
In today’s cloud-driven business environment, organizations increasingly rely on Software as a Service (SaaS) applications to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and drive growth. However, this widespread adoption of SaaS solutions brings significant security and compliance challenges that demand careful attention. As businesses integrate multiple SaaS vendors into their software supply chain, conducting thorough vendor risk assessments becomes crucial for maintaining security, ensuring compliance, and protecting sensitive data.
The modern enterprise typically uses 80+ SaaS applications on average, making vendor risk management a complex but essential process. This comprehensive guide explores how to effectively audit your SaaS software supply chain, implement robust security measures, and maintain compliance across all vendor relationships.
Understanding SaaS Vendor Risk Assessment
SaaS vendor risk assessment is a systematic evaluation process that examines the security, compliance, and operational reliability of third-party software providers. This critical practice helps organizations identify potential vulnerabilities, ensure regulatory compliance, and make informed decisions about which SaaS solutions to integrate into their business operations.
The assessment encompasses several key areas including data security protocols, compliance certifications, business continuity measures, and vendor financial stability. By conducting thorough risk assessments, organizations can proactively address potential issues before they impact business operations or compromise sensitive information.
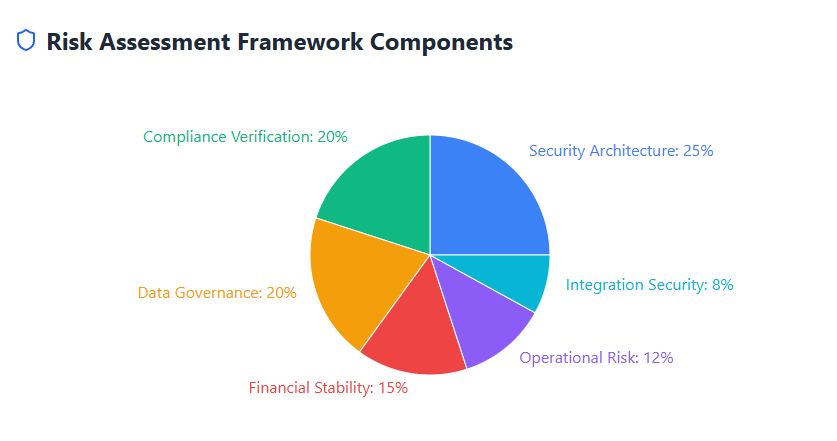
Key Components of Vendor Risk Assessment
Security Architecture Evaluation: This involves examining the vendor’s security infrastructure, including data encryption methods, access controls, authentication mechanisms, and network security measures. Organizations should verify that vendors implement industry-standard security practices and maintain robust cybersecurity frameworks.
Compliance Verification: Ensuring that SaaS vendors meet relevant regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, or industry-specific standards is crucial for maintaining organizational compliance. This verification process includes reviewing certification documents, audit reports, and compliance policies.
Data Governance Assessment: Understanding how vendors handle, store, and process organizational data is fundamental to risk assessment. This includes evaluating data retention policies, backup procedures, data portability options, and deletion processes.
Business Continuity Analysis: Assessing the vendor’s ability to maintain service availability, disaster recovery capabilities, and financial stability ensures long-term reliability of critical business applications.
The Growing Importance of SaaS Security
The shift toward cloud-based software solutions has fundamentally transformed how organizations approach IT security. Unlike traditional on-premises software where companies maintain direct control over their infrastructure, SaaS applications operate in shared responsibility models where security obligations are distributed between the vendor and the customer.
This shared responsibility model for cloud security requires organizations to understand exactly which security aspects they control and which remain under vendor management. The complexity increases exponentially when dealing with multiple SaaS providers, each with different security architectures and responsibility frameworks.
Emerging Security Challenges
Shadow IT Proliferation: Unmanaged SaaS adoption creates security blind spots where organizations lack visibility into which applications employees are using and how sensitive data is being handled. This Shadow IT phenomenon poses significant security risks that require proactive management strategies.
Data Sovereignty Issues: As organizations expand globally, understanding where SaaS vendors store and process data becomes crucial for compliance with regional data protection laws. Different jurisdictions have varying requirements for data localization and cross-border data transfers.
Integration Security Risks: Modern SaaS applications often integrate with numerous other systems through APIs and third-party connectors. Each integration point represents a potential security vulnerability that must be evaluated and monitored continuously.
Vendor Consolidation Risks: While using fewer vendors can simplify management, over-reliance on single providers creates concentration risks that can severely impact business operations if vendor services become unavailable.
Building a Comprehensive Vendor Assessment Framework
Creating an effective vendor risk assessment framework requires a structured approach that addresses all aspects of vendor evaluation and ongoing management. This framework should be scalable, consistent, and adaptable to different types of SaaS applications and risk levels.
Pre-Assessment Preparation
Before engaging with potential vendors, organizations should establish clear security and compliance requirements. This preparation phase involves defining risk tolerance levels, identifying critical data types, and establishing minimum security standards that all vendors must meet.
Risk Classification Matrix: Develop a classification system that categorizes SaaS applications based on their access to sensitive data, business criticality, and potential impact if compromised. This matrix helps prioritize assessment efforts and allocate appropriate resources to high-risk vendors.
Security Requirements Documentation: Create detailed security requirement documents that outline mandatory security controls, compliance certifications, and operational standards. These requirements serve as evaluation criteria during the vendor selection process.
Assessment Team Formation: Assemble a cross-functional team including IT security professionals, compliance specialists, legal experts, and business stakeholders. This diverse team ensures comprehensive evaluation from multiple perspectives.
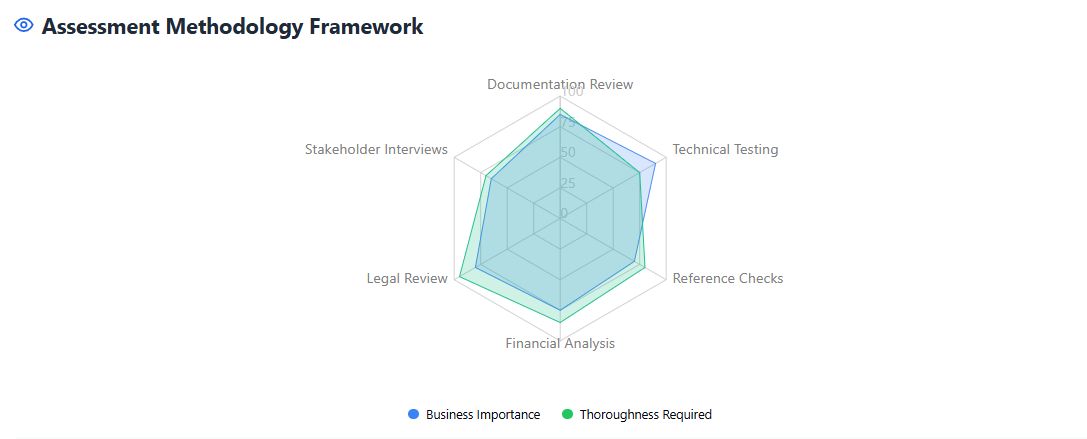
Security Assessment Methodology
A thorough security assessment examines multiple layers of vendor security architecture and operational practices. This multi-faceted approach ensures no critical security aspects are overlooked during the evaluation process.
Infrastructure Security Review: Evaluate the vendor’s cloud infrastructure security, including physical security measures, network architecture, server hardening practices, and vulnerability management programs. Request detailed documentation about their hosting environment and security controls.
Application Security Analysis: Examine the security of the SaaS application itself, including secure coding practices, input validation mechanisms, session management, and protection against common vulnerabilities such as those identified in the OWASP Top 10.
Data Protection Evaluation: Assess how vendors protect data at rest and in transit, including encryption algorithms used, key management practices, and data loss prevention measures. Verify that encryption meets current industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Access Control Assessment: Review vendor access control mechanisms including user authentication methods, authorization frameworks, privileged access management, and audit logging capabilities. Ensure that role-based access controls are properly implemented and regularly reviewed.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory compliance represents one of the most critical aspects of SaaS vendor risk assessment. Organizations must ensure that their chosen vendors meet all applicable regulatory requirements and can demonstrate ongoing compliance through regular audits and certifications.
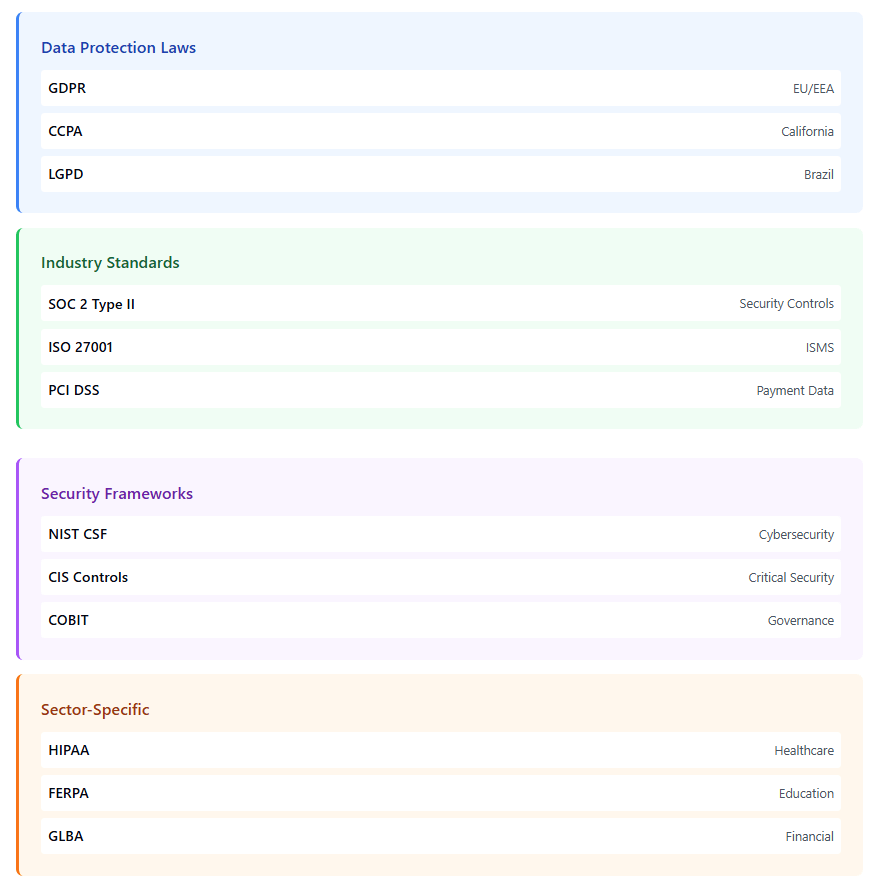
Key Compliance Frameworks
SOC 2 Type II Compliance: Service Organization Control (SOC) 2 reports provide detailed information about a vendor’s internal controls related to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. Type II reports are particularly valuable as they test the effectiveness of controls over time rather than just their existence.
ISO 27001 Certification: This international standard for information security management systems demonstrates that vendors have implemented comprehensive security management practices. Look for vendors with current ISO 27001 certifications and regular surveillance audits.
Industry-Specific Compliance: Depending on your industry, vendors may need to comply with specific regulations such as HIPAA for healthcare, PCI DSS for payment processing, or FERPA for educational institutions. Verify that vendors understand and meet these specialized requirements.
Regional Data Protection Laws: With the implementation of GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and similar laws in other jurisdictions, vendors must demonstrate compliance with applicable data protection regulations. This includes having proper data processing agreements, privacy impact assessments, and breach notification procedures.
Ongoing Compliance Monitoring
Compliance is not a one-time assessment but requires continuous monitoring and verification. Establish processes to regularly review vendor compliance status and respond to any changes in regulatory requirements or vendor certifications.
Regular Audit Review: Schedule periodic reviews of vendor audit reports and compliance certifications. Set up alerts for when certifications are due for renewal to ensure continuous compliance coverage.
Breach Notification Procedures: Establish clear procedures for how vendors must notify your organization of security incidents or compliance violations. Ensure that notification timelines meet regulatory requirements and internal policies.
Compliance Gap Analysis: Regularly assess whether vendor compliance capabilities continue to meet evolving regulatory requirements. This is particularly important as new regulations are introduced or existing ones are updated.
Data Governance and Privacy Assessment
Effective data governance is essential for managing risks associated with SaaS vendor relationships. Organizations must understand exactly how their data is collected, processed, stored, and potentially shared by vendors.
Data Flow Mapping
Create comprehensive data flow maps that document how data moves between your organization and SaaS vendors, including any sub-processors or third parties that may have access to your data. This mapping exercise helps identify potential privacy risks and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
Data Classification: Work with vendors to classify the types of data being processed and stored. Different data types may require different levels of protection and may be subject to different regulatory requirements.
Cross-Border Data Transfers: If vendors store or process data in multiple jurisdictions, understand the legal frameworks governing these transfers. Ensure appropriate safeguards are in place, such as Standard Contractual Clauses or adequacy decisions.
Data Retention and Deletion: Establish clear policies for how long vendors will retain your data and procedures for secure data deletion when the business relationship ends. Verify that vendors can provide certificates of data destruction when required.
Privacy Impact Assessment
Conduct privacy impact assessments (PIAs) for high-risk SaaS implementations to identify and mitigate potential privacy risks. These assessments help ensure compliance with privacy regulations and demonstrate due diligence in protecting personal data.
Third-Party Risk Evaluation: Assess whether vendors use sub-processors and understand the privacy implications of these relationships. Ensure that the same privacy standards apply throughout the entire processing chain.
Individual Rights Management: Verify that vendors can support your obligations under privacy laws, such as providing data access, rectification, portability, and deletion upon request from data subjects.
Financial and Operational Risk Assessment
Beyond security and compliance considerations, organizations must evaluate the financial stability and operational reliability of SaaS vendors. These factors directly impact business continuity and the long-term viability of vendor relationships.
Financial Stability Analysis
Financial Health Review: Analyze vendor financial statements, credit ratings, and market position to assess their long-term viability. This is particularly important for smaller or newer SaaS providers that may face greater financial uncertainty.
Funding and Investment History: Review the vendor’s funding history, investor relationships, and growth trajectory. Understanding their financial backing helps assess their ability to continue operations and invest in security improvements.
Market Competition Analysis: Evaluate the competitive landscape to understand market pressures that might affect vendor stability or pricing. Consider whether the vendor has sustainable competitive advantages and a clear path to profitability.
Business Continuity Assessment
Disaster Recovery Capabilities: Evaluate vendor disaster recovery plans, backup procedures, and recovery time objectives. Ensure that these align with your organization’s business continuity requirements and that recovery plans are regularly tested.
Service Level Agreements: Review SLA terms carefully, paying attention to uptime guarantees, response times for support requests, and penalties for service failures. Ensure that SLAs are measurable, enforceable, and aligned with business needs.
Exit Strategy Planning: Develop comprehensive exit strategies that include data export procedures, transition timelines, and contingency plans for vendor service disruptions. Having effective SaaS renewal strategies helps manage these transitions smoothly.
Technology and Integration Risk Assessment
The technical architecture and integration capabilities of SaaS vendors significantly impact both security posture and operational efficiency. A thorough technical assessment ensures that vendor solutions integrate securely with existing systems and support scalability requirements.
API Security Evaluation
Authentication and Authorization: Assess how vendors secure their APIs, including authentication mechanisms, token management, and authorization controls. Ensure that API access follows the principle of least privilege and includes proper rate limiting.
Data Transmission Security: Verify that all API communications use current encryption standards and that vendors regularly update their security protocols. Check for support of modern TLS versions and proper certificate management.
API Monitoring and Logging: Evaluate vendor capabilities for monitoring API usage, detecting anomalies, and providing detailed audit logs. This visibility is crucial for detecting potential security incidents and ensuring compliance.
Integration Architecture Review
Single Sign-On (SSO) Support: Assess vendor support for enterprise SSO solutions and their compatibility with your existing identity management infrastructure. Proper SSO implementation reduces password-related security risks and improves user experience.
Identity and Access Management: Review how vendor systems integrate with your identity management platforms and whether they support modern authentication protocols such as SAML 2.0 or OpenID Connect.
Third-Party Integration Security: If the SaaS application integrates with other systems through third-party connectors or middleware, evaluate the security implications of these integration points and ensure proper access controls are maintained.
Vendor Due Diligence Process
Implementing a systematic due diligence process ensures consistent and thorough evaluation of all potential SaaS vendors. This process should be documented, repeatable, and scalable across different types of applications and risk levels.
Information Gathering Phase
Security Questionnaires: Develop comprehensive security questionnaires that cover all aspects of vendor security, compliance, and operational practices. Standardize these questionnaires to enable consistent comparison across vendors.
Documentation Review: Request and review key vendor documents including security policies, incident response plans, business continuity procedures, and compliance certifications. Verify that documentation is current and regularly updated.
Reference Checks: Contact existing vendor customers, particularly those in similar industries or with comparable security requirements. These references provide valuable insights into vendor performance and reliability.
Technical Validation
Penetration Testing Results: Review vendor penetration testing reports and vulnerability assessments. Ensure that vendors conduct regular security testing and promptly address identified vulnerabilities.
Security Architecture Deep Dive: Conduct detailed reviews of vendor security architecture, including network design, data flow diagrams, and security control implementations. This technical assessment helps identify potential security gaps.
Performance and Scalability Testing: Evaluate vendor system performance under various load conditions and assess their ability to scale with your organization’s growth. Poor performance can impact business operations and user productivity.
Ongoing Vendor Management and Monitoring
Vendor risk assessment is not a one-time activity but requires continuous monitoring and management throughout the vendor relationship lifecycle. Establishing ongoing oversight processes helps identify emerging risks and ensures vendor performance remains aligned with organizational requirements.
Continuous Monitoring Framework
Regular Risk Reassessment: Schedule periodic risk reassessments to account for changes in vendor services, security posture, or compliance status. The frequency of reassessments should be based on the vendor’s risk level and the criticality of their services.
Security Incident Monitoring: Establish processes to monitor vendor security incidents and assess their potential impact on your organization. This includes tracking public security breaches, vendor security advisories, and industry threat intelligence.
Performance Metrics Tracking: Implement systems to continuously monitor vendor performance against established SLAs and key performance indicators. Regular performance reviews help identify potential issues before they impact business operations.
Vendor Relationship Management
Regular Business Reviews: Conduct periodic business reviews with key vendors to discuss performance, upcoming changes, and strategic alignment. These reviews provide opportunities to address concerns and negotiate improvements.
Contract Management: Maintain current vendor contracts and monitor key dates such as renewal periods, price escalation clauses, and termination notice requirements. Proactive contract management helps avoid unexpected costs or service disruptions.
Change Management: Establish procedures for managing vendor changes that might impact security or compliance posture. This includes new feature releases, infrastructure changes, and acquisition or merger activities.
Implementing SaaS Management Tools for Risk Oversight
Modern SaaS management tools provide essential capabilities for maintaining visibility and control over vendor relationships. These platforms help organizations discover shadow IT, monitor usage patterns, and ensure compliance across their entire SaaS portfolio.
Key Management Capabilities
Discovery and Inventory: Use automated discovery tools to maintain accurate inventories of all SaaS applications in use across your organization. This visibility is essential for effective risk management and compliance oversight.
Usage Analytics: Monitor actual usage patterns to identify underutilized applications, security risks from inactive accounts, and opportunities for SaaS optimization. Usage analytics help inform renewal decisions and license rightsizing.
Compliance Monitoring: Implement automated monitoring for compliance status, certification renewals, and security incidents across all vendor relationships. Automated alerts ensure timely response to compliance issues.
Cost Management: Track vendor costs and identify opportunities for cost optimization. Understanding the total cost of SaaS relationships helps make informed decisions about vendor selection and contract negotiations.
Integration with Risk Management Processes
Workflow Automation: Automate routine risk management tasks such as vendor assessments, compliance monitoring, and renewal processes. Automation reduces manual effort and ensures consistent application of risk management procedures.
Risk Scoring and Prioritization: Implement automated risk scoring systems that help prioritize vendor management activities based on risk levels, business criticality, and compliance requirements.
Reporting and Analytics: Generate comprehensive reports on vendor risk posture, compliance status, and performance metrics. These reports support executive decision-making and regulatory reporting requirements.
Building Vendor Risk Culture and Awareness
Creating a strong vendor risk culture requires organization-wide awareness and commitment to proper vendor management practices. This cultural foundation supports effective risk management and ensures consistent application of vendor assessment procedures.
Training and Education Programs
Employee Awareness: Develop training programs that educate employees about vendor risk management, appropriate SaaS usage, and their role in maintaining security and compliance. Regular awareness training helps prevent shadow IT adoption and security incidents.
Procurement Training: Train procurement professionals on security and compliance requirements for SaaS vendors. This education ensures that risk considerations are integrated into the vendor selection process from the beginning.
Executive Education: Provide executive leadership with education on vendor risk management, regulatory requirements, and business implications of vendor security incidents. Executive support is crucial for maintaining adequate investment in risk management capabilities.
Policy Development and Enforcement
Vendor Risk Policies: Develop comprehensive policies that define vendor risk management procedures, approval processes, and ongoing management requirements. Clear policies provide consistent guidance for vendor management activities.
Procurement Policies: Integrate security and compliance requirements into procurement policies to ensure that all vendor selections include appropriate risk assessments. This integration prevents security gaps and compliance violations.
Incident Response Procedures: Establish clear procedures for responding to vendor security incidents, compliance violations, and service disruptions. Well-defined procedures ensure rapid response and minimize business impact.
Future Trends in SaaS Vendor Risk Management
The landscape of SaaS vendor risk management continues to evolve with technological advances, regulatory changes, and emerging security threats. Understanding these trends helps organizations prepare for future challenges and opportunities.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI-powered tools are increasingly being used for automated vendor risk assessment, anomaly detection, and predictive risk analytics. These technologies can process large volumes of vendor data and identify patterns that might indicate emerging risks.
Zero Trust Security Models: The adoption of zero trust security architectures is changing how organizations approach vendor access controls and security monitoring. This model requires continuous verification of all access requests, regardless of source.
Quantum Computing Implications: As quantum computing technology advances, organizations must consider the long-term implications for encryption and data security. Vendors must demonstrate plans for quantum-resistant security measures.
Regulatory Evolution
Enhanced Data Protection Laws: New privacy regulations continue to emerge globally, requiring organizations to reassess vendor compliance capabilities and data protection measures. Staying current with regulatory changes is essential for maintaining compliance.
Supply Chain Security Regulations: Governments are increasingly focusing on supply chain security, which may result in new requirements for vendor risk assessment and management in critical industries.
Cross-Border Data Governance: International agreements and frameworks for cross-border data transfers continue to evolve, affecting how organizations assess and manage vendor relationships across different jurisdictions.
Conclusion
Effective SaaS vendor risk assessment requires a comprehensive, systematic approach that addresses security, compliance, operational, and financial considerations. Organizations must develop robust frameworks for evaluating vendors, implement continuous monitoring processes, and maintain strong governance over their entire software supply chain.
The complexity of modern SaaS environments demands sophisticated management tools and processes that can provide visibility, control, and automation across vendor relationships. By implementing the assessment frameworks, monitoring capabilities, and governance structures outlined in this guide, organizations can effectively manage vendor risks while realizing the full benefits of cloud-based software solutions.
Success in SaaS vendor risk management requires ongoing commitment, adequate resources, and organizational culture that prioritizes security and compliance. As the SaaS landscape continues to evolve, organizations that invest in comprehensive vendor risk management capabilities will be better positioned to navigate emerging challenges and maintain competitive advantages in the digital economy.
Through proper implementation of vendor risk assessment processes, continuous monitoring, and proactive management of vendor relationships, organizations can confidently leverage SaaS solutions while maintaining appropriate levels of security, compliance, and operational resilience. The investment in comprehensive vendor risk management pays dividends through reduced security incidents, improved compliance posture, and more reliable business operations.

