
Software as a Service (SaaS) adoption has transformed how organizations operate, offering unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, this digital transformation brings significant governance and compliance challenges that many organizations struggle to address effectively. The rapid proliferation of SaaS applications across enterprise environments creates a complex web of regulatory, security, and financial risks that require careful management.
The intersection of SaaS spend management and compliance alignment represents one of the most critical challenges facing modern organizations. As businesses increasingly rely on diverse SaaS solutions to drive operations, the need for robust governance frameworks that ensure regulatory compliance while optimizing costs becomes paramount. This challenge is particularly acute for organizations operating in highly regulated industries where compliance failures can result in substantial financial penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
The complexity of governance risk in SaaS environments stems from several factors: the distributed nature of SaaS procurement decisions, the difficulty of maintaining visibility across all SaaS subscriptions, the challenge of ensuring consistent security and compliance standards across multiple vendors, and the need to balance cost optimization with risk management. Organizations must navigate these challenges while ensuring that their SaaS management approach aligns with both internal governance policies and external regulatory requirements.
This comprehensive guide explores the strategies, frameworks, and tools necessary to tackle governance risk while maintaining effective SaaS spend management. By understanding the relationship between compliance requirements and SaaS spending decisions, organizations can build resilient governance frameworks that support both operational efficiency and regulatory adherence.
Understanding SaaS Governance and Compliance Challenges
The modern enterprise SaaS landscape presents unique governance challenges that differ significantly from traditional software deployment models. Unlike on-premises solutions where organizations maintain direct control over infrastructure and data, SaaS applications introduce shared responsibility models that can obscure accountability and create compliance gaps.
One of the primary governance challenges in SaaS environments is the phenomenon of shadow IT, where employees and departments independently procure SaaS solutions without going through formal approval processes. This decentralized adoption pattern, while often driving innovation and productivity, creates significant risks from both compliance and cost management perspectives. Organizations may find themselves using SaaS applications that don’t meet regulatory requirements, lack proper security controls, or duplicate functionality across multiple departments.
The compliance landscape for SaaS applications is particularly complex because it requires organizations to understand and manage risks across multiple dimensions simultaneously. Data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA impose strict requirements on how personal and sensitive data is processed, stored, and transmitted. When this data flows through SaaS applications, organizations must ensure that their vendors maintain appropriate security controls, data residency requirements, and breach notification procedures.
Financial compliance adds another layer of complexity to SaaS governance. Organizations subject to financial regulations like SOX, PCI DSS, or banking regulations must ensure that their SaaS applications meet stringent controls around financial data processing, audit trails, and segregation of duties. The subscription-based nature of SaaS solutions also creates ongoing compliance obligations, as organizations must continuously monitor vendor certifications, security postures, and compliance attestations.
The distributed nature of SaaS procurement compounds these challenges by making it difficult to maintain centralized oversight of compliance obligations. Different departments may select SaaS solutions based primarily on functional requirements without fully considering compliance implications. This can result in a patchwork of applications with varying levels of compliance maturity, creating gaps that expose the organization to regulatory risk.
The Risk Landscape in SaaS Environments
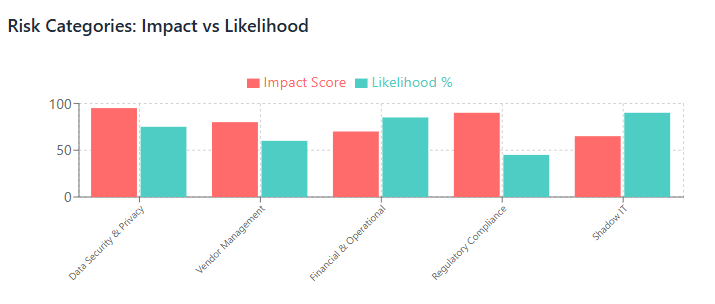
Understanding the full spectrum of risks in SaaS environments is essential for developing effective governance strategies. These risks can be categorized into several key areas: data security and privacy risks, vendor management risks, financial and operational risks, and regulatory compliance risks.
Data security and privacy risks represent perhaps the most significant concern for organizations adopting SaaS solutions. When sensitive data is processed or stored in SaaS applications, organizations must rely on vendor security controls rather than maintaining direct control over data protection measures. This creates risks related to data breaches, unauthorized access, data loss, and inadequate encryption. The multi-tenant nature of many SaaS applications adds complexity, as organizations must trust that proper isolation exists between different customers’ data.
Vendor management risks emerge from the need to rely on third-party providers for critical business functions. These risks include vendor financial stability, service availability, data portability, and the potential for vendor lock-in. Organizations must also consider the compliance implications of vendor changes, such as mergers, acquisitions, or changes in service terms that could affect regulatory compliance.
Financial and operational risks in SaaS environments include subscription sprawl, where organizations accumulate multiple subscriptions that may overlap in functionality or go unused. This not only increases costs but can also create compliance risks if unused applications contain sensitive data or maintain access to corporate systems. Additionally, the subscription-based pricing model can make it difficult to predict and control costs, particularly when usage-based pricing models are involved.
Regulatory compliance risks arise when SaaS applications don’t meet specific regulatory requirements or when organizations fail to properly assess and monitor vendor compliance capabilities. These risks are particularly acute for organizations in highly regulated industries where non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties, operational restrictions, or reputational damage.
The interconnected nature of these risks means that governance failures in one area can cascade into other areas, amplifying the overall risk profile. For example, a data breach in a SaaS application could trigger regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and financial losses simultaneously.
Building a Compliance-Aligned SaaS Governance Framework
Developing an effective SaaS governance framework requires a systematic approach that addresses both cost optimization and compliance requirements. This framework should establish clear policies, procedures, and controls that govern how SaaS applications are selected, implemented, managed, and decommissioned throughout their lifecycle.
The foundation of any effective SaaS governance framework is a comprehensive risk assessment process that evaluates both functional and compliance requirements before SaaS procurement decisions are made. This assessment should consider data classification requirements, regulatory obligations, security standards, integration needs, and total cost of ownership. Organizations should develop standardized evaluation criteria that balance functional capabilities with compliance requirements, ensuring that cost considerations don’t override essential governance needs.
Central to the governance framework is the establishment of clear roles and responsibilities for SaaS management. This includes defining who has authority to procure SaaS solutions, who is responsible for ongoing compliance monitoring, and how different departments coordinate on SaaS-related decisions. Many organizations benefit from establishing a SaaS governance committee that includes representatives from IT, legal, compliance, procurement, and business units to ensure that all perspectives are considered in governance decisions.
Policy development is another critical component of the governance framework. Organizations need clear policies that address SaaS procurement processes, data handling requirements, security standards, vendor management protocols, and compliance monitoring procedures. These policies should be specific enough to provide clear guidance but flexible enough to accommodate the diverse needs of different business units and use cases.
The governance framework should also establish standardized processes for SaaS lifecycle management, including vendor due diligence, contract negotiation, implementation oversight, ongoing monitoring, and decommissioning procedures. Each of these processes should include specific compliance checkpoints and approval gates to ensure that governance requirements are met throughout the SaaS lifecycle.
Technology plays a crucial role in enabling effective SaaS governance. Organizations should implement SaaS management tools that provide visibility into SaaS usage, costs, and compliance status. These tools should support automated discovery of SaaS applications, centralized contract and vendor management, usage monitoring, and compliance reporting capabilities.
SaaS Spend Management Through a Compliance Lens
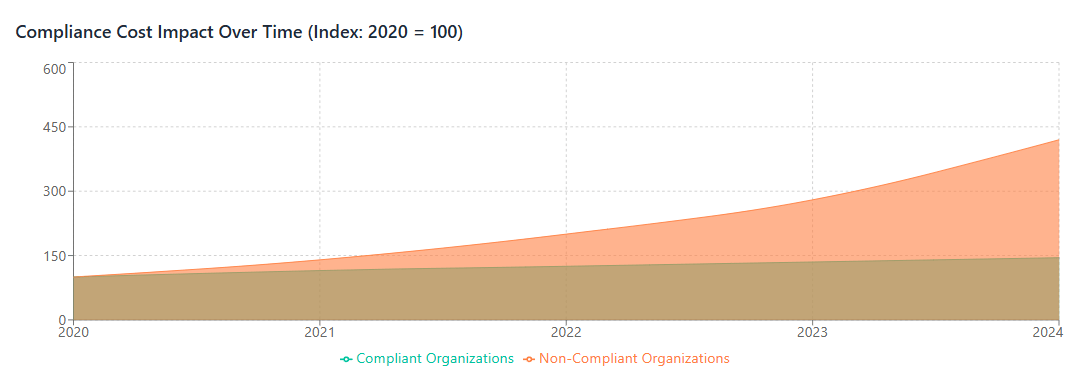
Effective SaaS spend management in a compliance-focused environment requires organizations to consider total cost of ownership beyond just subscription fees. Compliance-related costs can include vendor due diligence activities, compliance monitoring tools, audit fees, legal reviews, and potential penalties for non-compliance. Organizations must factor these costs into their SaaS procurement decisions to make informed choices that balance functionality, cost, and risk.
The procurement process itself should be designed to support both cost optimization and compliance objectives. This includes establishing preferred vendor programs that pre-approve SaaS providers who meet compliance requirements, implementing standardized contract terms that address compliance obligations, and developing procurement workflows that include compliance reviews as part of the approval process.
Budget allocation for SaaS solutions should include dedicated funding for compliance-related activities such as vendor assessments, security reviews, and ongoing monitoring. Organizations should also maintain contingency funding for compliance remediation activities that may be required if governance gaps are identified.
Cost optimization strategies must be balanced against compliance requirements. For example, while consolidating SaaS vendors might reduce costs, organizations must ensure that consolidated solutions still meet all regulatory requirements. Similarly, while moving to lower-cost SaaS alternatives might be attractive from a budget perspective, organizations must verify that these alternatives maintain appropriate compliance capabilities.
Regular SaaS renewal processes should include compliance reviews to ensure that vendors continue to meet regulatory requirements and that contract terms remain appropriate for the organization’s compliance needs. This is particularly important as regulatory requirements evolve and as organizations’ compliance obligations change over time.
Organizations should also implement chargeback or cost allocation models that appropriately attribute compliance-related costs to the business units that benefit from SaaS solutions. This helps ensure that business units make informed decisions about SaaS procurement that consider both functional benefits and compliance costs.
Regulatory Requirements and SaaS Procurement
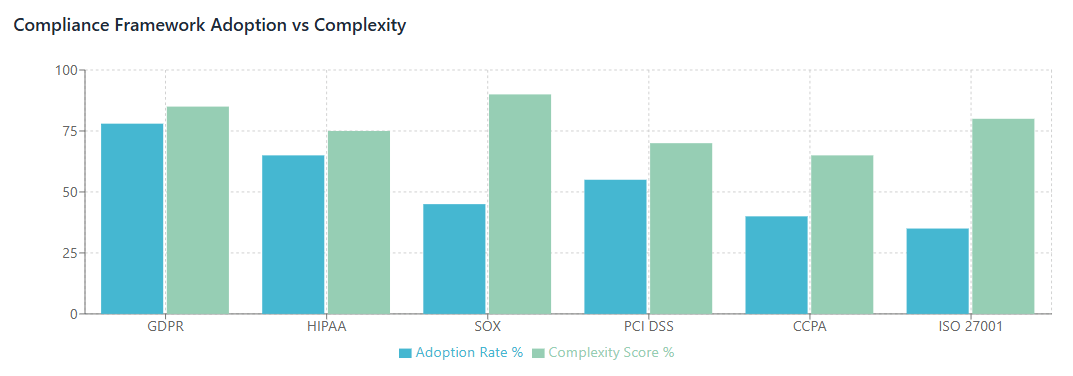
Different regulatory frameworks impose specific requirements that must be considered during SaaS procurement and management processes. Understanding these requirements and how they apply to SaaS environments is essential for maintaining compliance while optimizing costs.
Data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA impose strict requirements on how personal data is processed, stored, and transferred. For SaaS applications that process personal data, organizations must ensure that vendors provide appropriate data processing agreements, maintain adequate security controls, support data subject rights, and comply with data residency requirements. The cost of compliance with these regulations can be significant, including fees for data protection impact assessments, privacy-enhancing technologies, and breach response capabilities.
Financial services regulations such as SOX, GLBA, and PCI DSS require specific controls around financial data processing and system access. SaaS applications used in financial services environments must maintain appropriate audit trails, support segregation of duties requirements, and provide necessary reporting capabilities for regulatory examinations. Organizations must also ensure that SaaS vendors maintain appropriate certifications and can provide necessary compliance documentation.
Healthcare organizations must consider HIPAA requirements when procuring SaaS solutions that process protected health information. This includes ensuring that vendors will sign business associate agreements, maintain appropriate security controls, and support breach notification requirements. The specialized nature of healthcare compliance often limits SaaS options and can increase costs compared to less regulated industries.
Industry-specific regulations may impose additional requirements that affect SaaS procurement decisions. For example, organizations in the defense industry must consider ITAR compliance, while pharmaceutical companies must address FDA validation requirements. These specialized compliance needs often require working with SaaS vendors who have specific industry expertise and certifications.
International organizations face additional complexity from cross-border data transfer requirements and varying regulatory frameworks in different jurisdictions. SaaS procurement decisions must consider data residency requirements, adequacy decisions for international data transfers, and the need to comply with multiple regulatory frameworks simultaneously.
Automated Compliance Monitoring for SaaS
Manual compliance monitoring for SaaS applications becomes impractical as organizations scale their SaaS portfolios. Automated monitoring solutions are essential for maintaining visibility into compliance status, identifying potential risks, and ensuring ongoing adherence to regulatory requirements.
Automated SaaS discovery tools help organizations maintain comprehensive inventories of SaaS applications in use across the enterprise. These tools can identify shadow IT applications, track usage patterns, and provide visibility into data flows between SaaS applications and corporate systems. This visibility is essential for compliance monitoring, as organizations cannot manage compliance for applications they don’t know exist.
Continuous compliance monitoring involves automated assessment of SaaS vendor compliance postures, including monitoring of security certifications, compliance attestations, and incident reports. Organizations should implement tools that can automatically track vendor compliance status and alert stakeholders when compliance issues arise or certifications expire.
Configuration monitoring ensures that SaaS applications are configured according to organizational security and compliance standards. This includes monitoring user access controls, data handling settings, integration configurations, and security settings. Automated tools can identify configuration drift and ensure that compliance-critical settings are maintained over time.
Data flow monitoring helps organizations understand how data moves between SaaS applications and other systems, which is essential for compliance with data protection regulations. Automated data classification and monitoring tools can identify when sensitive data is being processed by SaaS applications and ensure that appropriate controls are in place.
Reporting and analytics capabilities provide stakeholders with visibility into compliance status across the SaaS portfolio. Automated reporting can support regulatory examinations, internal audits, and management oversight by providing comprehensive views of compliance metrics, risk indicators, and remediation activities.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Effective risk mitigation in SaaS environments requires a multi-layered approach that addresses risks at the vendor, application, data, and process levels. Organizations should implement both preventive controls that reduce the likelihood of compliance issues and detective controls that identify problems when they occur.
Vendor risk mitigation begins with thorough due diligence processes that evaluate vendor compliance capabilities, financial stability, and security postures. Organizations should maintain approved vendor lists that pre-qualify SaaS providers based on compliance requirements and should regularly reassess vendor risk profiles. Contractual risk mitigation involves negotiating terms that appropriately allocate compliance responsibilities, include necessary compliance warranties, and provide audit rights and compliance reporting requirements.
Technical risk mitigation strategies include implementing data loss prevention tools, encryption solutions, and access controls that provide additional protection for sensitive data processed in SaaS applications. Organizations should also implement network controls that monitor and control data flows between SaaS applications and corporate systems.
Process-based risk mitigation involves establishing clear procedures for SaaS lifecycle management, incident response, and compliance monitoring. These processes should include regular compliance assessments, vendor management reviews, and employee training programs that help ensure that SaaS applications are used in compliance with organizational policies and regulatory requirements.
Cloud cost optimization strategies should also consider risk mitigation benefits. For example, implementing automated cost controls can help prevent unauthorized SaaS spending that might circumvent compliance processes. Similarly, rightsizing SaaS subscriptions can reduce the attack surface and compliance scope by eliminating unnecessary access and functionality.
Incident response planning specifically for SaaS environments should address scenarios such as vendor security breaches, service outages, and compliance violations. Organizations should maintain playbooks that define roles, responsibilities, and procedures for responding to different types of SaaS-related incidents while meeting regulatory notification requirements.
Industry-Specific Compliance Considerations
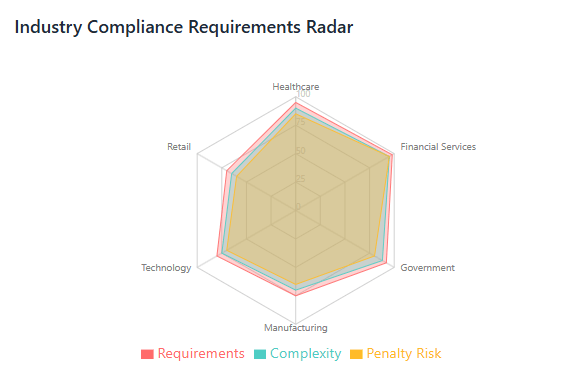
Different industries face unique compliance challenges that affect how organizations approach SaaS governance and spend management. Understanding these industry-specific requirements is essential for developing appropriate governance frameworks and making informed SaaS procurement decisions.
Healthcare organizations must navigate HIPAA compliance requirements that impose strict controls on protected health information. SaaS applications used in healthcare environments must support business associate agreements, maintain appropriate security controls, and provide audit trails for access to patient data. The specialized nature of healthcare compliance often limits SaaS options and requires working with vendors who have specific healthcare expertise.
Financial services organizations face complex regulatory requirements from multiple agencies including banking regulators, securities regulators, and consumer protection agencies. SaaS applications used in financial services must support stringent audit requirements, maintain appropriate data retention capabilities, and provide necessary reporting for regulatory examinations. The high-risk nature of financial services also requires more rigorous vendor management and ongoing monitoring processes.
Government agencies and contractors must consider additional requirements such as FedRAMP authorization for cloud services, ITAR compliance for defense-related data, and various security clearance requirements. These specialized compliance needs often significantly limit SaaS options and can increase costs due to the specialized nature of compliant solutions.
Manufacturing and critical infrastructure organizations must consider regulations such as NERC CIP for electric utilities, FDA regulations for pharmaceutical manufacturing, and various safety and environmental regulations. SaaS applications used in these environments must support specialized compliance requirements and may need to integrate with operational technology systems.
International organizations face the additional complexity of complying with multiple regulatory frameworks simultaneously. This includes managing data residency requirements, cross-border data transfer restrictions, and varying privacy and security requirements across different jurisdictions.
Tools and Technologies for Governance Alignment
Implementing effective SaaS governance requires leveraging appropriate tools and technologies that support both compliance monitoring and cost optimization objectives. Organizations should evaluate and implement solutions that provide comprehensive visibility, automated monitoring, and integrated risk management capabilities.
SaaS management platforms provide centralized visibility into SaaS usage, costs, and compliance status across the enterprise. These platforms should support automated SaaS discovery, contract and vendor management, usage monitoring, and compliance reporting. Leading solutions integrate with financial systems to provide comprehensive cost tracking and with security tools to monitor compliance postures.
Cloud cost intelligence tools help organizations understand the total cost of ownership for SaaS solutions, including compliance-related costs. These tools should provide detailed cost analytics, budget tracking, and forecasting capabilities that help organizations make informed decisions about SaaS investments.
Governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) platforms provide frameworks for managing compliance requirements across SaaS portfolios. These platforms should support risk assessment workflows, compliance monitoring, vendor management, and audit reporting capabilities. Integration with SaaS management tools helps ensure that compliance considerations are embedded in SaaS procurement and management processes.
Identity and access management (IAM) solutions help organizations maintain appropriate controls over SaaS access while supporting compliance requirements. These solutions should provide single sign-on capabilities, multi-factor authentication, privileged access management, and comprehensive audit trails for SaaS access.
Data protection and privacy tools help organizations monitor and control sensitive data in SaaS environments. These tools should provide data discovery and classification capabilities, data loss prevention, encryption management, and privacy impact assessment support.
Future-Proofing Your SaaS Governance Strategy
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with new privacy laws, security requirements, and industry-specific regulations being introduced regularly. Organizations must build governance frameworks that can adapt to changing requirements while maintaining cost effectiveness and operational efficiency.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are being increasingly integrated into SaaS solutions, creating new compliance considerations around algorithmic bias, data ethics, and AI governance. Organizations should anticipate these developments and ensure that their governance frameworks can address emerging AI-related compliance requirements.
The trend toward industry-specific SaaS solutions means that organizations may need to work with more specialized vendors who understand specific regulatory requirements. This specialization can provide compliance benefits but may also increase costs and reduce vendor options. Organizations should plan for this evolution in their vendor management and procurement strategies.
Regulatory convergence trends, such as the increasing alignment between privacy regulations globally, may simplify some aspects of compliance while creating new requirements in others. Organizations should monitor regulatory developments and adjust their governance frameworks accordingly.
The increasing importance of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) considerations in business operations is also affecting SaaS procurement decisions. Organizations may need to evaluate SaaS vendors based on their own ESG practices and ensure that SaaS usage aligns with broader sustainability and social responsibility objectives.
Conclusion
Successfully tackling governance risk while maintaining effective SaaS spend management requires a comprehensive approach that balances cost optimization with compliance requirements. Organizations must develop robust governance frameworks that address the unique challenges of SaaS environments while providing the flexibility needed to support business innovation and growth.
The key to success lies in understanding that compliance and cost optimization are not opposing objectives but complementary aspects of effective SaaS management. By implementing appropriate governance frameworks, leveraging automation tools, and maintaining focus on both cost and compliance objectives, organizations can build resilient SaaS portfolios that support business objectives while managing regulatory risks.
As the SaaS landscape continues to evolve, organizations that invest in strong governance capabilities will be better positioned to take advantage of new opportunities while managing emerging risks. The integration of compliance considerations into SaaS spend management processes helps ensure that cost optimization efforts don’t compromise regulatory compliance, while compliance-focused governance frameworks support informed decision-making about SaaS investments.
The future of SaaS governance will likely involve increased automation, more sophisticated risk assessment capabilities, and greater integration between compliance and cost management processes. Organizations that begin building these capabilities now will be better prepared to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape while maximizing the value of their SaaS investments.
Through careful planning, appropriate tool selection, and ongoing attention to both compliance and cost considerations, organizations can successfully align their SaaS governance strategies with their broader business objectives, creating sustainable competitive advantages in an increasingly digital business environment.

