations with seasonal usage patterns or project-based work cycles.
Vendor consolidation strategies may become advantageous as purchasing power increases. Larger startups can often negotiate enterprise agreements that bundle multiple tools from single vendors at discounted rates. However, consolidation decisions should prioritize functional fit over cost savings to avoid compromising operational efficiency.
Cross-functional optimization requires breaking down silos between departments to identify shared needs and potential efficiencies. As organizations grow, opportunities often emerge for shared services that can reduce per-user costs while improving functionality for all teams.
Strategic planning integration should incorporate SaaS spend management into broader business planning processes. Rather than treating software costs as isolated expenses, mature startups integrate these decisions into strategic planning cycles that align technology investments with business objectives.
Tools and Platforms for Effective SaaS Management
The irony of SaaS spend management is that it often requires additional SaaS tools to do effectively. However, the right management platforms can provide substantial returns on investment through optimization opportunities they enable.
Comprehensive spend management platforms like Binadox provide centralized visibility into all SaaS subscriptions across an organization. These platforms typically offer features like automated discovery of shadow IT, usage analytics, renewal tracking, and optimization recommendations. For startups with complex SaaS environments, these tools can quickly pay for themselves through identified savings.
Financial management integration becomes important as SaaS spend represents larger portions of overall budgets. Tools that integrate SaaS spend tracking with broader financial management systems provide better visibility into total cost structures and enable more accurate budgeting and forecasting.
Automated optimization features can help busy startup teams maintain efficient SaaS spend without constant manual oversight. Features like automated license reassignment, usage alerts, and renewal notifications help prevent common sources of waste while requiring minimal ongoing attention.
Vendor management capabilities help startups maintain better relationships with software providers while tracking contract terms, renewal dates, and negotiation opportunities. These features become particularly valuable as the number of vendor relationships grows.
Reporting and analytics functionality should provide insights that enable strategic decision-making rather than just expense tracking. The most valuable platforms offer predictive analytics that help forecast future costs under different growth scenarios and identify optimization opportunities before they become problems.
For startups implementing SaaS spend management strategies, the key is finding tools that provide immediate value while scaling with organizational needs. The investment in proper management infrastructure typically pays dividends through improved cost visibility and optimization opportunities.
Conclusion
Effective SaaS spend management represents a critical competency for modern startups navigating the balance between operational efficiency and budget constraints. As software continues to become the primary infrastructure for business operations, the ability to optimize these investments directly impacts both immediate cash flow and long-term growth potential.
The strategies outlined in this guide provide a framework for building sustainable SaaS management practices that evolve with organizational needs. From establishing centralized procurement processes to implementing sophisticated analytics platforms, startups have numerous tools available to optimize their software investments while maintaining the agility that competitive markets demand.
Success in SaaS spend management requires treating it as an ongoing strategic process rather than a periodic cost-cutting exercise. Organizations that embed these practices into their operational culture create sustainable competitive advantages through more efficient resource utilization and better strategic decision-making.
The investment in proper SaaS spend management infrastructure typically provides substantial returns through identified savings, improved operational efficiency, and better strategic alignment between technology investments and business objectives. For startups where every dollar counts, these benefits can significantly impact growth trajectories and market positioning.
As the SaaS ecosystem continues evolving with new distribution models, pricing structures, and integration capabilities, startups that master these management principles will be better positioned to leverage emerging opportunities while avoiding common pitfalls that drain resources and complicate operations.
By implementing comprehensive SaaS spend management strategies from early stages, startups create foundations for sustainable growth that maximize the value of their software investments while maintaining the financial flexibility necessary for success in dynamic markets.

