Introduction
The digital transformation of healthcare is not a trend—it’s a fundamental shift. Hospitals, clinics, and medical research centers increasingly rely on cloud technologies to streamline operations, store massive volumes of sensitive patient data, and deploy innovative services like telemedicine and AI-driven diagnostics. But with this digital leap comes a significant challenge: how can healthcare organizations optimize cloud costs without sacrificing strict HIPAA compliance and patient data privacy?
Balancing regulatory requirements and budgetary discipline is not just a matter of technical finesse—it’s a core business imperative. Cloud overspending can drain precious resources from patient care, while lapses in compliance can result in reputational damage and severe penalties. In this article, we explore practical strategies for achieving both goals: a cloud environment that is HIPAA-compliant yet cost-efficient.
The Regulatory Landscape: Why HIPAA Matters in Cloud Spend
First, let’s clarify why HIPAA is non-negotiable in the healthcare cloud context. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) establishes rules for the protection of sensitive patient health information (PHI), regardless of where that data lives—on-premises or in the cloud. Any cloud service storing, processing, or transmitting PHI must meet HIPAA’s stringent privacy and security requirements.
HIPAA compliance in the cloud goes beyond “checking the box.” It involves:
- Encryption of data at rest and in transit
- Audit controls and logging
- Role-based access and user authentication
- Data backup, disaster recovery, and breach notification procedures
- Business Associate Agreements (BAA) with all cloud vendors
While these safeguards ensure regulatory alignment and patient trust, they also impact cloud costs by dictating architectural choices, toolsets, and sometimes even which vendors are eligible.
The High Cost of Cloud in Healthcare
Cloud platforms (like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) offer immense flexibility, scalability, and innovation potential. But these benefits come with risk:
- Underutilized resources: Idle virtual machines, over-provisioned storage, and orphaned workloads are all too common.
- Compliance-related overhead: Features for auditing, advanced encryption, and multi-zone redundancy drive up costs.
- Shadow IT and SaaS sprawl: Clinicians and admins may sign up for SaaS apps without central oversight, leading to redundant spending and security gaps.
The result? Many healthcare organizations pay for far more cloud than they actually use. Gartner reports that organizations waste up to 30% of their cloud spend on average. In a sector where every dollar matters, this is unsustainable.
Cost Optimization: A Compliance-First Approach
Achieving HIPAA-compliant cost optimization starts with a paradigm shift: Security and compliance are not separate from cost efficiency—they are core to it. A security breach or compliance violation is, in itself, a massive cost. Conversely, strong cost governance enhances security by providing visibility and control.
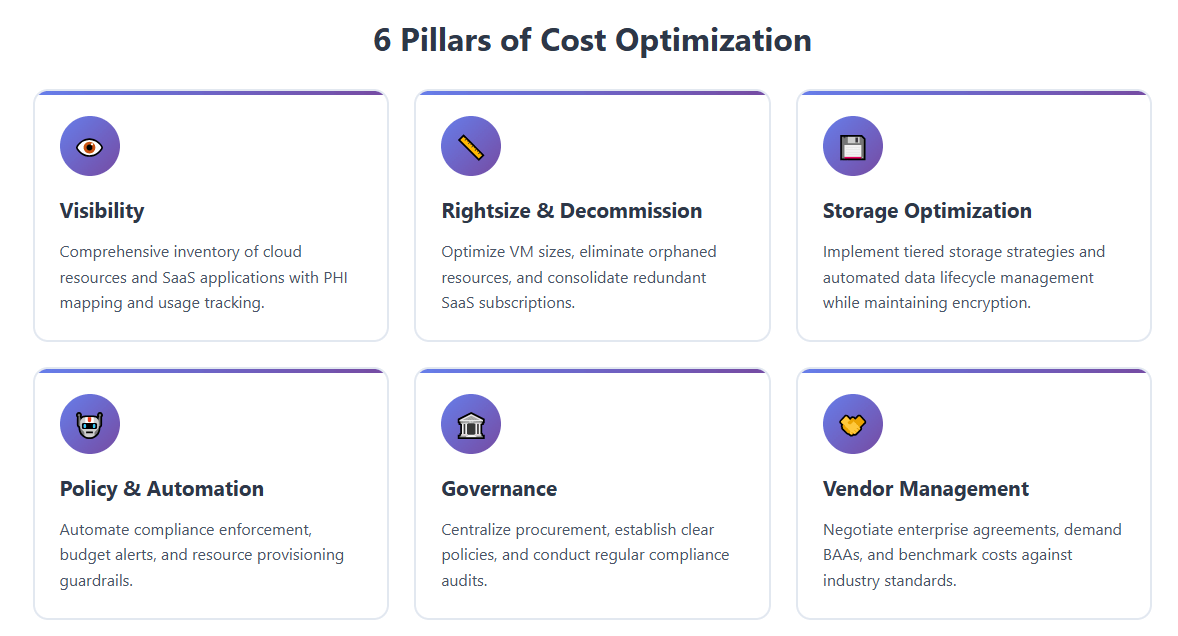
Here are the pillars of an effective approach:
1. Visibility: Know What You Have
You cannot optimize what you can’t see. Start with a comprehensive inventory of your cloud resources—across IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS—and map which workloads handle PHI.
Modern platforms like Binadox are designed for exactly this, providing a single-pane-of-glass dashboard to track usage, spending, and compliance status across multiple cloud vendors and SaaS toolsDemo. Features include:
- Cloud Utilization Dashboards: See all your cloud and SaaS spending, broken down by team, application, or geography.
- Tagging and Custom Labels: Organize cloud assets for cost allocation, compliance tracking, and reporting.
- User-level Analytics: Identify which users and departments are driving costs—and whether those costs align with actual patient care or administrative needs.
2. Rightsize and Decommission
Once you have visibility, act on it:
- Rightsize Instances: Use analytics to determine if your VMs, storage volumes, or databases are over-provisioned. For HIPAA workloads, make sure downsizing doesn’t compromise redundancy or security, but don’t pay for more than you need.
- Automate Cleanup: Schedule workflows to shut down or decommission idle resources. Orphaned disks and snapshots, particularly those storing PHI, are both a compliance and a cost risk.
- Eliminate Redundant SaaS: Healthcare often has shadow IT—departments buying their own SaaS tools. Conduct regular audits to cancel unused subscriptions and consolidate licenses.
3. Optimize Storage Strategies
Healthcare data is massive and ever-growing—think imaging, EHRs, genomics. HIPAA requires careful stewardship, but that doesn’t mean expensive storage by default.
- Tiered Storage: Store frequently accessed PHI on premium, encrypted storage; move older data to secure, lower-cost archives that still meet HIPAA retention policies.
- Automated Data Lifecycle Management: Use tools to automate data movement between storage classes, based on access frequency and compliance mandates.
- Encrypt Everything: Use built-in cloud encryption services (which are often cheaper than third-party solutions) to meet HIPAA without extra complexity.
4. Policy and Automation: Guardrails for Cost and Compliance
Human error is a primary source of both cost overruns and compliance lapses. Automate wherever possible:
- Policy-Driven Automation: Implement policies that enforce encryption, tagging, and approved regions (data residency). Use automation to prevent resource creation outside these guardrails.
- Budget Alerts and Anomaly Detection: Get real-time alerts on cost spikes or suspicious activity. Binadox offers custom alerts and reports so you can act fast when something’s off.
- Renewals Calendar and License Manager: Never get caught by surprise renewals—automated license and contract management saves both money and compliance headaches.
5. Governance and Centralization
HIPAA compliance and cost control are easiest when managed centrally:
- Centralize Procurement: All cloud and SaaS purchasing goes through a single process, ensuring contract review, BAA compliance, and avoidance of redundant purchases.
- Establish Clear Governance Policies: Define how PHI can be stored and processed in the cloud, who has access, and what gets monitored.
- Regular Audits: Schedule periodic reviews of all cloud resources and SaaS applications, checking for both cost waste and compliance drift.
6. Vendor Management: Negotiate Smarter
- Enterprise Agreements: Negotiate discounts and custom terms with your major cloud and SaaS vendors. HIPAA requirements may give you leverage to request tailored solutions.
- Demand BAAs: Never use a cloud or SaaS vendor that won’t sign a HIPAA Business Associate Agreement.
- Benchmark Costs: Use external data and internal analytics to ensure you’re getting fair pricing—both for the cloud services themselves and for the compliance features you require.
Binadox: A Practical Solution for Healthcare Cloud Cost Optimization
Binadox is specifically designed to help organizations—including those in healthcare—optimize their cloud and SaaS spend while remaining compliant. Key features for healthcare organizations include:
- Multi-Cloud & SaaS Visibility: Unified dashboards for AWS, Azure, GCP, and over 40 popular SaaS apps.
- Spend by Team, Department, or Tag: Essential for organizations needing to allocate costs by clinical vs. administrative functions.
- Automated Alerts: Custom alerts for cost spikes, compliance risks, and expiring contracts.
- License and Renewals Calendar: Never miss a contract renewal; always know which subscriptions you can trim.
- User and Access Analytics: Quickly identify accounts with unnecessary access to PHI—a compliance and cost risk.
Learn more about how to track cloud spending and set up cost alerts with Binadox’s guide to cloud computing terminology.

Case Study: Optimizing Cloud Spend in a HIPAA Context
Let’s walk through a simplified, real-world scenario:
A large regional hospital system uses AWS for its EHR system, Azure for collaboration tools, and several specialized SaaS apps for imaging and telemedicine.
Pain Points
- Cloud costs have doubled in the past two years.
- Multiple departments have signed up for overlapping SaaS services.
- Compliance audits reveal several orphaned storage volumes containing PHI.
Solution
Step 1: Inventory and Tagging
- Use Binadox to inventory all cloud and SaaS assets.
- Apply tags: “PHI,” “Research,” “Admin,” etc.
Step 2: Rightsizing and Cleanup
- Automated recommendations identify over-provisioned VMs.
- Unused SaaS subscriptions and idle storage are flagged for removal.
- Orphaned PHI volumes are encrypted, archived, and scheduled for secure deletion after retention expires.
Step 3: Automate Cost and Compliance Alerts
- Set up budget alerts and compliance policy monitoring.
- Use the Renewals Calendar to track all SaaS contracts.
Step 4: Reporting
- Generate monthly executive reports showing cost savings and compliance metrics.
- Tie cloud spend directly to business outcomes—patient throughput, research output, etc.
Result: Cloud spend drops by 25% in the first six months, with improved audit readiness and zero compliance violations.
Trends: AI, Automation, and the Future of Healthcare Cloud
The landscape is changing fast. Here are three trends to watch:
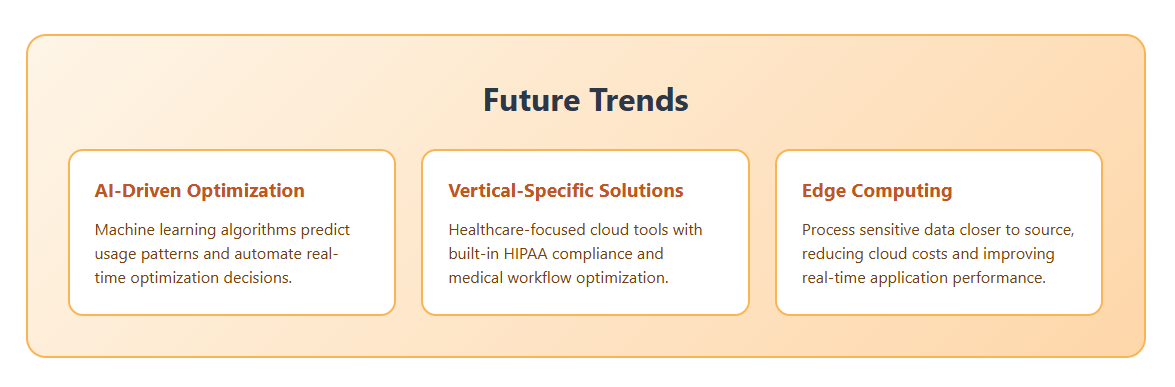
1. AI-Driven Optimization
AI and ML are increasingly embedded in cloud management tools. They can predict usage spikes, recommend optimal storage classes, and even automate compliance reporting. The integration of AI with spend management allows for real-time optimization, which is essential as healthcare workloads become more dynamic and complex.
2. Vertical-Specific Solutions
Healthcare is seeing a rise in cloud and SaaS tools built specifically for HIPAA and medical workflows, from EHRs to telemedicine platforms. These often have built-in compliance automation—and may offer better value than generic tools.
3. Edge Computing
Not all healthcare data can (or should) live in the cloud. Edge computing—processing data closer to where it is generated—can reduce latency for real-time applications (like remote monitoring) and limit how much sensitive data is sent to the public cloud, reducing both risk and cost.
Best Practices: A Checklist for Healthcare Cloud Cost Optimization
1. Establish Cloud and SaaS Inventory:
Maintain a living list of all cloud assets and SaaS subscriptions, tagging those handling PHI.
2. Regularly Audit Utilization:
Identify and remediate underused resources, both for cloud and SaaS.
3. Automate Policy Enforcement:
Use tools like Binadox to automate enforcement of compliance and cost-saving policies.
4. Plan for Data Lifecycle:
Automate data archiving, deletion, and retention in line with HIPAA rules.
5. Centralize Vendor Management:
Negotiate contracts centrally, demand BAAs, and monitor vendor compliance.
6. Educate Staff:
Ensure IT and business users understand both cost impacts and compliance risks of their choices.
7. Measure and Report:
Generate executive-friendly reports tying cost savings to improved patient care, research productivity, and compliance status.
In healthcare, the pressure to innovate is matched only by the responsibility to protect patient privacy and control costs. Optimizing cloud spend under HIPAA is not a one-time task—it’s a continuous, strategic process that demands both technology and culture change.
By adopting centralized visibility tools, rightsizing strategies, automated compliance enforcement, and strong governance, healthcare organizations can deliver HIPAA-compliant services and stay cost-efficient. The result? More resources for patient care, greater organizational agility, and lower risk.
Platforms like Binadox are at the forefront, helping healthcare organizations thrive in the cloud era. With the right strategies and tools, “HIPAA-compliant yet cost-efficient” isn’t just possible—it’s the new standard.

