Introduction
As we progress into 2025, cloud cost optimization remains at the forefront of every CIO’s agenda. With digital transformation accelerating, organizations are leveraging public cloud services more than ever. The “big three” — Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure — continue to dominate the landscape, each offering a dizzying array of pricing models, services, and optimization tools.
But as cloud bills keep rising, businesses are asking the million-dollar question: Which cloud provider offers the best cost optimization strategies and actually saves you more money in 2025?
This article offers a deep dive into cost management features, best practices, and real-world use cases for AWS, GCP, and Azure. We’ll also highlight actionable insights and tools — including the Binadox platform — to help you maximize savings, minimize waste, and make smarter decisions.
The Cloud Cost Challenge: Why Optimization Matters
Cloud spending is expected to exceed $700 billion globally in 2025, fueled by the explosion of SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS models. However, Gartner estimates that over 30% of cloud spend is wasted due to idle resources, overprovisioned instances, forgotten subscriptions, and lack of visibility.
All three hyperscalers provide hundreds of SKUs, tiered pricing, complex billing, and dynamic discounts — creating both opportunity and confusion. Without the right optimization practices, businesses risk cloud sprawl, unexpected overages, and diminishing ROI.
The Big Three at a Glance: AWS, GCP, and Azure
AWS (Amazon Web Services)
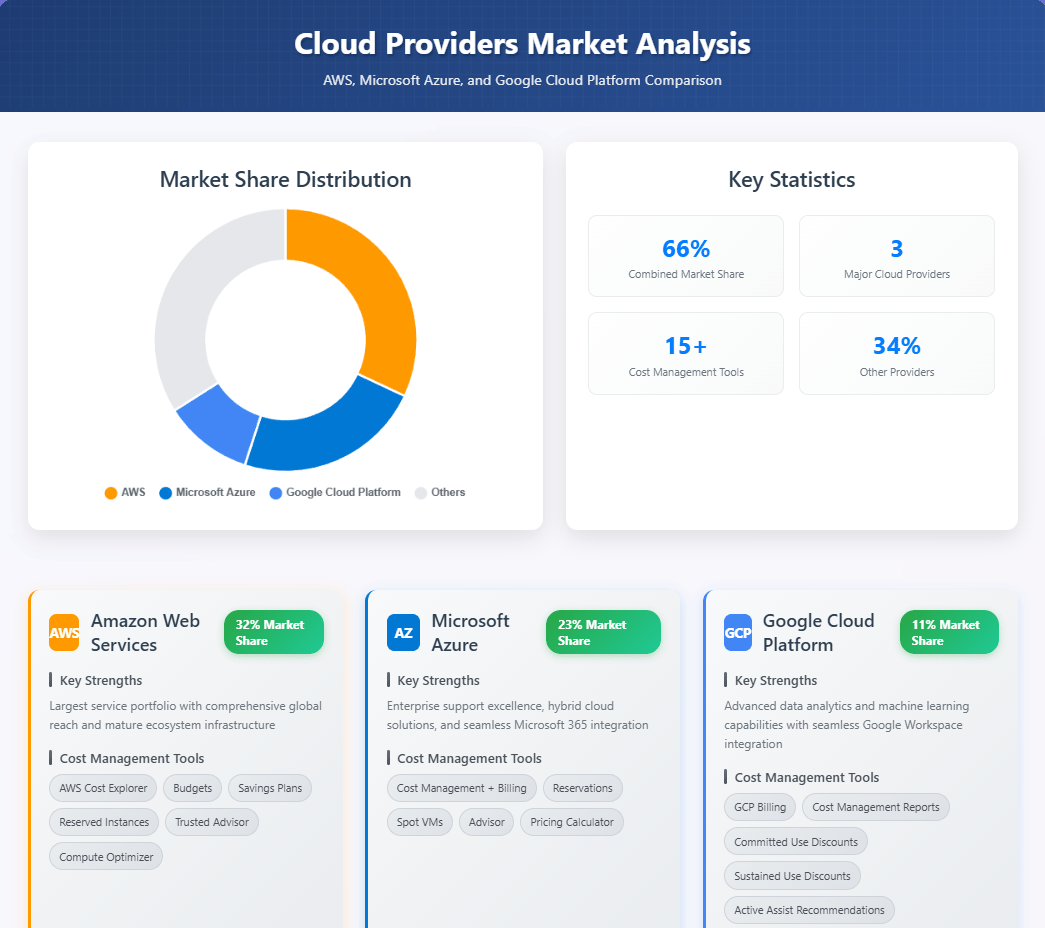
- Market share: ~32%
- Strengths: Largest service portfolio, global reach, mature ecosystem.
- Cost tools: AWS Cost Explorer, Budgets, Savings Plans, Reserved Instances, Trusted Advisor, Compute Optimizer.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Market share: ~11%
- Strengths: Data analytics, machine learning, seamless integration with Google Workspace.
- Cost tools: GCP Billing, Cost Management Reports, Committed Use Discounts, Sustained Use Discounts, Active Assist Recommendations.
Microsoft Azure
- Market share: ~23%
- Strengths: Enterprise support, hybrid cloud, integration with Microsoft 365.
- Cost tools: Azure Cost Management + Billing, Reservations, Spot VMs, Advisor, Pricing Calculator.
Each platform brings powerful cost optimization features — but the devil is in the details.
| Feature / Provider | AWS (Amazon Web Services) | Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Microsoft Azure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Share | ~32% | ~11% | ~23% |
| Strengths | Largest service portfolio, global reach, mature ecosystem | Data analytics, ML, integration with Google Workspace | Enterprise support, hybrid cloud, integration with Microsoft 365 |
| Cost Tools | Cost Explorer, Budgets, Savings Plans, Reserved Instances, Trusted Advisor, Compute Optimizer | Billing, Cost Reports, Committed Use Discounts, Sustained Use Discounts, Active Assist | Cost Management + Billing, Reservations, Spot VMs, Advisor, Pricing Calculator |
| Discount Programs | Reserved Instances, Savings Plans, Spot Instances | Committed Use Discounts, Sustained Use Discounts, Preemptible VMs | Reservations, Spot VMs |
| Billing Transparency | Detailed usage reports, tagging, forecasting | Real-time insights, budget alerts, dashboards | Granular views, alerting, Power BI integration |
| Automation | Lambda, SSM, Trusted Advisor | Custom scripts, Active Assist, Recommender | Automation, Logic Apps, Advisor |
Comparing Core Cost Optimization Strategies
1. Right-Sizing and Instance Optimization
- AWS: Offers robust recommendations via AWS Compute Optimizer and Trusted Advisor. Users can downsize or shift workloads based on CPU, memory, and utilization.
- GCP: Google’s Active Assist provides automatic insights for rightsizing VMs. Sustained Use Discounts kick in automatically for workloads running consistently.
- Azure: Azure Advisor delivers rightsizing and underutilized resource suggestions. Azure also provides an “auto-scale” capability for many services.
Takeaway: All three provide automated recommendations, but GCP’s Sustained Use Discounts automatically reduce costs without reservations, making it attractive for variable workloads. AWS and Azure require more active management for comparable savings.
2. Discount Models: Reserved, Committed, and Spot/Preemptible
- AWS: Savings Plans and Reserved Instances (1- or 3-year terms) deliver up to 72% savings. Spot Instances can be 90% cheaper but are interruptible.
- GCP: Committed Use Discounts (CUDs) offer 1- or 3-year commitment discounts. Preemptible VMs are short-lived but up to 80% cheaper.
- Azure: Reservations (VMs, SQL, Cosmos DB) provide 1- or 3-year discounts. Spot VMs can offer big savings, ideal for batch or flexible jobs.
Takeaway: The best model depends on workload predictability. GCP’s CUDs are simple and flexible; AWS’s Savings Plans now cover more services, while Azure offers broad coverage. Spot/Preemptible/Spot VMs are ideal for non-critical, interruptible jobs on all platforms.
3. Automated Scheduling and Resource Clean-Up
- AWS: Users can automate shutdowns with Lambda or SSM, and leverage tools to identify orphaned EBS volumes, unattached IPs, etc.
- GCP: Google recommends using custom scripts or third-party tools to schedule instance up/down times. GCP Recommender highlights idle resources.
- Azure: Azure Automation and Logic Apps can enforce scheduling and cleanup. Advisor flags unused resources and potential savings.
Takeaway: All three support automation, but AWS and Azure have more mature native scheduling features. Google relies more on scripting or third-party solutions.
4. Billing Transparency and Visibility
- AWS: AWS Cost Explorer, Budgets, and Cost & Usage Reports (CUR) provide detailed breakdowns, tagging, and forecasting.
- GCP: GCP Billing reports offer real-time insights, budget alerts, and custom dashboards.
- Azure: Azure Cost Management offers granular views, alerting, and native Power BI integration.
Takeaway: All platforms offer rich reporting, but Azure’s native integration with Power BI is powerful for enterprises with existing Microsoft ecosystems.
5. Integrations with Third-Party Tools: The Role of Binadox
Regardless of provider, native tools have limits. Multi-cloud organizations need a single pane of glass to monitor, optimize, and automate cloud costs across platforms. This is where tools like Binadox shine.
With Binadox, you can:
- Aggregate costs across AWS, GCP, Azure, SaaS, and on-prem.
- Visualize spending, utilization, and trends in one dashboard.
- Get actionable recommendations for rightsizing, tag hygiene, and unused resources.
- Automate policies for cost anomalies, renewal management, and moreDemo.
Explore a Binadox client demo to see these features in action.
Real-World Cost Optimization Use Cases
Case Study 1: A SaaS Startup Using GCP
A growing SaaS company moved its entire backend to GCP for advanced ML capabilities. By relying on Google’s Sustained Use Discounts and proactive rightsizing with Active Assist, the company reduced compute spend by 25%. However, cost visibility was a challenge, solved by integrating Binadox for centralized reporting across their cloud and SaaS stack.
Case Study 2: Enterprise Fintech on AWS
A financial services company, running thousands of EC2 instances on AWS, used Savings Plans and automated Lambda scripts to stop dev/test environments overnight. Combined with Binadox’s anomaly detection and spend allocation by team, the firm cut waste by 30% and gained better control over shadow ITDemo.
Case Study 3: Global Retailer Leveraging Azure
A retailer with heavy reliance on Microsoft 365 used Azure Reservations and Cost Management, integrated with Power BI for reporting. Azure Advisor’s recommendations helped optimize VM sizes, while Binadox provided extra value by consolidating cloud and SaaS expenses for all business units.
Key Metrics to Watch in 2025
- Cloud spend as a percentage of IT budget: Up to 50% for cloud-first organizations.
- Idle/underutilized resource rate: Goal should be <10%.
- Rate of cost anomalies: Automated alerts can help catch surprise spikes.
- SaaS/Cloud integration: Tools like Binadox now unify cloud and SaaS spend.
Read more about SaaS spend management best practices.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Lack of Tagging Discipline: Unlabeled resources create reporting blind spots and billing chaos.
- Forgetting Reserved/Committed Expirations: Expired reservations revert to on-demand pricing. Use calendar alerts and renewal management.
- Zombie Resources: Unused VMs, storage, and IPs quietly drain budgets.
- Ignoring SaaS Subscriptions: Unmanaged SaaS grows cloud spend invisibly.
- Siloed Cost Management: Multi-cloud and SaaS require unified tools and processes.
Making the Right Choice: AWS vs GCP vs Azure in 2025
So, which cloud provider saves you more money? The answer depends on your workloads, organization, and approach:
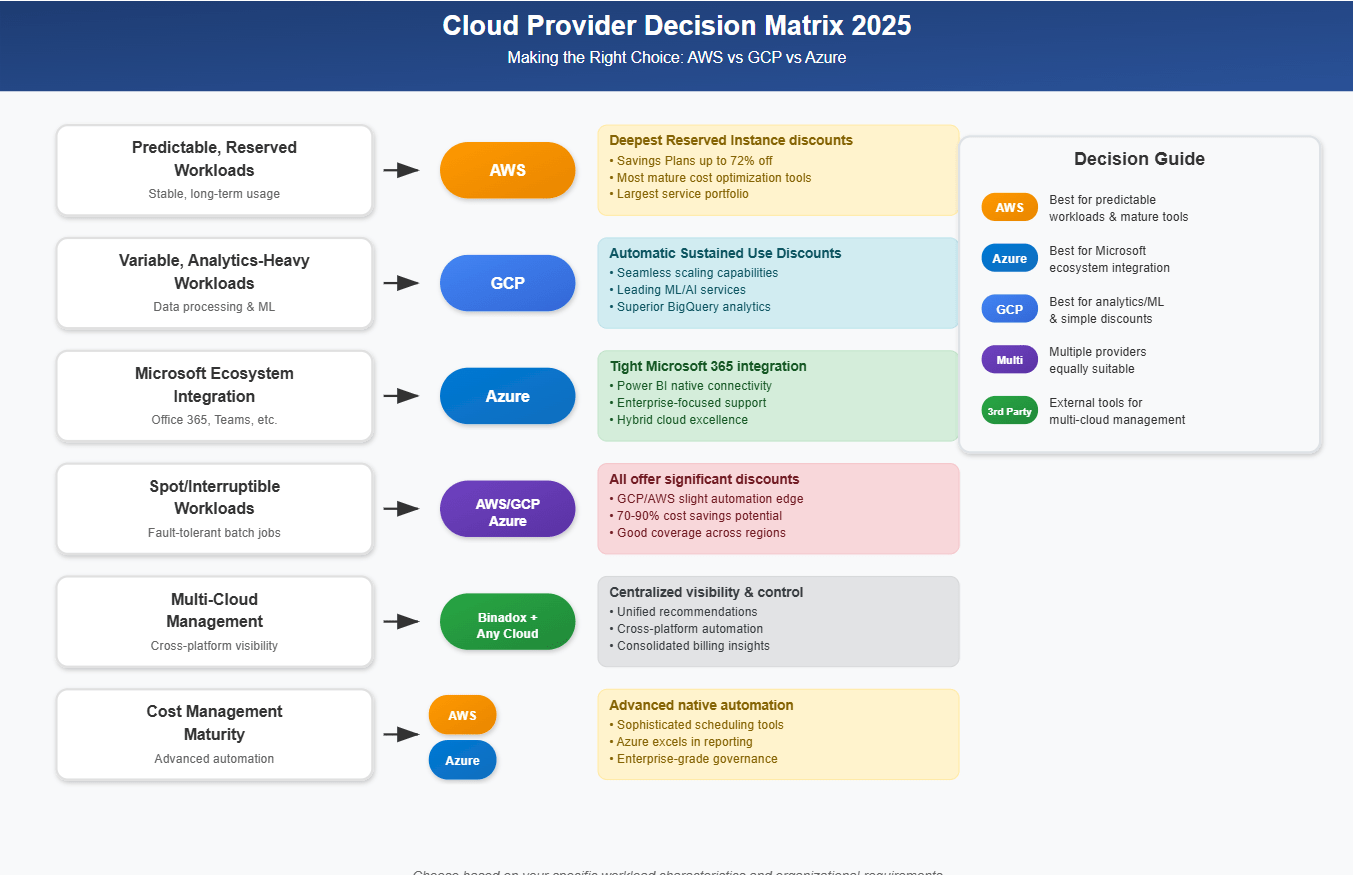
- AWS often provides the deepest discounts for predictable, reserved workloads, with the most mature ecosystem and optimization tools.
- GCP is outstanding for variable, analytics-heavy workloads thanks to automatic discounts and seamless scaling.
- Azure is a strong choice for enterprises committed to Microsoft, offering tight integration and solid cost management.
| Scenario / Criteria | Best Choice | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Predictable, Reserved Workloads | AWS | Deepest discounts via Reserved Instances and Savings Plans. Most mature cost tools. |
| Variable, Analytics-Heavy Workloads | GCP | Automatic Sustained Use Discounts, seamless scaling, ML strengths. |
| Microsoft Ecosystem Integration | Azure | Tight integration with Microsoft 365, Power BI, enterprise focus. |
| Spot/Interruptible Workloads | AWS / GCP / Azure | All offer big discounts; GCP and AWS slightly ahead for automation and coverage. |
| Multi-Cloud Management | Use Binadox + Any | Centralized visibility, unified recommendations, automation across platforms. |
| Cost Management Maturity | AWS & Azure | More advanced native automation and scheduling; Azure excels with reporting. |
| Simplicity of Discounts | GCP | Sustained Use and Committed Use Discounts apply automatically with minimal configuration. |
Cloud Cost Optimization Best Practices for 2025
- Centralize Cloud and SaaS Spend Management: Aggregate all cloud and SaaS costs in one place.
- Automate Rightsizing and Scheduling: Use provider tools and third-party platforms to shrink idle resources.
- Implement Robust Tagging: Standardize tags for cost allocation, ownership, and chargebacks.
- Monitor, Audit, and Renew Regularly: Avoid zombie resources, missed renewals, and unused SaaS licenses.
- Embrace Cost Optimization as a Culture: Make it a regular process, not a one-time project.
Explore essential cloud cost optimization strategies.
Conclusion: The Future of Cloud Savings
No cloud provider is a silver bullet — but with the right tools and practices, cost optimization is achievable on AWS, GCP, or Azure. As multi-cloud and SaaS usage grow, visibility and automation will separate leaders from laggards. Whether you’re running massive EC2 fleets, leveraging Google’s ML stack, or integrating Azure with Microsoft 365, success depends on consistent, data-driven optimization.

