In today’s volatile economic environment, organizations face unprecedented challenges in predicting and managing their software expenditures. SaaS spend forecasting has become increasingly complex as businesses navigate market uncertainties, changing workforce dynamics, and evolving technology needs. Traditional budgeting approaches often fall short when dealing with the dynamic nature of software subscriptions and the unpredictable shifts in business requirements.
Scenario planning emerges as a critical methodology for SaaS budget planning, enabling organizations to prepare for multiple potential futures while maintaining operational flexibility. This comprehensive approach to SaaS cost optimization allows businesses to make informed decisions about their software investments, even when facing significant budget uncertainty.
The integration of cloud cost management principles with SaaS spend strategies has become essential as organizations increasingly adopt hybrid and multi-cloud environments. By implementing robust scenario planning frameworks, companies can achieve better SaaS spend visibility and make strategic decisions that align with their long-term objectives while remaining adaptable to changing circumstances.
Understanding SaaS Spend Forecasting in Uncertain Times
SaaS spend forecasting involves predicting future software subscription costs based on various internal and external factors. Unlike traditional software purchases, SaaS subscriptions create ongoing financial commitments that can scale dynamically with business needs. This scalability, while advantageous for growth, introduces complexity when attempting to forecast expenses accurately.
The subscription-based model of SaaS applications means that costs can fluctuate based on user count, feature utilization, data consumption, and service tiers. Additionally, the rapid pace of SaaS innovation often leads to new features, pricing models, and competitive alternatives that can significantly impact long-term spending projections.
Organizations must also consider the interconnected nature of their software subscription management ecosystem. Dependencies between applications, integration costs, and the cumulative effect of multiple subscriptions create a complex web of financial relationships that require sophisticated forecasting approaches.
Cloud spend forecasting adds another layer of complexity, as many SaaS applications rely on underlying cloud infrastructure that may have variable costs based on usage patterns, geographic distribution, and performance requirements. Understanding these relationships is crucial for accurate SaaS financial planning.
The Challenge of Budget Uncertainty
Budget uncertainty in SaaS spending stems from multiple sources that can dramatically impact financial projections. Economic volatility, regulatory changes, and market competition create external pressures that influence both the availability of budget resources and the strategic priorities of organizations.
Internal factors contribute equally to uncertainty. Organizational growth or contraction affects user licensing requirements, while changing business priorities may necessitate new software capabilities or render existing subscriptions obsolete. Remote work trends, digital transformation initiatives, and evolving security requirements further complicate SaaS expense tracking and budget allocation decisions.
The challenge is compounded by the fact that many SaaS contracts include automatic renewal clauses, usage-based pricing tiers, and complex licensing structures that can lead to unexpected cost escalations. Without proper SaaS cost control mechanisms, organizations may find themselves committed to expenses that no longer align with their strategic objectives or financial capabilities.
Traditional budgeting cycles, typically annual or quarterly, often cannot keep pace with the rapid changes in SaaS requirements and market conditions. This misalignment between planning horizons and operational realities necessitates more flexible and responsive approaches to SaaS budget management.
Scenario Planning Fundamentals
Scenario planning provides a structured approach to exploring multiple potential futures and their implications for SaaS spending. Rather than attempting to predict a single “most likely” outcome, scenario planning acknowledges uncertainty by developing several plausible scenarios that represent different combinations of key variables and their potential impacts.
The foundation of effective scenario planning lies in identifying the most critical uncertainties that could affect SaaS spend analysis. These uncertainties typically fall into categories such as business growth patterns, market conditions, technology evolution, and regulatory changes. By systematically exploring how these factors might unfold, organizations can develop more robust and adaptable spending strategies.
Effective scenario planning requires balancing detail with practicality. Scenarios must be specific enough to generate actionable insights while remaining broad enough to capture the range of plausible outcomes. This balance ensures that the planning process yields useful guidance without becoming overwhelmed by excessive complexity.
The iterative nature of scenario planning makes it particularly well-suited to the dynamic SaaS environment. As new information becomes available and circumstances change, scenarios can be updated and refined to maintain their relevance and utility for decision-making.
Building Effective SaaS Spend Scenarios
Creating meaningful scenarios for SaaS procurement and budget planning requires a systematic approach that considers both quantitative factors and qualitative insights. The process begins with establishing a baseline scenario that reflects current spending patterns, contracted commitments, and known upcoming changes.
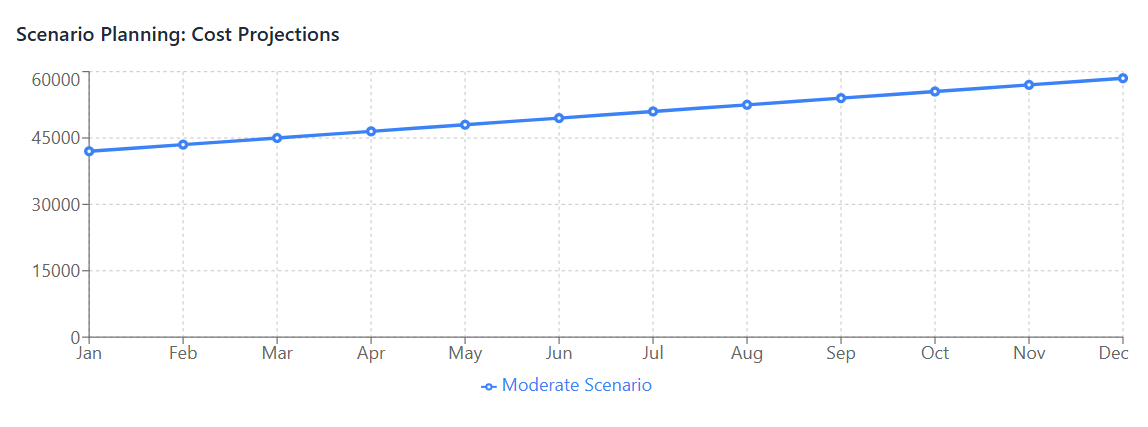
From this baseline, organizations should develop alternative scenarios that explore different trajectories for key variables. A typical approach involves creating optimistic, pessimistic, and moderate scenarios that span the range of plausible outcomes. Each scenario should be internally consistent and based on realistic assumptions about cause-and-effect relationships.
Growth scenarios might explore the implications of rapid business expansion, including increased user licensing, additional feature requirements, and potential economies of scale from volume discounts. These scenarios help organizations understand the spending implications of success and ensure adequate budget flexibility to support growth opportunities.
Contraction scenarios examine the potential for reduced business activity, whether due to economic downturns, competitive pressures, or strategic pivots. These scenarios focus on identifying which SaaS investments are truly essential and which might be reduced or eliminated without compromising core operations.
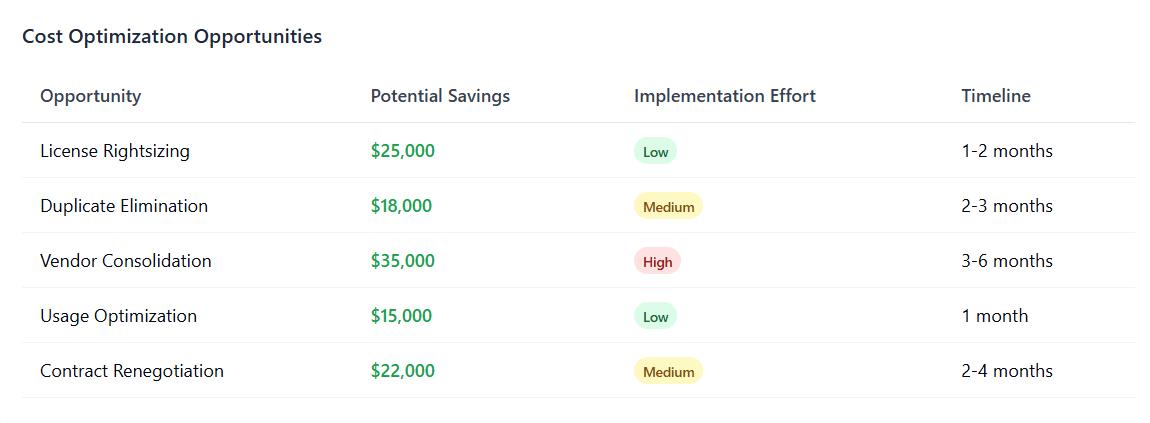
Technology evolution scenarios consider how changes in the SaaS landscape might affect spending patterns. This includes the emergence of new solutions, consolidation opportunities, pricing model changes, and shifts in vendor relationships that could significantly impact SaaS cost reduction strategies.
Key Variables in SaaS Spend Forecasting
Successful SaaS spend forecasting depends on identifying and modeling the key variables that drive spending variations. User count represents one of the most significant variables, as most SaaS applications employ per-user pricing models. However, user count forecasting requires consideration of employee turnover, seasonal variations, contractor usage, and potential changes in user role definitions.
Usage intensity variables capture how actively users engage with SaaS applications and consume resources. These variables are particularly important for applications with usage-based pricing or those where heavy usage might trigger automatic upgrades to higher service tiers. Understanding usage patterns helps organizations anticipate when they might exceed current plan limits and incur additional costs.
Feature adoption rates affect spending when organizations utilize tiered pricing models or add-on features. The pace at which teams adopt new capabilities can significantly impact costs, especially when advanced features carry premium pricing. Scenario planning should account for both organic feature adoption and strategic decisions to implement new capabilities.
Multi-cloud cost management considerations introduce additional variables related to infrastructure scaling, data transfer costs, and integration complexity. As SaaS applications increasingly rely on cloud infrastructure, understanding these underlying cost drivers becomes essential for accurate forecasting.
Vendor relationship factors, including contract negotiation outcomes, volume discounts, and competitive pricing pressures, represent another category of variables that can substantially impact spending projections. Organizations should model different outcomes for contract renewals and vendor negotiations within their scenarios.
Scenario Planning Models for SaaS Budgeting
Several modeling approaches can support effective scenario planning for SaaS budget planning. Monte Carlo simulation techniques allow organizations to model uncertainty in key variables and generate probability distributions for potential spending outcomes. This approach is particularly valuable when dealing with multiple interacting variables and complex dependency relationships.
Decision tree models provide a structured way to explore how different strategic choices might unfold over time. These models are especially useful for analyzing decisions about SaaS consolidation, vendor selection, and timing of technology investments. By mapping out decision points and their potential consequences, organizations can better understand the risk-return profile of different strategies.
Sensitivity analysis models help identify which variables have the greatest impact on spending outcomes. This insight allows organizations to focus their attention and resources on monitoring and managing the factors that matter most for SaaS cost optimization. Sensitivity analysis also helps prioritize data collection efforts and investment in forecasting capabilities.
System dynamics models can capture the feedback loops and time delays that characterize SaaS spending patterns. For example, the relationship between user satisfaction, feature adoption, and subscription renewals creates dynamic interactions that traditional linear models might miss. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for cloud budget planning in complex organizational environments.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Effective scenario planning must include comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential threats to budget stability and operational continuity. SaaS expense tracking reveals historical patterns that can inform risk identification, including seasonal variations, unexpected usage spikes, and vendor-initiated pricing changes.
Vendor concentration risk represents a significant concern when organizations become heavily dependent on a small number of SaaS providers. Scenario planning should explore the implications of vendor service disruptions, significant pricing increases, or strategic changes that might affect service availability or functionality.
Budget overage risks arise when actual spending exceeds planned allocations due to usage growth, feature adoption, or user count increases. Organizations should develop clear protocols for managing these situations, including approval processes for budget overruns and criteria for making mid-cycle adjustments to subscriptions.
Integration and compatibility risks can emerge when SaaS applications fail to work together effectively or when vendors make changes that disrupt existing workflows. These risks can force organizations to invest in additional tools or services to maintain functionality, potentially disrupting carefully planned budgets.
Mitigation strategies should address both the likelihood and impact of identified risks. Contract negotiations that include usage caps, price protection clauses, and flexible termination terms can help manage vendor-related risks. Diversification strategies that avoid over-reliance on single vendors or platforms can reduce concentration risks.
Tools and Technologies for Scenario Planning
Modern SaaS spend management platforms provide sophisticated capabilities for scenario modeling and analysis. These tools integrate with existing financial systems and SaaS applications to provide real-time visibility into spending patterns and usage trends. Advanced platforms offer predictive analytics capabilities that can identify emerging patterns and potential budget impacts before they materialize.
Binadox offers comprehensive scenario planning capabilities that enable organizations to model different spending trajectories and assess their implications. The platform’s analytics engine can process complex relationships between variables and generate detailed projections for different scenarios. Integration with existing SaaS applications provides the data foundation necessary for accurate modeling.
Cloud cost management tools complement SaaS-focused platforms by providing visibility into underlying infrastructure costs that support SaaS operations. These tools help organizations understand the total cost of ownership for their software investments and identify optimization opportunities that span both application and infrastructure layers.
Spreadsheet-based models remain valuable for smaller organizations or those with simpler SaaS portfolios. While less sophisticated than specialized platforms, well-designed spreadsheet models can provide meaningful insights and support decision-making when properly maintained and updated.
Implementation Best Practices
Successfully implementing scenario planning for SaaS cost control requires establishing clear processes and responsibilities. Organizations should designate specific roles for scenario development, data collection, and analysis to ensure consistency and quality in the planning process.
Data quality represents a critical success factor for scenario planning initiatives. Organizations must invest in systems and processes that capture accurate, timely information about SaaS usage, costs, and performance. This includes integrating data from multiple sources and establishing validation procedures to ensure reliability.
Stakeholder engagement ensures that scenario planning reflects the perspectives and insights of different organizational functions. IT teams provide technical insights about application capabilities and limitations, while finance teams contribute budgetary constraints and forecasting expertise. Business unit leaders offer strategic context and priorities that shape scenario assumptions.
Regular scenario review and updating maintains the relevance and utility of the planning process. Organizations should establish scheduled review cycles that coincide with budget planning periods and major strategic decisions. Ad hoc reviews may be necessary when significant changes in market conditions or organizational priorities occur.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Scenarios
Effective scenario planning requires ongoing monitoring to track actual performance against projected outcomes and identify when scenarios need updating. SaaS spend visibility tools provide the real-time data necessary to assess scenario accuracy and identify emerging trends that might affect future projections.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established for each major scenario variable to enable systematic tracking and early warning of significant deviations. These KPIs might include user growth rates, usage intensity metrics, cost per user trends, and vendor pricing changes. Regular monitoring of these indicators helps organizations stay ahead of budget impacts.
Variance analysis helps organizations understand why actual outcomes differ from scenario projections and refine their modeling approaches accordingly. This analysis should examine both the accuracy of underlying assumptions and the effectiveness of modeling techniques in capturing relevant relationships.
Adaptive management approaches enable organizations to adjust their SaaS strategies based on scenario monitoring results. This might involve accelerating or delaying planned investments, renegotiating vendor contracts, or implementing additional cost control measures to stay within budget constraints.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
A mid-size technology company implemented comprehensive scenario planning after experiencing significant budget overruns in their software subscription management. By modeling different growth scenarios and implementing automated monitoring, they reduced unexpected spending by 35% while maintaining the flexibility to support rapid scaling when opportunities arose.
A healthcare organization used scenario planning to navigate regulatory uncertainty affecting their SaaS investments. By developing scenarios around different regulatory outcomes and their technology implications, they maintained compliance while optimizing costs across multiple potential regulatory environments.
A financial services firm applied scenario planning to manage the complexity of multi-cloud cost management across their diverse SaaS portfolio. The approach helped them identify consolidation opportunities and negotiate better terms with vendors, resulting in 20% cost savings while improving service quality.
Future-Proofing Your SaaS Investment Strategy
The evolving SaaS landscape requires organizations to build adaptability and resilience into their investment strategies. SaaS financial planning must account for emerging trends such as artificial intelligence integration, vertical-specific solutions, and changing pricing models that could significantly impact future spending patterns.
Edge computing developments may affect how SaaS applications are delivered and priced, potentially creating new cost structures that current scenario models don’t capture. Organizations should monitor these technological trends and periodically assess their implications for long-term spending projections.
Regulatory changes, particularly around data privacy and security, may require additional SaaS investments or changes to existing subscriptions. Scenario planning should consider the potential cost implications of compliance requirements and their effect on software selection and configuration decisions.
The increasing sophistication of SaaS analytics and AI-driven optimization tools offers opportunities for more precise forecasting and automated cost management. Organizations should evaluate how these emerging capabilities might enhance their scenario planning processes and improve their ability to manage spending uncertainty.
Conclusion
Scenario planning represents a critical capability for organizations seeking to optimize their SaaS spend management in an uncertain economic environment. By systematically exploring multiple potential futures and their implications, businesses can make more informed decisions about their software investments while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances.
The methodology provides a structured approach to SaaS cost optimization that goes beyond traditional budgeting to embrace uncertainty as a manageable challenge rather than an insurmountable obstacle. Through careful modeling of key variables and regular monitoring of actual outcomes, organizations can achieve better SaaS spend visibility and more effective resource allocation.
Success in scenario planning requires investment in appropriate tools, processes, and capabilities. Platforms like Binadox provide the technical foundation necessary for sophisticated modeling and analysis, while organizational commitment ensures that insights translate into actionable strategies and improved outcomes.
As the SaaS landscape continues to evolve, organizations that master scenario planning will be better positioned to navigate uncertainty, optimize their software investments, and maintain competitive advantage through effective cloud cost management and SaaS budget planning. The investment in these capabilities pays dividends not only in cost savings but also in organizational resilience and strategic flexibility.
By implementing comprehensive scenario planning frameworks, businesses can transform budget uncertainty from a source of anxiety into a catalyst for more thoughtful, strategic, and ultimately successful SaaS investment decisions. The key lies in embracing the process, investing in the necessary capabilities, and maintaining the discipline to regularly update and refine scenarios as new information becomes available.

