The modern SaaS ecosystem has transformed how organizations approach software deployment and customization. With businesses using an average of 80 SaaS applications, the question is no longer whether to adopt cloud-based solutions, but rather how to optimize them for maximum value. The economics of SaaS customization presents three primary pathways: configuring existing features, integrating with other systems, or building custom solutions from scratch.
Understanding when to pursue each approach requires a comprehensive analysis of costs, benefits, risks, and long-term strategic alignment. This decision-making framework becomes increasingly critical as SaaS spending continues to grow, with the global market projected to reach $601 billion by 2028, representing a 26.7% compound annual growth rate.
Understanding SaaS Customization Options
The Three Pillars of SaaS Customization
Modern SaaS platforms offer unprecedented flexibility through three distinct customization approaches, each with unique economic implications and technical considerations.
Configuration represents the most accessible form of customization, leveraging built-in features and settings within existing SaaS applications. This approach utilizes the native capabilities that vendors have designed into their platforms, allowing organizations to tailor functionality without requiring additional development resources or third-party interventions.
Integration involves connecting multiple SaaS applications or linking SaaS solutions with existing on-premises systems to create cohesive workflows. This approach capitalizes on the distributed nature of modern software ecosystems, where specialized tools excel in specific domains but require coordination to deliver comprehensive business value.
Building custom solutions entails developing proprietary functionality either within existing SaaS platforms through APIs and custom code or creating entirely new applications to address unique business requirements. This approach offers maximum control and specificity but requires significant investment in development resources and ongoing maintenance.
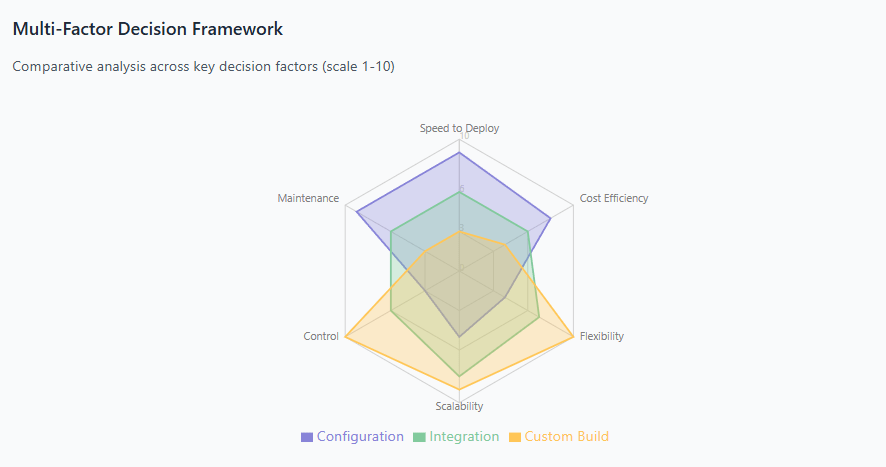
The economic implications of each approach vary dramatically based on factors including organizational size, technical complexity, regulatory requirements, and long-term strategic objectives. Companies must evaluate not only immediate costs but also hidden expenses, scalability limitations, and opportunity costs associated with each customization strategy.
The Evolution of SaaS Customization Capabilities
The SaaS industry has evolved significantly since its early days, when applications offered limited customization options. Today’s leading platforms provide sophisticated configuration tools, extensive API ecosystems, and marketplace integrations that expand customization possibilities without requiring extensive development efforts. Organizations can learn more about building effective strategies by exploring cloud management best practices that support their customization initiatives.
This evolution reflects the maturation of the SaaS distribution model, where vendors recognize that flexibility and adaptability are crucial for customer retention and expansion. Cloud computing infrastructure now supports more complex customization scenarios, enabling real-time data synchronization, advanced workflow automation, and seamless user experiences across integrated applications.
The Economic Framework for Decision Making
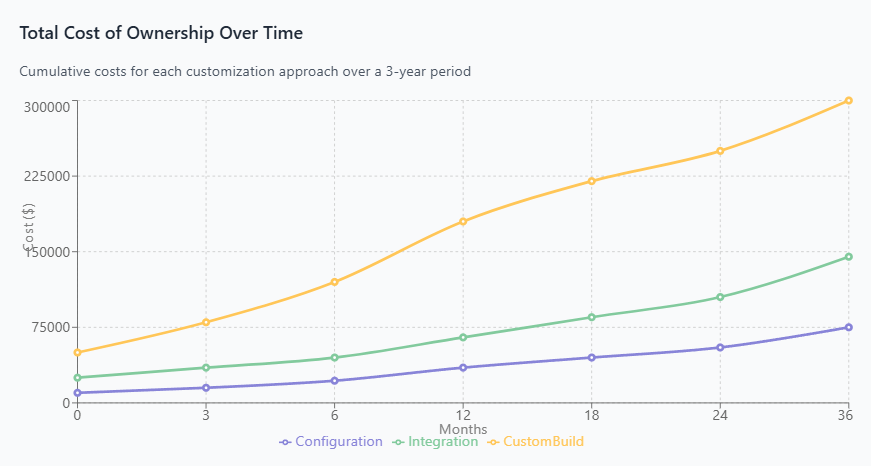
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Effective SaaS customization decisions require comprehensive total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis that extends beyond initial implementation costs. Organizations must consider direct expenses such as licensing fees, development costs, and third-party integration tools, alongside indirect costs including training, maintenance, security compliance, and opportunity costs from delayed implementations.
The TCO framework should evaluate costs across multiple time horizons, recognizing that configuration-heavy approaches may have lower upfront costs but potentially higher long-term expenses due to vendor lock-in and limited scalability. Conversely, custom development may require substantial initial investment but offer greater flexibility and lower ongoing licensing costs.
Time to value represents another critical economic consideration. Configuration-based customizations often deliver immediate results, allowing organizations to realize benefits quickly and generate early ROI. Integration projects typically require moderate implementation timelines but can unlock significant value through process automation and data consolidation. Custom development projects generally have the longest implementation cycles but may provide the greatest long-term competitive advantages. Understanding cloud cost optimization strategies becomes essential when evaluating these different approaches and their associated infrastructure costs.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Each customization approach carries distinct risk profiles that impact economic outcomes. Configuration-based customizations face risks related to vendor roadmap changes, feature deprecation, and limited control over functionality evolution. Organizations investing heavily in specific configuration setups may find themselves constrained by vendor decisions that don’t align with their business needs.
Integration approaches introduce technical risks related to API stability, data security, and system compatibility. As SaaS vendors update their platforms, integrations may require ongoing maintenance and updates, creating potential points of failure and unexpected costs. However, these risks can be mitigated through careful vendor selection, robust error handling, and diversified integration strategies.
Custom development carries the highest technical and operational risks but also provides maximum control over functionality and evolution. Organizations pursuing this approach must consider their internal development capabilities, ongoing maintenance requirements, and the potential for technical debt accumulation over time.
When to Configure: Leveraging Built-in Flexibility
Maximizing Native Platform Capabilities
Configuration represents the most cost-effective customization approach when SaaS platforms provide sufficient flexibility to meet business requirements. Modern SaaS solutions offer extensive configuration options including custom fields, workflow automation, user role management, and reporting capabilities that can address many organizational needs without additional development.
The economic advantages of configuration-based customization include minimal upfront investment, rapid implementation timelines, and reduced ongoing maintenance requirements. Organizations can typically deploy configured solutions within days or weeks rather than months, enabling faster time to value and earlier ROI realization.
User adoption benefits significantly from configuration-based approaches since they maintain familiar interfaces and user experiences. Training requirements are minimized when customizations work within existing platform paradigms, reducing change management costs and accelerating productivity gains.
Best Practices for Configuration-Driven Customization
Successful configuration strategies begin with comprehensive platform evaluation to understand available customization options and their limitations. Organizations should map business requirements to native platform capabilities, identifying areas where configuration can deliver required functionality and highlighting gaps that may require alternative approaches.
Governance frameworks become essential when multiple teams or departments pursue independent configuration efforts. Without centralized oversight, organizations risk creating inconsistent user experiences, conflicting business rules, and administrative complexity that undermines the economic benefits of configuration-based customization.
Documentation and knowledge management practices ensure that configuration decisions can be maintained and evolved over time. As organizations grow and requirements change, well-documented configuration strategies enable efficient updates and prevent the need for costly re-implementation projects.
Configuration Limitations and Economic Implications
Despite their advantages, configuration-based approaches have inherent limitations that impact long-term economic outcomes. Vendor-dependent functionality means that organizations cannot control feature evolution or deprecation, potentially requiring expensive migrations or workarounds when platform changes conflict with business needs.
Scalability constraints may emerge as organizations grow or requirements become more complex. Configuration options that work effectively for small teams or simple workflows may become inadequate as transaction volumes increase or business processes evolve, necessitating more sophisticated customization approaches. Understanding scalability in cloud computing helps organizations plan for future growth and avoid costly architectural limitations.
Advanced functionality requirements often exceed configuration capabilities, particularly in areas such as complex data transformations, specialized integrations, or industry-specific workflows. Organizations may find themselves constrained by platform limitations, requiring expensive workarounds or complete platform migrations to achieve desired functionality.
When to Integrate: Connecting Your SaaS Stack
The Strategic Value of SaaS Integration
Integration-based customization leverages the distributed nature of modern SaaS ecosystems, connecting specialized applications to create comprehensive business solutions. This approach recognizes that no single SaaS platform excels in every functional area, and economic optimization often requires combining best-of-breed solutions through strategic integrations.
The economic rationale for integration centers on maximizing the value of existing SaaS investments while avoiding the costs and risks associated with platform consolidation or custom development. Organizations can maintain specialized tools for specific functions while ensuring data consistency and workflow continuity across their technology stack.
Data synchronization represents a primary driver for integration investments, enabling organizations to maintain single sources of truth while supporting distributed work processes. Real-time data integration eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and enables more sophisticated analytics and reporting capabilities.
Integration Architecture and Economic Considerations
Modern integration approaches range from simple point-to-point connections to sophisticated iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) solutions that support complex workflow orchestration and data transformation. The economic implications vary significantly based on architectural choices and implementation complexity. Organizations must also consider whether to pursue hybrid cloud vs. multi-cloud strategies when planning their integration architectures.
Native integrations provided by SaaS vendors often represent the most cost-effective option when available, typically offering pre-built connectors with minimal implementation requirements. However, these integrations may have limited customization options and functionality constraints that impact long-term scalability.
Third-party integration platforms provide greater flexibility and functionality but introduce additional licensing costs and technical complexity. Organizations must evaluate these platforms based on their ability to support current and future integration requirements while minimizing vendor lock-in and technical debt accumulation.
Managing Integration Complexity and Costs
As organizations expand their SaaS portfolios, integration complexity grows exponentially, potentially creating maintenance burdens that outweigh initial economic benefits. Each new SaaS application may require connections to multiple existing systems, creating web-like architectures that are difficult to manage and modify.
API management becomes critical for maintaining integration reliability and performance. Organizations must monitor API usage, manage authentication and authorization, and handle version updates across multiple vendor platforms. These operational requirements introduce ongoing costs that must be factored into integration economics.
Error handling and data quality management represent hidden costs in integration-heavy environments. As data flows between systems, opportunities for errors and inconsistencies multiply, requiring robust monitoring and correction processes that add operational overhead and potential business risks.
When to Build: Custom Development Considerations
Strategic Rationale for Custom Development
Custom development represents the highest-investment customization approach but offers maximum control over functionality, user experience, and long-term evolution. Organizations typically pursue custom development when existing SaaS solutions cannot adequately address unique business requirements or when competitive differentiation requires proprietary functionality.
The economic justification for custom development often centers on competitive advantage and operational efficiency gains that exceed the costs of development and maintenance. Organizations with highly specialized processes or regulatory requirements may find that custom solutions provide better long-term economics despite higher upfront investments.
Intellectual property considerations play a significant role in build versus buy decisions. Custom development creates proprietary assets that organizations own and control, potentially providing competitive advantages and future monetization opportunities that offset development costs.
Development Approaches and Cost Structures
Modern custom development options range from low-code platforms that accelerate development timelines to full-scale custom applications built on cloud infrastructure. Each approach offers different cost structures and capability trade-offs that impact economic outcomes.
Low-code and no-code platforms have democratized custom development, enabling business users to create sophisticated applications without traditional programming skills. These platforms can significantly reduce development costs and timelines while maintaining professional functionality and scalability.
Traditional custom development using cloud infrastructure and modern development frameworks provides maximum flexibility but requires significant technical expertise and project management capabilities. Organizations must consider their internal development capabilities or factor in the costs of external development partners.
Long-term Economic Implications of Custom Development
Custom development creates ongoing obligations for maintenance, security updates, and feature enhancements that must be factored into long-term economic analysis. Unlike SaaS solutions where vendors handle infrastructure and maintenance, custom applications require dedicated resources for ongoing operation and evolution.
Technical debt management represents a hidden cost in custom development projects, particularly when development timelines are compressed or when applications evolve rapidly. Organizations must balance feature velocity with code quality to avoid expensive refactoring projects that can undermine economic benefits.
Scalability planning becomes critical for custom applications that may need to support growing user bases or increased transaction volumes. Cloud infrastructure provides elastic scaling capabilities, but applications must be designed to leverage these capabilities effectively, requiring architectural decisions that impact both development costs and long-term operational economics.
Cost Analysis and ROI Calculations
Comprehensive Cost Modeling Framework
Effective SaaS customization decisions require sophisticated cost modeling that captures both direct and indirect expenses across multiple time horizons. Organizations must develop frameworks that account for implementation costs, ongoing operational expenses, and opportunity costs associated with different customization approaches.
Direct costs include obvious expenses such as software licenses, development resources, and third-party integration tools. However, these visible costs often represent only a portion of total economic impact, making comprehensive modeling essential for accurate decision-making.
Indirect costs encompass training expenses, productivity impacts during implementation, security and compliance overhead, and the opportunity costs of delayed implementations or suboptimal functionality. These factors can significantly impact ROI calculations and must be carefully evaluated for each customization approach.
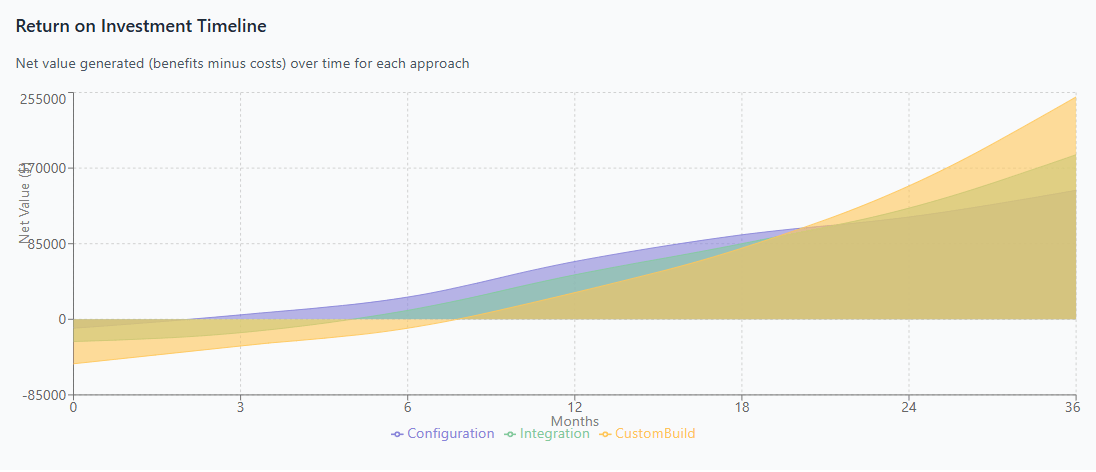
ROI Measurement and Optimization Strategies
Return on investment calculations for SaaS customization must consider both quantitative benefits such as process automation and cost savings, and qualitative benefits including improved user satisfaction and competitive positioning. Organizations should establish baseline metrics before implementation to enable accurate benefit measurement.
Time-based ROI analysis recognizes that different customization approaches deliver benefits at different rates and scales. Configuration-based customizations may provide immediate benefits but limited long-term value, while custom development may require extended implementation periods but deliver sustained competitive advantages.
Optimization strategies should focus on maximizing value realization while minimizing implementation risks and costs. This may involve phased implementation approaches that deliver incremental benefits while building toward comprehensive solutions, or hybrid strategies that combine multiple customization approaches for optimal economic outcomes.
SaaS Spend Management and Optimization Strategies
Centralized SaaS Spend Management
As organizations pursue various customization strategies across their SaaS portfolios, centralized spend management becomes essential for maintaining economic efficiency and preventing redundant investments. Effective SaaS spend management provides visibility into subscription costs, usage patterns, and optimization opportunities across the entire software portfolio.
SaaS spend management tools like Binadox enable organizations to track all SaaS applications and customization investments from a centralized platform, providing comprehensive visibility into costs and usage patterns. These platforms can identify underutilized licenses, redundant applications, and optimization opportunities that improve overall economic outcomes. For organizations managing multiple subscriptions, understanding SaaS subscription management best practices becomes essential for maintaining cost control.
Centralized procurement processes ensure that customization decisions align with organizational standards and strategic objectives. By evaluating customization requests through consistent frameworks, organizations can avoid duplicative investments and ensure that customization approaches support broader business goals.
Optimization Through Usage Analytics
Detailed usage analytics provide insights into how customized SaaS applications deliver value across different user segments and use cases. This data enables organizations to optimize customization investments by identifying high-value features and eliminating underutilized functionality.
License rightsizing represents a critical optimization opportunity, particularly for highly customized SaaS applications where usage patterns may differ significantly from standard implementations. Organizations can use usage data to optimize subscription levels and avoid paying for unused customization features. Learning how to deal with underutilized instances provides practical strategies for identifying and addressing these inefficiencies.
Performance monitoring helps organizations understand the impact of customizations on application performance and user experience. Customizations that negatively impact performance may require optimization or alternative approaches to maintain user productivity and satisfaction.
Cost Control and Governance Frameworks
Effective governance frameworks establish clear guidelines for when different customization approaches are appropriate, preventing ad hoc decisions that may not align with long-term economic objectives. These frameworks should consider organizational capabilities, risk tolerance, and strategic priorities. Implementing FinOps in cloud computing principles ensures that financial management practices keep pace with technical customization decisions.
Budget allocation strategies should recognize that different customization approaches have different cost structures and timelines. Organizations need flexible budgeting processes that can accommodate the varying cash flow requirements of configuration, integration, and custom development projects.
Vendor management practices become increasingly important as organizations pursue diverse customization strategies across multiple SaaS platforms. Effective vendor relationships can provide access to roadmap information, preferential pricing, and technical support that improves customization economics.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Configuration Success: Salesforce Customization
A mid-sized manufacturing company successfully customized their Salesforce implementation using primarily configuration-based approaches, achieving a 300% ROI within 18 months. By leveraging custom fields, workflow automation, and reporting capabilities, they created a comprehensive customer management system without requiring external development resources.
The economic success resulted from rapid implementation (completed in 6 weeks), minimal training requirements, and immediate productivity improvements. The company avoided the costs and risks associated with custom development while achieving functionality that met their specific business requirements.
However, as the company grew, they encountered limitations in Salesforce’s native reporting capabilities that required additional investments in third-party analytics tools, demonstrating the importance of considering long-term scalability in configuration-based strategies.
Integration Excellence: Multi-Platform E-commerce Solution
An online retailer created a comprehensive e-commerce platform by integrating Shopify for storefront management, NetSuite for ERP functionality, and Klaviyo for marketing automation. This integration-heavy approach enabled them to leverage best-of-breed solutions while maintaining operational efficiency.
The economic benefits included reduced licensing costs compared to enterprise platforms, faster implementation than custom development, and maintained flexibility to replace individual components as requirements evolved. Total implementation costs were 60% lower than comparable enterprise solutions.
Long-term success required ongoing investment in integration maintenance and data quality management, highlighting the importance of considering operational overhead in integration-heavy strategies. The company established dedicated technical resources to manage their integration architecture.
Custom Development Investment: Proprietary Logistics Platform
A logistics company invested $2.3 million in developing a custom fleet management platform that integrated with their existing SaaS applications for accounting and customer management. This substantial investment was justified by unique operational requirements that existing SaaS solutions could not adequately address.
The custom platform delivered competitive advantages including 40% improvement in route optimization, 25% reduction in fuel costs, and enhanced customer service capabilities. ROI exceeded 200% within three years, demonstrating the potential value of strategic custom development investments.
However, ongoing maintenance costs averaged $400,000 annually, and the company required dedicated technical staff to support platform evolution and security compliance, illustrating the long-term commitments associated with custom development approaches.
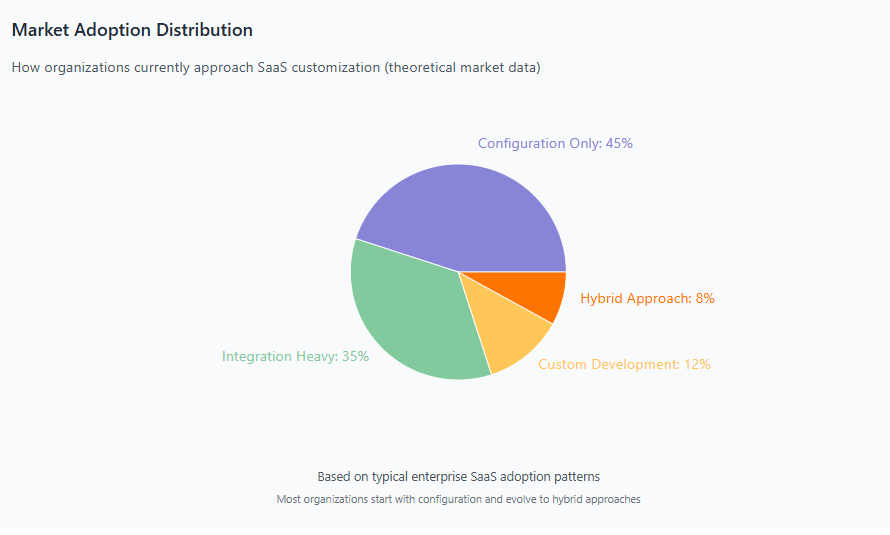
Future Trends in SaaS Customization
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
The integration of AI and ML technologies into SaaS platforms is transforming customization economics by enabling more sophisticated automation and personalization capabilities. These technologies can reduce the development effort required for custom functionality while improving user experiences and business outcomes.
Intelligent configuration tools are emerging that can automatically optimize SaaS settings based on usage patterns and business objectives. These capabilities reduce the expertise required for effective customization while improving outcomes compared to manual configuration approaches.
Predictive analytics powered by AI can help organizations make better customization decisions by forecasting the long-term value and costs of different approaches. This capability is particularly valuable for complex integration projects where traditional ROI analysis may be challenging.
Low-Code and No-Code Platform Evolution
The continued evolution of low-code and no-code platforms is democratizing custom development capabilities, enabling business users to create sophisticated applications without traditional programming expertise. This trend is shifting the economics of custom development by reducing resource requirements and implementation timelines.
Citizen development programs are emerging as organizations recognize the potential for business users to create customized solutions using low-code platforms. This approach can significantly reduce development costs while improving solution relevance and user adoption.
Platform-specific low-code tools provided by major SaaS vendors are blurring the lines between configuration and custom development, offering enhanced customization capabilities while maintaining the support and reliability advantages of vendor-provided solutions.
Edge Computing and Distributed SaaS Architectures
Edge computing is creating new customization opportunities by enabling hybrid architectures where some processing occurs locally while maintaining cloud connectivity. This trend is particularly relevant for organizations with latency-sensitive applications or data sovereignty requirements.
Distributed customization approaches may emerge where organizations can customize local processing capabilities while maintaining integration with centralized SaaS platforms. This could provide performance benefits while preserving the operational advantages of cloud-based solutions.
The economic implications of edge-enabled customization are still emerging, but early indicators suggest potential for improved performance and reduced bandwidth costs in exchange for increased architectural complexity and local infrastructure requirements.
Conclusion
The economics of SaaS customization require careful consideration of multiple factors including immediate costs, long-term value, risk profiles, and strategic alignment. Organizations must develop sophisticated decision-making frameworks that evaluate configuration, integration, and custom development approaches based on their specific requirements and capabilities.
Configuration-based customization offers the most cost-effective approach when SaaS platforms provide sufficient flexibility to meet business requirements. This approach delivers rapid implementation, minimal risk, and immediate value, making it ideal for organizations with standard processes and limited technical resources.
Integration strategies provide balanced approaches that leverage specialized SaaS applications while maintaining operational efficiency. These approaches require more sophisticated technical capabilities and ongoing management but can deliver significant value by connecting best-of-breed solutions.
Custom development represents the highest-investment option that provides maximum control and competitive differentiation. Organizations pursuing this approach must carefully evaluate their long-term commitments and ensure adequate resources for ongoing maintenance and evolution.
Successful SaaS customization strategies often combine multiple approaches, using configuration for standard requirements, integration for connecting specialized tools, and custom development for unique competitive advantages. The key to economic success lies in matching customization approaches to specific business requirements while maintaining visibility into costs and value realization.
As the SaaS ecosystem continues to evolve with new technologies such as AI, low-code platforms, and edge computing, organizations must remain flexible in their customization strategies while maintaining focus on economic efficiency and long-term value creation. By leveraging comprehensive spend management tools and governance frameworks, organizations can optimize their customization investments and maximize the value of their SaaS portfolios.
The future of SaaS customization will likely involve more intelligent, automated approaches that reduce the complexity and costs associated with customization decisions. Organizations that invest in developing sophisticated customization capabilities and decision-making frameworks will be best positioned to leverage these emerging opportunities while maintaining economic efficiency in their software investments.

