
The Software as a Service (SaaS) landscape has evolved dramatically over the past decade, moving beyond generic, one-size-fits-all solutions to highly specialized applications designed for specific industries. This shift toward vertical SaaS represents a fundamental change in how businesses approach software procurement and management, particularly when it comes to controlling costs and optimizing value.
Unlike horizontal SaaS solutions that serve broad market segments across multiple industries, vertical SaaS applications are purpose-built to address the unique challenges, regulatory requirements, and operational workflows of specific sectors. While these specialized solutions often provide superior functionality and compliance capabilities, they also introduce new complexities in SaaS spend management and cost optimization.
As organizations increasingly rely on industry-specific software to maintain competitive advantages and meet regulatory standards, understanding how to effectively manage spending on these niche applications becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of vertical SaaS spend management, providing actionable strategies for organizations looking to optimize their investments in specialized software solutions.
What is Vertical SaaS?
Vertical SaaS refers to cloud-based software applications specifically designed to serve the unique needs of particular industries, professions, or market segments. Unlike horizontal SaaS platforms that offer generic functionality applicable across various sectors, vertical software solutions are tailored to address industry-specific challenges, regulatory requirements, and specialized workflows.
These specialized SaaS solutions incorporate deep domain expertise and industry knowledge into their design, often featuring built-in compliance tools, industry-standard reporting capabilities, and workflows that mirror established practices within their target sectors. For example, a vertical SaaS solution for healthcare might include HIPAA compliance features, medical billing integration, and patient management workflows that wouldn’t be relevant or necessary in a generic project management platform.
The key distinguishing factors of vertical SaaS include:
- Industry-Specific Features: Built-in functionality that addresses unique industry challenges, such as regulatory compliance tools, specialized reporting capabilities, and industry-standard integrations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Pre-configured compliance frameworks and security measures that meet industry-specific regulatory requirements, reducing the burden on organizations to implement these features independently.
- Specialized Workflows: User interfaces and process flows designed around industry-standard practices and terminology familiar to professionals in the target sector.
- Domain Expertise Integration: Features developed in collaboration with industry experts and practitioners, ensuring the software addresses real-world challenges faced by professionals in the field.
Industries Leading Vertical SaaS Adoption
Several industries have emerged as leaders in vertical SaaS adoption, driven by unique operational requirements, regulatory pressures, and the need for specialized functionality that generic software cannot adequately address.
Healthcare and Medical Services lead the charge in vertical SaaS adoption, with applications covering electronic health records (EHR), practice management, telehealth platforms, medical billing, and patient engagement systems. The healthcare sector’s complex regulatory environment, including HIPAA compliance requirements and medical coding standards, makes industry-specific software essential rather than optional.
Financial Services represent another major vertical SaaS market, encompassing solutions for portfolio management, risk analysis, regulatory compliance, trading platforms, and customer relationship management tailored to banking and investment firms. The sector’s strict regulatory requirements and need for real-time data processing make specialized solutions particularly valuable.
Real Estate has embraced vertical SaaS for property management, customer relationship management, transaction management, and market analysis tools designed specifically for real estate professionals. These applications integrate with Multiple Listing Services (MLS), property databases, and industry-specific communication protocols.
Legal Services utilize vertical SaaS for case management, document automation, billing and time tracking, legal research, and compliance management. Legal professionals require software that understands legal workflows, court filing requirements, and attorney-client privilege considerations.
Construction and Engineering sectors rely on vertical SaaS for project management, building information modeling (BIM), compliance tracking, equipment management, and safety monitoring. These applications must integrate with industry-specific tools and standards while supporting complex project workflows.
Manufacturing organizations use vertical SaaS for supply chain management, quality control, regulatory compliance, and production planning. These solutions often integrate with industrial equipment and manufacturing execution systems.
Key Characteristics of Vertical SaaS Applications
Understanding the unique characteristics of vertical SaaS applications is essential for effective spend management, as these features often influence pricing models, implementation complexity, and total cost of ownership.
Deep Integration Requirements characterize most vertical SaaS solutions, as they typically need to connect with industry-specific systems, databases, and third-party services. For healthcare applications, this might include integration with laboratory systems, imaging equipment, and insurance databases. In financial services, vertical SaaS solutions often require connections to trading platforms, regulatory reporting systems, and financial data providers.
Compliance and Security Features are built into vertical SaaS applications rather than added as afterthoughts. Healthcare vertical SaaS includes HIPAA compliance tools, audit trails, and data encryption specifically designed for medical information. Financial services vertical SaaS incorporates SOX compliance, regulatory reporting capabilities, and security measures that meet industry standards.
Specialized User Interfaces designed for industry professionals rather than general business users characterize vertical SaaS applications. Legal practice management software includes interfaces familiar to attorneys, with terminology, workflows, and features specific to legal practice. Construction management platforms use industry-standard project phases, terminology, and reporting formats familiar to construction professionals.
Industry-Specific Analytics and Reporting capabilities distinguish vertical SaaS from horizontal solutions. Real estate vertical SaaS provides market analysis, comparative market analysis (CMA) tools, and property valuation features not found in generic business applications. Manufacturing vertical SaaS includes production efficiency analytics, quality control reporting, and supply chain optimization tools.
Regulatory Reporting Automation built into vertical SaaS solutions helps organizations meet industry-specific reporting requirements without manual intervention. Healthcare vertical SaaS automatically generates regulatory reports required by government agencies, while financial services vertical SaaS produces compliance reports required by financial regulators.
Challenges in Managing Vertical SaaS Spending
Managing spending on vertical SaaS applications presents unique challenges that differ significantly from those associated with horizontal SaaS solutions. Organizations must navigate complex pricing structures, limited vendor alternatives, and industry-specific requirements that can significantly impact cost-effective app management strategies.
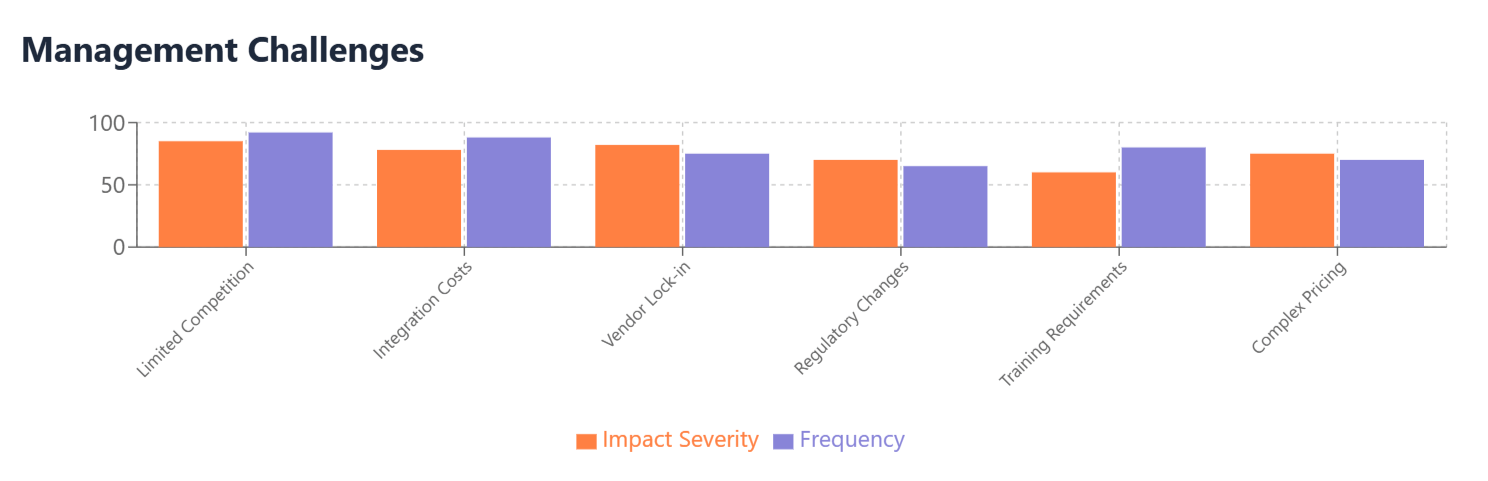
Limited Vendor Competition in many vertical markets means fewer alternatives and less pricing pressure on vendors. Unlike horizontal SaaS markets where numerous competitors offer similar functionality, vertical SaaS markets often have only a few established players with deep industry expertise. This reduced competition can lead to higher prices and less flexible pricing terms.
Complex Integration Costs associated with vertical SaaS implementations often extend beyond the basic subscription fees. These applications typically require integration with existing industry-specific systems, data migration from legacy platforms, and customization to meet unique organizational requirements. The total cost of ownership for vertical SaaS frequently exceeds initial subscription pricing due to these implementation and maintenance costs.
Regulatory Change Impact affects vertical SaaS costs as regulatory updates often require software modifications, additional features, or enhanced compliance capabilities. When healthcare regulations change, vertical SaaS vendors may need to update their platforms, potentially passing these costs to customers through price increases or additional feature charges.
Specialized Training Requirements for vertical SaaS applications can add significant costs to implementations. While horizontal SaaS solutions often feature intuitive interfaces designed for general business users, vertical SaaS applications may require specialized training to maximize their industry-specific capabilities.
Vendor Lock-in Risks are particularly pronounced with vertical SaaS solutions due to the specialized nature of the data and workflows they manage. Organizations often invest heavily in customizing these platforms and training users on industry-specific features, making it expensive and disruptive to switch vendors.
Industry-Specific Pricing Models used by vertical SaaS vendors can make cost comparisons and budgeting challenging. Some vendors charge based on industry-specific metrics like patient encounters in healthcare, assets under management in financial services, or square footage managed in real estate, making it difficult to predict costs as business volumes fluctuate.
Current State of the Vertical SaaS Market
The vertical SaaS market has experienced tremendous growth as organizations recognize the value of specialized SaaS solutions tailored to their specific industry requirements. This growth trajectory reflects a broader shift away from generic, horizontal software toward purpose-built applications that address unique industry challenges.
Market research indicates that the vertical SaaS market reached approximately $120 billion in 2024, with projected growth rates of 15-20% annually through 2028. This growth significantly outpaces the overall SaaS market, indicating strong demand for industry-specific software solutions across various sectors.
Healthcare Vertical SaaS represents the largest segment of the vertical market, driven by digital transformation initiatives, regulatory requirements, and the need for improved patient outcomes. Electronic health records (EHR) systems, telehealth platforms, and practice management solutions have seen particularly strong adoption rates.
Financial Services Vertical SaaS has grown rapidly, fueled by regulatory compliance requirements, the need for real-time risk management, and digital transformation initiatives in banking and investment services. Regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions and financial planning platforms have emerged as particularly high-growth segments.
Industry Consolidation has become a significant trend in vertical SaaS markets, with larger horizontal SaaS vendors acquiring specialized vertical players to expand their market reach. This consolidation can impact pricing, feature development, and customer service levels for organizations using vertical SaaS solutions.
Emerging Vertical Markets continue to develop as software vendors identify underserved industries with specific software needs. Agriculture, logistics, education, and energy sectors have seen increased vertical SaaS development as vendors recognize opportunities to create specialized solutions for these industries.
Integration Platform Growth has accompanied vertical SaaS expansion, as organizations need tools to connect specialized applications with their existing technology stacks. This has created a secondary market for integration platforms and middleware solutions specifically designed for vertical SaaS environments.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Vertical SaaS Solutions
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of vertical SaaS solutions is crucial for making informed decisions about SaaS spend management and determining when specialized applications justify their typically higher costs compared to horizontal alternatives.
Benefits of Vertical SaaS Solutions
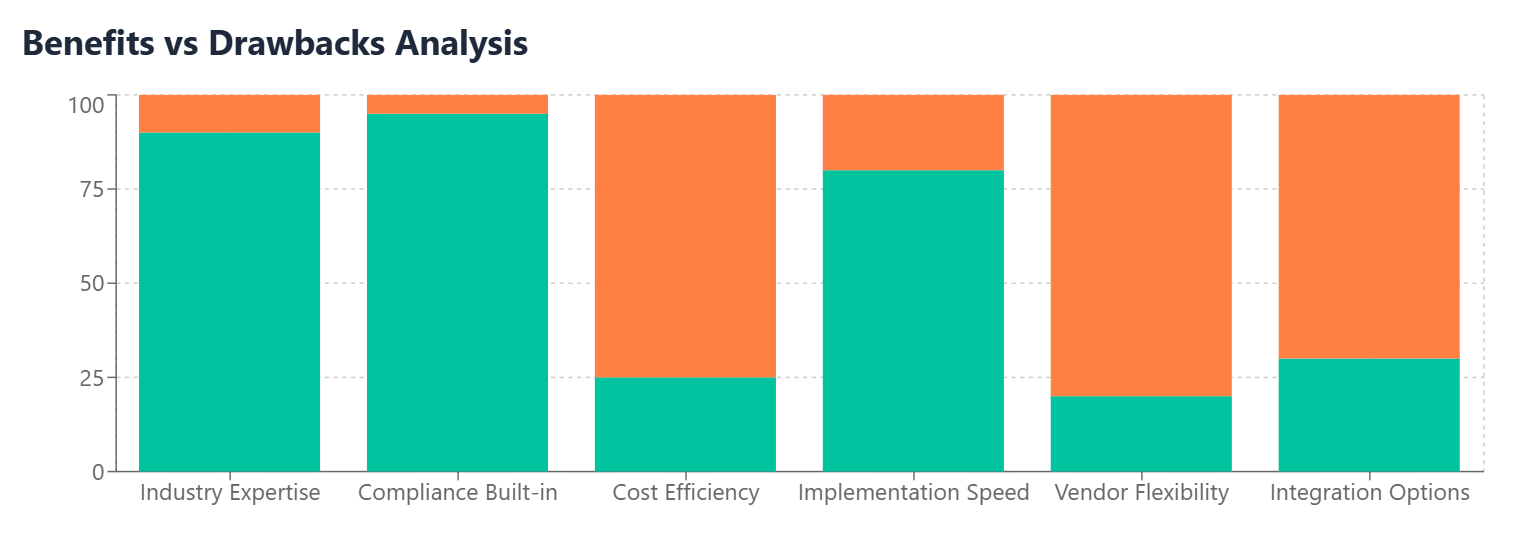
Industry Expertise Integration provides immediate access to best practices, regulatory knowledge, and specialized functionality developed by industry experts. Organizations benefit from software designed by professionals who understand their specific challenges and requirements.
Regulatory Compliance Built-In reduces the burden on organizations to implement and maintain compliance frameworks independently. Vertical SaaS solutions often include automated compliance reporting, audit trails, and security measures specifically designed to meet industry regulatory requirements.
Faster Implementation can result from pre-configured industry-standard workflows, templates, and integrations. Organizations spend less time customizing generic software to meet their needs when using purpose-built vertical solutions.
Enhanced Productivity occurs when software interfaces, terminology, and workflows align with established industry practices. Users can be more productive when using familiar interfaces and processes designed specifically for their profession.
Competitive Advantage may result from using advanced industry-specific features not available in horizontal solutions. Organizations can differentiate themselves by leveraging specialized capabilities that improve their service delivery or operational efficiency.
Drawbacks of Vertical SaaS Solutions
Higher Costs typically characterize vertical SaaS solutions due to limited competition, specialized development requirements, and smaller addressable markets that require higher per-customer pricing to achieve profitability.
Vendor Lock-in Risks increase with vertical SaaS due to specialized data formats, industry-specific integrations, and customized workflows that make switching vendors more complex and expensive.
Limited Integration Options may exist with non-industry-specific systems, as vertical SaaS solutions often prioritize integration with industry-standard platforms over broader business applications.
Slower Innovation Cycles can occur in vertical SaaS markets with limited competition, as vendors may have less pressure to innovate rapidly or introduce new features frequently.
Scalability Limitations may exist if vertical SaaS solutions are designed for specific industry segments or business sizes, potentially requiring organizations to switch platforms as they grow or diversify.
Strategies for Optimizing Vertical SaaS Spending
Effective SaaS cost optimization in vertical markets requires specialized strategies that account for the unique characteristics of industry-specific applications. Organizations must balance the value of specialized functionality against the typically higher costs associated with vertical solutions.
Comprehensive Cost-Benefit Analysis
Developing thorough cost-benefit analyses for vertical SaaS solutions requires evaluating both direct and indirect costs against quantifiable business benefits. Direct costs include subscription fees, implementation costs, training expenses, and ongoing support charges. Indirect costs encompass integration expenses, data migration costs, and potential productivity losses during implementation.
Benefits should be quantified wherever possible, including productivity improvements, compliance cost reductions, risk mitigation value, and competitive advantages gained through specialized functionality. Organizations should also consider the cost of alternatives, including building custom solutions, using horizontal SaaS with extensive customization, or maintaining legacy systems.
Vendor Negotiation Strategies
Negotiating with vertical SaaS vendors requires understanding their business models, competitive landscape, and the value they provide to your specific industry segment. Organizations should research vendor financial health, customer base, and development roadmaps to understand their negotiating position.
Multi-year contracts often provide better pricing in vertical SaaS markets, but organizations should ensure they include provisions for performance standards, feature development commitments, and reasonable termination clauses. Volume commitments may unlock better pricing, particularly for organizations with multiple locations or business units.
Reference customer agreements can provide value to vertical SaaS vendors, potentially resulting in better pricing or terms in exchange for case studies, references, or speaking opportunities at industry events.
Strategic Vendor Relationships
Building strategic relationships with vertical SaaS vendors can provide benefits beyond cost savings, including early access to new features, influence over product development priorities, and enhanced support levels. Organizations should engage with vendor advisory boards, user groups, and industry councils to maximize their influence and value from vendor relationships.
Partnership opportunities may exist for organizations willing to provide feedback, participate in beta testing, or serve as reference customers. These partnerships can result in reduced costs, customized features, or priority support arrangements.
Alternative Sourcing Models
Industry consortiums sometimes negotiate group licensing agreements for vertical SaaS solutions, providing member organizations with better pricing and terms through collective bargaining power. Professional associations or industry groups may offer these opportunities.
Hybrid deployment models combining vertical SaaS for core industry-specific functions with horizontal SaaS for general business functions can optimize costs while maintaining necessary specialized capabilities.
Best Practices for Vertical SaaS Management
Implementing effective management practices for vertical SaaS requires specialized approaches that account for the unique characteristics of industry-specific applications while maintaining centralized app management capabilities.
Governance Framework Development
Establishing governance frameworks specifically for vertical SaaS requires understanding the unique risk profiles, compliance requirements, and business criticality of industry-specific applications. Governance policies should address vendor selection criteria, implementation standards, and ongoing management requirements specific to vertical solutions.
Risk assessment processes for vertical SaaS should evaluate vendor financial stability, regulatory compliance capabilities, data security measures, and business continuity planning. Industry-specific risk factors, such as regulatory change impact or integration complexity, require specialized evaluation criteria.
Approval processes for vertical SaaS should involve industry experts or department heads who understand the specialized requirements and can evaluate the business value of proposed solutions. Technical evaluation should include assessment of integration requirements, compliance capabilities, and long-term scalability.
Usage Monitoring and Optimization
Monitoring vertical SaaS usage requires understanding industry-specific usage patterns and value metrics. Healthcare applications might be measured by patient encounters or clinical workflows, while financial services applications might be evaluated based on transaction volumes or assets under management.
Feature utilization analysis should focus on industry-specific capabilities that justify the higher costs of vertical solutions. Organizations should regularly assess whether they’re utilizing specialized features that differentiate vertical SaaS from less expensive horizontal alternatives.
User adoption tracking for vertical SaaS should consider the specialized training requirements and learning curves associated with industry-specific applications. Low adoption rates might indicate training deficiencies rather than software problems.
Integration Management
Managing integrations for vertical SaaS requires understanding industry-standard data formats, communication protocols, and system interfaces. Organizations should maintain inventories of integrations, monitor performance, and plan for updates when regulatory or industry standards change.
Data flow mapping becomes particularly important with vertical SaaS solutions that often handle sensitive or regulated data. Organizations must ensure integrations maintain compliance requirements and security standards throughout data transfer processes.
Vendor Relationship Management
Active vendor relationship management for vertical SaaS should include regular business reviews, performance assessments, and strategic planning discussions. Organizations should engage with vendor product management teams to influence development priorities and ensure solutions continue meeting evolving industry requirements.
Contract management for vertical SaaS requires attention to industry-specific terms, compliance requirements, and performance standards. Organizations should regularly review contracts to ensure they remain aligned with business needs and industry developments.
Case Studies: Good vs. Poor Vertical SaaS Spending
Real-world examples of vertical SaaS spending practices illustrate the impact of effective management strategies on both costs and business outcomes. These case studies demonstrate the importance of strategic planning, vendor management, and ongoing optimization in vertical SaaS environments.
Good Vertical SaaS Spending Practices
Healthcare Network Optimization Case Study
A regional healthcare network with 15 locations successfully optimized their vertical SaaS spending by implementing centralized SaaS procurement processes and conducting comprehensive vendor consolidation. Initially, different locations used various electronic health record (EHR) systems, practice management platforms, and telehealth solutions, resulting in high total costs and integration challenges.
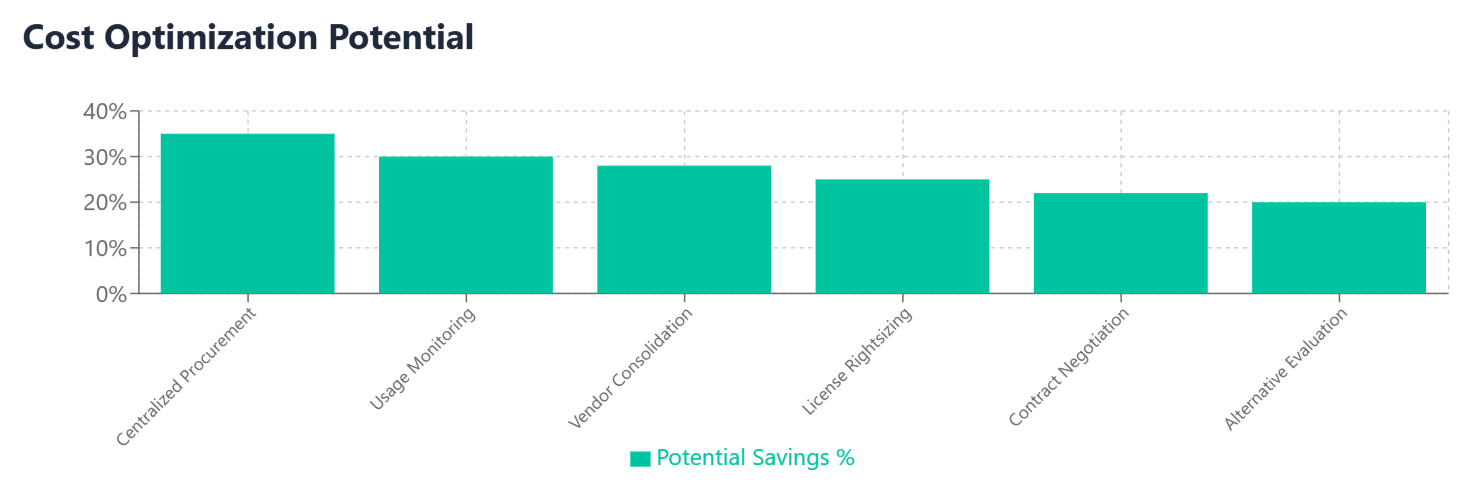
The organization conducted a comprehensive assessment of their vertical SaaS landscape, identifying redundant applications and negotiating enterprise-wide agreements with preferred vendors. By standardizing on a single EHR platform across all locations, they achieved 35% cost savings through volume discounts while improving interoperability and patient care coordination.
Key Success Factors:
- Executive sponsorship for standardization initiatives
- Involvement of clinical staff in vendor selection processes
- Phased implementation approach minimizing disruption
- Comprehensive training programs for new platforms
- Regular usage monitoring and optimization reviews
Financial Services Firm Integration Success
A mid-sized investment management firm optimized their vertical SaaS spending by implementing integrated solutions that eliminated redundant systems and improved workflow efficiency. Previously, the firm used separate platforms for portfolio management, client relationship management, regulatory reporting, and performance analysis.
By selecting an integrated vertical SaaS platform that provided comprehensive functionality, the firm reduced their software costs by 28% while improving operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. The integrated platform eliminated manual data transfers between systems and reduced the risk of compliance errors.
Key Success Factors:
- Comprehensive requirements analysis including regulatory needs
- Pilot implementation with key user groups
- Integration planning with existing systems
- Change management support for affected users
- Regular performance monitoring and optimization
Poor Vertical SaaS Spending Practices
Construction Company Overspending Case Study
A large construction company experienced significant vertical SaaS overspending due to uncontrolled adoption of specialized applications across different project teams and geographic locations. Without centralized app management, individual project managers subscribed to various vertical SaaS solutions for project management, scheduling, equipment tracking, and compliance reporting.
The lack of oversight resulted in substantial redundant spending, with multiple teams subscribing to similar applications and purchasing more licenses than needed. The company discovered they were spending 45% more than necessary on vertical SaaS solutions and facing integration challenges due to incompatible platforms.
Key Problems:
- Lack of centralized procurement oversight
- No standardization of vertical SaaS solutions
- Inadequate usage monitoring and license management
- Poor integration planning resulting in data silos
- Absence of vendor management processes
Legal Firm License Waste Example
A large law firm experienced significant license waste in their vertical SaaS legal practice management platform due to poor SaaS subscription tracking and inadequate user management processes. The firm subscribed to licenses based on peak usage projections without implementing processes to adjust subscriptions based on actual usage patterns.
The firm discovered that 30% of their licenses were unutilized or underutilized, representing substantial wasted spending. Additionally, they failed to negotiate enterprise pricing despite their size, paying premium rates for individual subscriptions rather than volume pricing.
Key Problems:
- Overestimation of license requirements
- Lack of usage monitoring and optimization
- Poor vendor negotiation strategies
- Inadequate license lifecycle management
- Missing cost optimization reviews
Tools and Platforms for Managing Vertical SaaS Costs
Effective SaaS spend management for vertical applications requires specialized tools and platforms that can handle the unique characteristics of industry-specific software while providing comprehensive visibility and control capabilities.
Specialized SaaS Management Platforms
Comprehensive SaaS management platforms like Binadox provide centralized visibility and control over both horizontal and vertical SaaS spending. These platforms offer features specifically designed to handle the complexities of vertical SaaS management, including industry-specific usage metrics, compliance tracking, and specialized reporting capabilities.
Key capabilities for vertical SaaS management include:
Usage Analytics Tailored to Vertical Applications: Monitoring capabilities that understand industry-specific usage patterns and can track utilization based on relevant metrics like patient encounters, cases managed, or transactions processed.
Integration Monitoring: Tracking of data flows and system integrations critical to vertical SaaS operations, ensuring performance and compliance requirements are maintained.
Compliance Reporting: Automated reporting capabilities that help organizations demonstrate compliance with industry regulations and standards related to their vertical SaaS usage.
Vendor Management Tools: Centralized vendor relationship management capabilities that track contract terms, performance metrics, and renewal dates specific to vertical SaaS agreements.
Financial Management Integration
Integration with financial management systems enables organizations to track vertical SaaS costs alongside other business expenses and allocate costs to appropriate departments, projects, or business units. This integration provides crucial visibility for budget management for startups and established organizations alike.
Cost allocation capabilities allow organizations to distribute vertical SaaS costs based on usage patterns, department requirements, or project assignments. This allocation provides department managers with visibility into their vertical SaaS spending and encourages responsible usage.
Budget planning and forecasting tools help organizations predict vertical SaaS costs based on business growth projections, regulatory changes, and planned implementations. These tools account for the unique cost structures of vertical SaaS solutions.
Implementation and Optimization Tools
Implementation planning tools help organizations manage the complex process of deploying vertical SaaS solutions, including integration requirements, training needs, and change management activities. These tools ensure implementations stay on budget and timeline while maximizing user adoption.
Optimization recommendation engines analyze vertical SaaS usage patterns and provide recommendations for cost reduction, feature optimization, and vendor consolidation opportunities. These recommendations account for industry-specific requirements and constraints.
Improve Vertical SaaS Cost Management with Binadox
Managing vertical SaaS spending requires specialized expertise and tools designed to handle the unique challenges of industry-specific applications. Binadox provides comprehensive SaaS management tools specifically designed to help organizations optimize their spending on both horizontal and vertical SaaS solutions.
Binadox offers centralized SaaS procurement capabilities that provide visibility across all SaaS subscriptions, including specialized vertical applications. The platform’s analytics and reporting features help organizations identify optimization opportunities, track usage patterns, and manage vendor relationships effectively.
Key Binadox capabilities for vertical SaaS management include comprehensive subscription tracking across all vertical applications, usage analytics tailored to industry-specific metrics, automated renewal management with compliance considerations, vendor performance monitoring and relationship management, and cost optimization recommendations specific to vertical SaaS environments.
The platform integrates with existing financial systems to provide complete visibility into vertical SaaS spending and enables organizations to implement governance policies that balance the value of specialized functionality with cost control requirements.
Organizations using Binadox for vertical SaaS management typically achieve 20-35% cost savings through improved visibility, optimization recommendations, and enhanced vendor negotiations. The platform’s specialized features ensure that cost optimization efforts don’t compromise the critical industry-specific capabilities that make vertical SaaS solutions valuable.
Future Trends in Vertical SaaS
The vertical SaaS landscape continues evolving rapidly, driven by technological advances, regulatory changes, and increasing demand for specialized SaaS solutions. Understanding these trends helps organizations plan their vertical SaaS strategies and spending optimization efforts.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI and machine learning integration in vertical SaaS solutions is accelerating, with vendors incorporating intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and decision support capabilities tailored to specific industries. Healthcare vertical SaaS platforms are integrating diagnostic assistance and treatment recommendation engines, while financial services vertical SaaS solutions are incorporating fraud detection and risk assessment algorithms.
This AI integration is changing vertical SaaS pricing models, with vendors increasingly offering tiered pricing based on AI feature usage or outcome-based pricing tied to AI-driven improvements. Organizations must evaluate the value of AI capabilities against their additional costs and consider the long-term competitive advantages they provide.
Edge Computing Impact
Edge computing adoption is influencing vertical SaaS architectures, particularly in industries requiring real-time processing or handling sensitive data. Manufacturing vertical SaaS solutions are incorporating edge processing for real-time production monitoring, while healthcare vertical SaaS platforms are using edge computing for patient monitoring and diagnostic equipment integration.
This architectural shift may impact vertical SaaS costs, as edge computing requirements could increase infrastructure costs while potentially reducing data transfer and cloud processing expenses. Organizations should evaluate edge computing implications when selecting vertical SaaS solutions and negotiating pricing terms.
Regulatory Technology Evolution
RegTech integration is becoming standard in vertical SaaS solutions across regulated industries, with automated compliance monitoring, regulatory reporting, and risk management capabilities becoming core features rather than add-ons. This integration is changing how organizations evaluate vertical SaaS solutions and their total cost of ownership.
Regulatory changes continue driving vertical SaaS development, with vendors required to rapidly adapt their platforms to meet evolving compliance requirements. Organizations should ensure their vertical SaaS contracts include provisions for regulatory updates and consider the vendor’s track record for compliance adaptation.
Industry Specialization Increase
Micro-vertical solutions targeting highly specific industry segments or use cases are emerging, offering even more specialized functionality for niche markets. These solutions may provide superior capabilities for specific use cases while potentially increasing the complexity of vertical SaaS management and integration.
Platform consolidation is also occurring, with larger vendors acquiring specialized vertical SaaS solutions to create comprehensive industry platforms. This consolidation may provide integration benefits while potentially reducing competition and increasing vendor lock-in risks.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Deployment
Hybrid deployment models combining on-premises, cloud, and edge computing are becoming common in vertical SaaS solutions, particularly for industries with strict data residency or security requirements. These hybrid models may offer improved performance and compliance capabilities while increasing deployment complexity and management requirements.
Multi-cloud strategies are emerging in vertical SaaS environments, with organizations using different cloud providers for different vertical applications based on specific requirements or vendor preferences. This approach may provide risk mitigation benefits while increasing management complexity.
Conclusion
Vertical SaaS represents a fundamental shift in software delivery, providing industry-specific software solutions that offer superior functionality and compliance capabilities compared to generic horizontal alternatives. However, managing spending on these specialized SaaS solutions requires sophisticated strategies that account for their unique characteristics, pricing models, and integration requirements.
Organizations must balance the significant benefits of vertical SaaS – including built-in regulatory compliance, industry expertise integration, and enhanced productivity – against typically higher costs and increased vendor lock-in risks. Success requires implementing comprehensive governance frameworks, maintaining active vendor relationships, and utilizing specialized management tools designed for vertical SaaS environments.
The key to effective vertical SaaS spend management lies in understanding that these solutions often justify higher costs through their specialized capabilities and business value. Organizations should focus on optimizing value rather than simply minimizing costs, ensuring they fully utilize the industry-specific features that differentiate vertical SaaS from less expensive alternatives.
Best practices for vertical SaaS management include implementing centralized SaaS procurement processes, conducting regular usage assessments, maintaining strategic vendor relationships, and utilizing specialized management platforms like Binadox that understand the unique requirements of vertical SaaS environments.
As the vertical SaaS market continues evolving with AI integration, edge computing adoption, and increasing regulatory complexity, organizations that implement effective spend management strategies will be better positioned to leverage these powerful tools while maintaining cost control. The future belongs to organizations that can successfully balance the specialized capabilities of vertical SaaS with disciplined spending optimization and strategic vendor management.
Through careful planning, ongoing optimization, and the right management tools, organizations can maximize the value of their vertical SaaS investments while maintaining financial discipline and operational efficiency. The key is recognizing that vertical SaaS management requires specialized approaches while building on proven SaaS cost optimization principles and practices.

